* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Using Photoshop V22.0004 - Computers in Principle & Practice I By
Anaglyph 3D wikipedia , lookup
Stereoscopy wikipedia , lookup
Original Chip Set wikipedia , lookup
Adobe Photoshop wikipedia , lookup
Waveform graphics wikipedia , lookup
Framebuffer wikipedia , lookup
MOS Technology VIC-II wikipedia , lookup
Stereo display wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix 4010 wikipedia , lookup
Spatial anti-aliasing wikipedia , lookup
Color Graphics Adapter wikipedia , lookup
Apple II graphics wikipedia , lookup
Image editing wikipedia , lookup
Portable Network Graphics wikipedia , lookup
List of 8-bit computer hardware palettes wikipedia , lookup
Hold-And-Modify wikipedia , lookup
Indexed color wikipedia , lookup
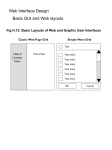
Graphics Overview: Using Photoshop V22.0004 - Computers in Principle & Practice I By Deena Engel with Sana’ Odeh - V22.0004 Computer graphics boil down to two basic types: (bitmaps and vectors ) 1. Bitmap (or raster) graphics: • • Bitmap graphics are stored as a series of tiny dots called pixels. Each pixel is assigned a color, and when they are viewed all together, they form the picture. Bitmap graphics can be edited by erasing or changing the color of individual pixels. There are many different bitmap file formats: • • • • TIFF for print; Photoshop's PSD and BMP; and GIF, JPG, and PNG for the Web. 2. Vector graphics: – Unlike bitmaps, vector graphics are not based on pixel patterns, but instead use mathematical formulas consisting of lines and curves that make shapes. – – – – Vector graphics are ideal for illustrations, line art, and type. However, with the exception of Flash and similar files, most browsers do not support vector graphics. As a result, vectors have to be converted to bitmap (rasterized) before being displayed on the Web. Some vector graphics file formats include: EPS; Illustrators' AI and WMF; and PICT for the Mac. Types of graphics 1. Photographic images: 2. Continuous tones, 24 bit color, no text, few lines and edges Graphics, Logos, Line art and Screen Captures: Solid colors, up to 256 colors, with text or lines and sharp edges Image mode (RGB, indexed color, Gray scale, CMYK) RGB: – Uses millions of colors. Flexible for editing. – Use when working on editing or creating an image (millions of colors). – Save file as .psd . Remember when saving in PSD, this will produce a large file and will not be viewed on the web. The PSD file is good to use while editing file. – Layers are available in this mode and not in gif or jpg, or png (they are compressed/ flattened files) – Jpg/png24, uses RGB but NOT gif. CMYK: The CMYK model is based on the light-absorbing quality of ink printed on paper. - Pure cyan (C), magenta (M), and yellow (Y) pigments should combine to absorb all light and produce black. For this reason these colors are called subtractive colors. - Use when working on images for print: save as .tiff and use high resolution (200-600). Indexed color mode: – 8bit or 256 colors. Used with .gif files. Not flexible to use while editing and you will get inconsistent results; it is better to work in RGB mode and then use FILE / SAVE FOR WEB for .gif images - Resolution Resolution – The resolution of an image describes how fine the dots are that make up that image. – The more dots, the higher the resolution (better quality). – Resolution for the screen/web (dependant on monitor size): When displayed on a monitor, the dots are called pixels. A 640-by-480-pixels on screen is capable of displaying 640 distinct dots on each of its 480 lines, or about (640 X 480) 300,000 pixels. Use 72 - 200 resolution for web (Note: if use higher resolution than 72, your file size will increase and dimensions of height and width as well) – Resolution for printer: A 300 dpi (dots per inch) printer is capable of printing 300 dots in a line “1 inch” long. This means it can print 90,000 (300 X 300) dots per square inch Use 200- 1200 resolution for printing Working with mode: To change your image over to RGB mode: - select Mode from the Image pull down menu and choose RGB Color. To resize image: go back to the Image pulldown and select Image Size. Enter in the size you want (either the pixel dimension or in inches - make sure the resolution box reads "72") and click OK. Graphic format for the web/screen: GIF: Graphic Interchange Format – First graphic format for the web created by CompuServ – Standard gif is 8bits or 216 colors – Transparent gif: GIF89a (No background color: blends into any background since it doesn’t have any background color of is own) – Gif uses “LZW” (Lemple-Zev-Welch) compression. – This compression takes advantage of the repetitions in data streams. – LZW is efficient for storing simple graphic, flat colors, Banners, logo’s (images with little color shading).. Graphic format for the web: Jpeg or JPG: Joint Photographic Experts 24 bits... Millions of colors used for photograph and complex images Uses Lossy compression method: – which compresses shades of tones that are not visible by the eye without loss of quality Used to compress photographs PNG (png8 and png 24): PNG: Portable Network Graphics Types of PNG: Png_8: 8 bits.. 256 colors, good for simple graphics .. Not too many shades of colors Png_24: 24 bits or millions of colors. Good for complicated images such as photographs. Lossless compression scheme and better compression than gif Format for Print/editing/scan: Tiff : (great quality image used for print) • • • • TIFF - Image File Format (.TIF files). TIF files are typically very large TIFF is a nearly universal format TIFF has been the format of choice for use for master copies of scanned data for years. • TIFF was developed by Aldus, before Adobe bought them, and is the most widely supported format across other platforms. • Not used on the web • Great for print (good quality), but remember that it’s a large file PSD: standard Photoshop file(.psd) • • • • • • Uses millions of colors (RGB: red, Green, & blue) (0-256 shades of red, 0-256 shades of Green, 0-256 shades of blue) Great for editing / work in progress Saves with layers / helpful while editing a file Very Large file PSD file format will not work on the web … (except in Safari under Mac OS X... Which will display a flattened version of your image.) Other formats: These formats are not commonly used on the web (as they are not supported by all browsers) • BMP (Windows Bitmap) • BMP will handle 24 bit data but it cannot be compressed. • BMP uses RLE (Run Length Encoding) to compress 8 bit data, which is effective in graphics, but much less effective in continuous tones like photos. • PICT (Macintosh Quickdraw) PICT is an older format which was used in page layout and graphics programs; it creates large files and is not suitable for exchange with Windows programs. Browser color palette: Browser Safe palate ( web): Browser uses 256 colors (8 bits). 40 colors are reserved for its own use 216 colors are used by the browser Dithering: browser tries to substitute colors if not part of its palate Interlace: browser will display image gradually Anti-alias: blending of pixel colors on perimeter of hard-edge shapes. Smooth edges (not jagged) Photoshop tips for the web Graphic format for the web/screen: File formats to use: gif, jpg or png To save for the web using Photoshop: – From the FILE menu, select SAVE FOR WEB and then select the desired web format from the window that comes up. – Make sure you select “0” dithering colors (minimal loss of color) General Photoshop tips (such as after scanning) To reduce image size and resolution: – From the image menu, select “image size” – You can also use the “Crop” tool to remove parts of the image along the perimeter You can change the orientation of the image: – From the image menu, select “Rotate canvas” To restore some lost information after resizing image (or scanning) – Apply “unsharp mask”: from “filter menu” choose sharpen then select “unsharp mask” – You can also try to adjust colors (after scanning or changing size of image): Image menu: select adjustments, then try the following – Curves – Auto levels – Auto contrast – Variations Useful Chart when working with images (web vs print) Image type Editing image/While working on Output to screen/web Output to printer with image Photograph (complicated image) Mode: RGB: best for web Save file as: .psd CMYK: mode used for printing Save file as: .tiff Format: Jpg or png Mode: RGB -Millions of colors Resolution: 72-200 The lower resolution, the lower file size Format: .tiff or .pict - mode: CMYK -Millions of colors -resolution200-600 Line art image (simple image) Mode: RGB: mode best for screen Save file as: .psd) Format: Gif or png8 -256 colors (mode: index) Resolution:72 The lower resolution, lower file size Format: .tiff or pict -Millions of colors -resolution: 200-600 Mode: CMYK CMYK:mode used for printing Save file as: .tiff Scanning Scan at high resolution 150-300 web 200-600 print After scanning and editing image, save for desired output as mentioned above Overview of Photoshop tools Move object tool - Rectangular marquee tool - press to select Elliptical Marquee tool - Crop tool - used to Shrink image. You can also use to enlarge image -Pencil tool: free hand drawing (uses foreground color) - Press on same tool to select a “Brush” tool - Paint bucket tool - used to paint large area of canvas. It uses colors in the foreground -Type tool - Eye dropper tool -to select a foreground color from image -Foreground color - used when using type, paint bucket, pencil, paint brush -Background color - used when “cut” from edit menu