* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Micro Ch 18- presentation 3 Short Run Long Run and Efficiency-0
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
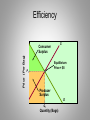
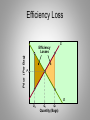
Short Run, Long Run and Efficiency Micro Chapter 18 Cross Elasticity of Demand • Measures how sensitive consumer purchases of one product are to a change in price of another product • Exy = Percentage change in Q demanded x/ Percentage change in price of Y Substitute Goods • If Cross elasticity is > 0, x and Y are substitutes • Ex- price of Coke goes up, more Pepsi is purchased Complements • Cross elasticity < 0, X and Y are complements • An increase in the price of X causes a decrease in the demand for Y • Ex- increase in the price of digital cameras leads to a decrease in the demand of memory cards Independent Goods • Zero or near zero cross elasticity means the items are unrelated • Ex- walnuts and plums Uses of Cross-Elasticity • Government uses cross elasticity when deciding whether mergers will violate antitrust laws Income Elasticity of Demand • Ei = % change in quantity demanded/ % change in income • Measures the degree to which consumers respond to a change in income in buying more or less of a particular good Normal (Superior) Good • Ei > 0 • More demand as income increases • Ex- cars, vacation, electronics Inferior Goods • Ei < 0 • Consumers decrease their purchases of inferior goods as income goes up • Ex- Ramen Noodles, retread tires Consumer Surplus • The difference between the amount consumer(s) are willing to pay and equil $ Consumer Surplus Equilibrium Price = $8 Producer Surplus • Difference between the actual price a producer receives and the min. acc. price Price (Per Bag) S Equilibrium Price = $8 P1 Producer Surplus Efficiency S Price (Per Bag) Consumer Surplus Equilibrium Price = $8 P1 Producer Surplus D Q1 Quantity (Bags) Efficiency/Deadweight Loss • Reductions of combined consumer and producer surpluses associated with underproduction or overproduction • Quantities < or > Q1 Efficiency Loss S Price (Per Bag) Efficiency Losses P1 D Q2 Q1 Q3 Quantity (Bags)