* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Essentials of marketing – Chapter 13
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
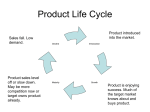
Chapter 13 Pricing concepts Learning objectives 1 Discuss the importance of pricing decisions to the economy and to the individual organisation 2 List and explain a variety of pricing objectives 3 Explain the role of demand in price determination 4 Describe cost-oriented pricing strategies Learning objectives (cont.) 5 Demonstrate how the product life cycle, competition, distribution and promotion strategies, customer demands, the Internet and extranets, and perceptions of quality can affect price 6 Describe the procedure for setting the right price 7 Identify the legal and ethical constraints on pricing decisions 8 Explain how discounts, geographic pricing and other special pricing tactics can be used to fine-tune the base price Learning objective 1 Discuss the importance of Define thedecisions term marketing pricing to the economy and to the individual organisation 1 What is price? Price is that which is given up in an exchange to acquire a good or service. 1 The importance of price To the seller… Price is revenue and profit source To the consumer… Price is the cost of something In the broadest sense, price allocates resources in a free-market economy 1 The importance of price to marketing managers Revenue The price charged to customers multiplied by the number of units sold. Profit Revenue minus expenses. 1 The importance of price Revenue = Unit price number of units sold • Revenue pays for every activity. • What’s left over is profit. Marketers must select a price that • is not too high • is not too low • equals the perceived value to target consumers Learning objective 2 Describe four marketing List and explain a variety management philosophies. of pricing objectives 2 Trends influencing price setting • High rate of new product introduction • Increased availability of bargainpriced dealer and generic brands • Price-cutting as a strategy to maintain or regain market share • More efficient and better-informed buyers 2 Pricing objectives • Profit-oriented pricing objectives • Sales-oriented pricing objectives • Status quo pricing objectives 2 Profit-oriented pricing objectives • Profit maximisation • Satisfactory profits • Target return on investment 2 Profit maximisation Setting prices so that total revenue is as large as possible relative to total costs. 2 Return on investment (ROI) Net profit after taxes divided by total assets. ROI = net profit after tax total assets 2 Sales-oriented pricing objectives • Market share • Sales maximisation 2 Market share A company’s product sales as a percentage of total sales for that industry. 2 Sales maximisation • Short-term objective to maximise sales • Ignores profits, competition and the marketing environment • May be used to sell off excess inventory 2 Status quo pricing Advantages Disadvantages • Simplicity • Strategy may ignore demand or cost • Safest route to long-term survival for small firms Learning objective 3 Explain the role of demand in price determination 3 Demand and supply Demand The quantity of a product that will be sold in the market at various prices for a specified period. Supply The quantity of a product that will be offered to the market by a supplier at various prices for a specific period. 3 Elasticity of demand Consumers’ responsiveness or sensitivity to changes in price. 3 Elasticity of demand (cont.) Elastic demand Consumers buy more or less of a product when the price changes Inelastic demand An increase or decrease in price will not significantly affect demand 3 Elasticity of demand (cont.) Price goes… Revenue goes… Demand is… down up elastic down down inelastic up up inelastic up down elastic 3 Factors that affect elasticity • Availability of substitutes • Price relative to purchasing power • Product durability • Product’s other uses Learning objective 4 Describe cost-oriented pricing strategies 4 The cost determinant of price Types of costs Variable costs Deviate with changes in level of output Fixed costs Do not deviate as level of output changes 4 The cost determinant of price (cont.) Methods used to set price • Markup pricing • Break-even pricing 4 Markup pricing Markup pricing The cost of buying the product from the producer plus amounts for profit and for expenses not otherwise accounted for. Example: If a pen costs $1.80 and sells for is $2.20, the markup is $0.40 or 22% of cost. 4 Break-even pricing Price 6 000 Total revenue 4 000 Total costs Break-even point 2 000 Fixed costs 0 1 000 2 000 3 000 Quantity 4 000 5 000 6 000 Learning objective 5 Demonstrate how the product life cycle, competition, distribution and promotion strategies, customer demands, the Internet and extranets, and perceptions of quality can affect price 5 Other determinants of price • Stages of the product life cycle • Competition • Distribution strategy • Promotion strategy • Perceived quality 5 Stages in the product life cycle Introductory stage Growth stage Maturity stage Decline stage $ $ $ $ High Stable Decrease Decrease Stable High 5 Distribution strategy Convincing distributors to carry product • Offer a larger profit margin • Give dealers a large trade allowance 5 The impact of the Internet • Allows price and product comparisons. • Prices are coming down. • Data collection allows sellers to tailor products and prices. 5 Extranet A private electronic network that links a company with its suppliers and customers. 5 Prestige pricing Charging a high price to help promote a highquality image. 5 Indicators of quality • Retailer reputation • Appearance • Price • Brand name Learning objective 6 Describe the procedure for setting the right price 6 Steps in setting the right price Establish pricing goals Estimate demand, costs and profits Choose a price strategy Fine-tune base price with pricing tactics Results lead to the right price 6 Pricing objectives • Profit-oriented pricing objectives • Sales-oriented pricing objectives • Status quo pricing objectives 6 Price strategy A basic, long-term pricing framework which establishes the initial price for a product and the intended direction for price movements over the product life cycle. 6 Choosing a price strategy Basic strategies for setting prices • Price skimming • Status quo • Penetration pricing 6 Price skimming Situations when price skimming is successful • Inelastic demand • Superior product • Legal protection of product • Technological breakthrough • Limited production 6 Penetration pricing A pricing policy whereby a firm charges a relatively low price for a product initially as a way to reach the mass market. 6 Penetration pricing (cont.) Advantages Disadvantages • Discourages or blocks competition from market entry • Requires gear up for mass production • Selling large volumes at low prices • Strategy to gain market share may fail Learning objective 7 Identify the legal and ethical constraints on pricing decisions 7 The legality and ethics of price strategy Issues that limit pricing decisions • Unfair trade • Price fixing • Price discrimination • Predatory pricing Learning objective 8 Explain how discounts, geographic pricing and other special pricing tactics can be used to fine-tune the base price 8 Tactics for fine-tuning the base price • Discounts • Geographic pricing • Special pricing tactics 8 Tactics for fine-tuning the base price (cont.) • • • • • • • Quantity discounts Cash discounts Functional discounts Seasonal discounts Promotional allowances Rebates Value-based pricing 8 Value-based pricing The price is set at a level that seems to the customer to be a good price compared to the prices of other options. 8 Geographic pricing • FOB pricing • Uniform delivered pricing • Zone pricing • Freight absorption pricing • Basing-point pricing 8 Special pricing tactics Single-price tactic All goods offered at the same price. Flexible pricing Different customers pay different price. Professional Used by professionals with experience, services pricing training or certification. Leader pricing Bait pricing Odd-even pricing Price bundling Two-part pricing Sell product at near or below cost. Lure customers through false or misleading price advertising. Odd-number prices imply bargain. Even-number prices imply quality. Combining two or more products in a single package. Two separate charges to consume a single good.