* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lizard Tortoise Pig Human
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
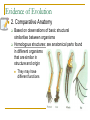
Introduction to Evolution Ms. Sing Do Now In your notebook, answer the following questions What is evolution? What evidence has been collected to support evolution? What is evolution? Change over time More specifically, change in gene frequencies of populations over time Which is an example of evolution? Situation 1: Imagine a year or two of drought in which there are few plants that these beetles can eat . All the beetles have the same chances of survival and reproduction, but because of food restrictions, the beetles in the population are a little smaller than the preceding generation of beetles Which is an example of evolution? Situation 2: Most of the beetles in the population (say 90%) have the genes for bright green coloration and a few of them (10%) have a gene that makes them more brown. Some number of generations later, things have changed: brown beetles are more common than they used to be and make up 70% of the population. Which is an example of evolution? Situation 1 Situation 2 Situation 2 because it demonstrates a change in gene frequency Evidence of Evolution Evidence of Evolution 1. Geological Records Scientists study records found in fossils Fossils are remnants or traces of an organism Fossils are often found in sedimentary rock Scientists assume that each layer is older than the layer above it Evidence of Evolution 2. Comparative Anatomy Based on observations of basic structural similarities between organisms Homologous structures: are anatomical parts found in different organisms that are similar in structure and origin They may have different functions Evidence of Evolution 3. Comparative Embryology Study of early embryonic development of various organisms suggests a common ancestor Lizard Tortoise Pig Human Evidence of Evolution The early embryos of fish, reptiles, birds, and humans closely resemble each other Evidence of Evolution 4. Comparative Cytology All living things are made up of cells Cell organelles (nucleus, mitochondria, etc.) are structurally and functionally similar in most organisms Evidence of Evolution 5. Comparative Biochemistry All living things contain DNA and RNA as well as proteins and enzymes The greater the biochemical similarity, the closer the relationship Who am I? HMS Beagle Charles Darwin (1809- 1882) Natural Selection is the result of The overproduction of offspring Variations among offspring How? The struggle for survival (competition) Adaptive value of certain variations Survival and increased reproduction of those best adapted to a particular environment moth animation Peppered Moth Game Reflection On a piece of paper write 2 things you learned during the lesson 1 thing you did not understand during the lesson