* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Sexuality
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
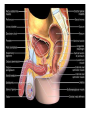
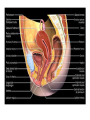
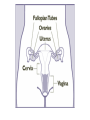
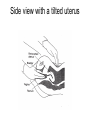
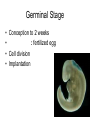
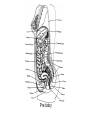
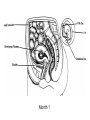
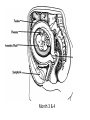
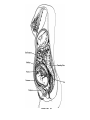
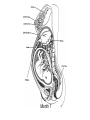
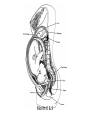
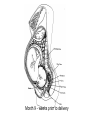
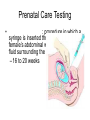
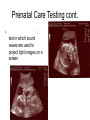
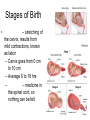
Human Sexuality Unit Male Reproductive System Function and structure • : male sex hormone, initiates physical change, including broadening of the shoulders, development of muscles, facial and body hair, deepening of the voice and sperm production • : male reproductive cell, resemble tadpoles External system • : two small glands that produce sperm, 100 million a day • – sac that holds the testes – Helps regulate the temperature of the sperm – Muscles raise and lower the sac • : a tube-shaped organ attached to the trunk of the body just above the testes – Spongy tissue that contains many blood vessels – – blood vessels fill with blood making the penis ridged – – muscular contractions Internal system • – temporary storage facility for sperm, sperm mature here • – tube that connect seminal vesicles and the prostate gland – Propel the sperm forward in powerful spurts • – contain fluid that give nutrients to the sperm Internal system cont. • – neutralizes the acid content before semen is ejaculated • –secretes, a thin, milky fluid that protects the sperm from acid • – passageway through which both semen and urine leave the body Additional terms • : a thick fluid containing sperm and other secretions – Seminal vesicles, Cowper’s gland, & Prostate gland • : the union of a reproductive cell • : surgical removal of the foreskin of the penis Care of the system • , protection, and self-examination • Testicle examination – Hold one testicle between – Gentle whole testicle around the Problems of the system • Sexually transmitted diseases • – part of an organ pushes through an opening of a membrane or muscle • : a condition in which a person is unable to reproduce – Produce too few sperm – Many reasons for it to happen Problems of the system cont. • – fungal infection that occurs in groin area – Thoroughly wash and dry groin area – Avoid wearing damp clothing • • Enlarged – wear protective gear – Caused by infection, tumor, or old age – Tend to squeeze the urethra, resulting infrequent or difficult urination Problems of the system cont. • Cancer of the – Cancer is an uncontrolled growth of cells – highest incidence of cancer in males • – Occur most frequently between the age – Slight enlargement of one testicle – of cases can be cured if caught early Female Reproductive System Functions & Structure • • : female reproductive cell : a muscular, elastic passageway that extend from the uterus to the outside of the body • : the process of releasing one mature ovum each month – Alternating ovary release time Functions & Structure cont. • : female sex gland that house the ova and produce female sex hormones – 400,00 immature ova (egg) at birth • : a pair of tubes with finger like projections that draw the ovum in – 4 inches long, 1/3 inch diameter – Sperm must meet the egg in there for Functions & Structure cont. • : cell that results from the union of sperm and ovum • : small, muscular, pair-shaped organ about the size of a fist – Zygote must attach to the wall Menstruation • Ovum does not become fertilized, the lining of the , tissue, and fluid which passes through the cervix and out of the vagina – : neck of uterus – Uterus walls thicken again • : time from the beginning of one menstrual period to the onset of the next one – 28 days Care of the system • Cleanliness is very important – Vagina is self cleaning - • Breast self-examination – Should be done , one week after the start of menstrual period – 3 ways - shower, front of minor, and lying down Care of the system cont. • Breast self-examination steps to follow – Look at the shape in the mirror - arm behind head and bending over – Use 3 finger and make a circling movement feeling for lumps – Don’t forget armpits and between breasts Problems with the system • : in ability of a woman to become pregnant • - fluid-filled sac on the ovary • Cancer develop some cancer – Pap test will detect cervical cancer Side view of pelvic exam Side view with a tilted uterus View of cervix and vagina Pap smear Problems with Menstruation • - abdominal cramps during menstrual period • (PMS) nervous, tension, anxiety, irritability, bloating, weight gain, depression, mood swings, and fatigue • (TSS) bacteria causes infection – Need to change tampons regularly Problems that can cause infertility • - leading cause of infertility – Caused by PID • - 2nd leading cause of infertility – Uterine tissue grows outside the uterus • (PID) infection of the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and surrounding area in a woman’s pelvis Life Cycle Conception Conception • Every person starts by connecting – the connecting of • egg and sperm • – cells begin to implant or attach to the lining of the uterus Genetics • : tiny structures within the nuclei of cells that carry info about heredity traits – Each cell as 46 chromosomes – 23 pairs – Made up of chemical compounds - DNA • : segments of DNA, that holds info about heredity traits • Each person receives half from mom and half from dad – 23 chromosomes in ova and sperm Genetics cont. • Dominant and recessive genes – – – will show up in the offspring – will not show up in offspring, unless there are 2 recessive genes together • Gender – sex chromosomes – Female – – Male - Twins • : one egg and one sperm, unite and split creating 2 babies • :2 eggs and 2 sperm Development • – thin membrane holding fluid that insulated the embryo – Amniotic fluid – fluid around the baby • : blood-rich tissue developed from an outer layer of cells from the embryo and tissue from the mother • : tube through which nutrients and oxygen pass from the mother’s blood into the embryo’s blood Life Cycle Prenatal Development Germinal Stage • Conception to 2 weeks • : fertilized egg • Cell division • Implantation Embryonic Stage • : cluster of developing cells following implantation – Size of the dot of the letter • 2 week to 8 weeks • Development of all organs – may not all function until closer to delivery Fetal Development • : name by which the embryo is known from the end of the 8 weeks • Fetal movement • Completing development • Growing bigger Pre baby Month 1 Month 3 & 4 Month 5 Month 7 Month 8 & 9 Month 9 - weeks prior to delivery Uterus Prenatal Care • • • • Regular Increase nutrients Monitor the growth of the Medicines should only be taken with doctors approval, most are dangerous Prenatal Care cont. • • – FAS – addiction and physical damage • • – stimulate – will cause premature birth and low birth weight – Will affect growth, mental development, and behavior Prenatal Care Testing • : procedure in which a syringe is inserted through the pregnant female’s abdominal wall into the amniotic fluid surrounding the developing fetus – 16 to 20 weeks Prenatal Care Testing cont. • : test in which sound waves are used to project light images on a screen Prenatal Care Testing cont. • : test in which a small piece of membrane is removed from the chorion, a layer of tissue that develops into the placenta – 8 weeks Complication during pregnancy • : spontaneous abortion – Prior to 20 weeks • : birth of a dead fetus – After 20 weeks Life Cycle Delivery Signs of labor • Loss of mucus plug • • Contractions – Staying consistent Stages of Birth • – stretching of the cervix, results from mild contractions, known as labor – Cervix goes from 0 cm to 10 cm – Average 6 to 18 hrs – – medicine in the spinal cord, so nothing can be felt Stages of Birth cont. • Passage of the – Requires the mother to push the baby down the birth canal – 1 to 2 hrs – –widen opening with surgical cut – Forceps or vacuum may be used Stages of Birth cont. • – contractions continue to eliminate the placenta – Mother usually does not even know this is happening – 15 to 30 minutes Cesarean Birth • : baby is delivered through a surgical incision in the mother’s abdomen – Bikini cut – very small incision • Used when mother or baby is at risk – Many mother who have had a C-section will choose to deliver their other children this way Checking the baby • : routine diagnostic test that determine an infant’s physical condition at birth – scale 0 to 2 – Appearance – Pulse – Grimace – Activity – Respiration Labor & Delivery Video • Rachel & Matt Life Cycle Newborns to Childhood Infancy • Birth to 1 ½ years • height doubles • Develop – Head to – Near to – Simple to – weight triples and Early Childhood • 2 to 3 yrs • Develop new physical and mental skills • Speech, controlling elimination of body wastes • : confidence that one can control one’s own body, impulses, and environment Childhood • 4 to 5 yrs • Initiate play activities rather then follow others • Make-believe, Late Childhood • 6 to 11yrs • Social, emotional, intellectual, physical and cultural growth • They need to try