* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Applied Female Reproductive Physiology and the anatomy of the
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
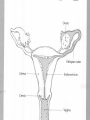
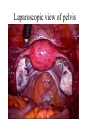
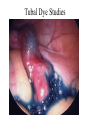
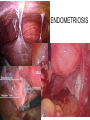
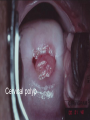
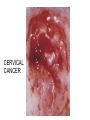
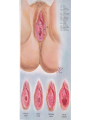
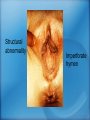
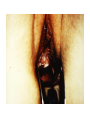
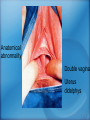
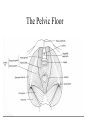
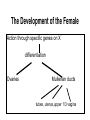
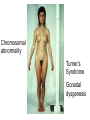
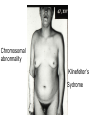
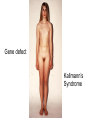
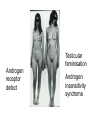
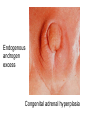
Applied Female Reproductive Physiology and the Anatomy of the Female Genitourinary System • Modified from material provided by Professor Michael Chapman • Revised February 2016 • Laparoscopic view of pelvis Tubal Dye Studies Normal Female Pelvis • ENDOMETRIOSIS • Cervical polyp CERVICAL CANCER External Genitalia (Female) • Structural abnormality Imperforate hymen Anatomical abnormality Double vagina Uterus didelphys The Pelvic Floor Course of the Ureter in Females Reproductive Physiology (Female) Female Menstrual Cycles Implantation ENDOMETRIAL CYCLE Changes in during cycle uterine lining Window of Receptivity The Development of the Female WHAT MAKES A GIRL, A GIRL? The Development of the Female XX vs XY Chromosomal Determination The Development of the Female Action through specific genes on X differentiation Ovaries Mullerian ducts tubes, uterus,upper 1/3 vagina The Development of the Male specific genes on Y chromosome (eg SRY-1) differentiation testis testosterone Internal genitalia prostate ,seminal vesicles, vas, epididymis, descent of testes AMH/MIF Mullerian duct suppression no uterus,tubes, upper vagina Abnormal Sexual Development - Chromosomal abnormalities Androgen receptor defects Enzyme deficiencies Exogenous/endogenous hormone exposure - Anatomical abnormality Chromosomal abnormality Turner’s Syndrome Gonadal dysgenesis Turner’s Syndrome • Chromosomes 45 XO • Short stature, low hairline, webbed neck, primary amenorrhoea • 1:5000 females but common aneuploidy in miscarriage • Normal female external & internal genitalia but with streak ovaries • Will “menstruate” on The Pill • Can carry a pregnancy if primed with E2 and PROG and donated egg/embryo Chromosomal abnormality Klinefelter’s Sydrome Klinefelter’s Syndrome • • • • Chromosomes 47 XXY Tall sometimes with gynaecomastia 1:750 males but may never be detected Normal male external genitalia but with small, soft testes and ↓testosterone • Commonly infertile with azospermia • Can be assisted to fatherhood using IVF/ICSI if any sperm can be found Gene defect Kallmann’s Syndrome Kallmann’s Syndrome • Chromosomes can be 46XY or 46XX • Absence of GnRH from the hypothalamus results in... • Hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism • Also have anosmia • 1:4,000 males and 1:12,000 females • Have male or female genitalia but will not enter puberty • Can be treated with sex steroids or FSH/LH Androgen receptor defect Testicular feminisation Androgen insensitivity syndrome Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome • Chromosomes 46XY • Classically a result of absent androgen receptors so all cells are unresponsive to testosterone • Have female external genitalia but absent uterus and vagina and undescended testes • Present with primary amenorrhoea but good breast development, absent pubic hair • Testes are usually surgically removed • But what do you tell these girls? Endogenous androgen excess Congenital adrenal hyperplasia Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia • Chromosomes can be 46XY or 46XX • A block in cortisol synthesis causes ↑ACTH and ↑androgens by the adrenals • Females will exhibit virilization • Babies have fused labia and clitoramegaly • May require urgent identification and treatment with cortisol etc soon after birth 5-alpha-reductase deficiency • This enzyme converts Testosterone to Dihydrotestosterone in peripheral tissue • Affects males i.e. those who are XY • Often raised as girls because testes are undescended at birth and external genitalia appear female with hypospadias • However identify as male & undergo spontaneous sex change at puberty when T levels rise and DHT is produced by alternative enzymes in the liver and testes • Autosomal recessive condition. Very rare, seen only in Dominican Republic, PNG and Turkey • Affects 1:90 males in the remote village of Salinas in the Dominican Republic where they are called “Guevedoces” = “penis at 12” Catherine and his cousin Carla “Guevedoces” from the Dominic Republic feature in Michael Mosely’s BBC Feature, “The Extraordinary Making of You” For further information on disorders of sexual development... • Consult “Intersex” on Wikipedia Please leave a note on the Welcome Page to this website Any Questions or Comments?