* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pedigree - Turner
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Human–animal hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
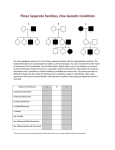
Chapter Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity 11 11.2 Complex Patterns of Inheritance Incomplete Dominance The heterozygous phenotype is an intermediate phenotype between the two homozygous phenotypes. Chapter Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity 11 11.2 Complex Patterns of Inheritance Codominance Both alleles are expressed in the heterozygous condition. Chapter Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity 11 11.2 Complex Patterns of Inheritance Multiple Alleles Blood groups in humans ABO blood groups have three forms of alleles. Chapter Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity 11 11.2 Complex Patterns of Inheritance Coat Color of Rabbits Multiple alleles can demonstrate a hierarchy of dominance. In rabbits, four alleles code for coat color: C, cch, ch, and c. Chapter Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity 11 11.2 Complex Patterns of Inheritance Coat Color of Rabbits Chinchilla Albino Light gray Dark gray Himalayan Chapter Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity 11 11.2 Complex Patterns of Inheritance Sex Determination Sex chromosomes determine an individual’s gender. Chapter Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity 11 11.2 Complex Patterns of Inheritance Dosage Compensation The X chromosome carries a variety of genes that are necessary for the development of both females and males. The Y chromosome mainly has genes that relate to the development of male characteristics. Chromosome inactivation Barr bodies Chapter Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity 11 11.2 Complex Patterns of Inheritance Polygenic Traits Polygenic traits arise from the interaction of multiple pairs of genes. Chapter Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity 11 11.2 Complex Patterns of Inheritance Environmental Influences Environmental factors Diet and exercise Sunlight and water Temperature Chapter Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity 11 11.2 Complex Patterns of Inheritance Twin Studies Helps scientists separate genetic contributions from environmental contributions Traits that appear frequently in identical twins are at least partially controlled by heredity. Traits expressed differently in identical twins are strongly influenced by environment. Chapter Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity 11 11.3 Chromosomes and Human Heredity Telomeres Telomere caps consist of DNA associated with proteins. Serves a protective function for the structure of the chromosome Chapter Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity 11 11.1 Basic Patterns of Human Inheritance Inferring Genotypes Knowing physical traits can determine what genes an individual is most likely to have. Predicting Disorders Record keeping helps scientists use pedigree analysis to study inheritance patterns, determine phenotypes, and ascertain genotypes. Chapter Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity 11 11.3 Chromosomes and Human Heredity Karyotype Studies Karyotype—micrograph in which the pairs of homologous chromosomes are arranged in decreasing size. Images of chromosomes stained during metaphase Chromosomes are arranged in decreasing size to produce a micrograph. Pedigree = Males Key: = Females Shading = Have trait (Attached Earlobes = f ) No Shading = Do not have trait (Free Earlobes = F) I 1 2 II 1 2 3 What are the Genotypes of the people shown below? Ff Ff 1 Ff 2 3 F? 1 F? 2 F? ff 3 ff 1 Ff 4 ff 4 II 5 2 F f I 6 F f 3 Ff What Does Each One Show? Divorce --- Adoption Not Married but Biological mom and dad Divorce and Death