* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
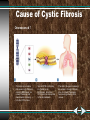
The Human Genome Human Chromosomes • Karyotype- diagram showing the complete set of chromosomes. • A karyotype shows us 46 human chromosomes. • 22 pairs are autosomes (main body parts) • 1 pair are sex chromosomes Normal Human Karyotype Determining Sex Females are XX, producing only X gametes. Males are XY, producing both X & Y gametes. Determining Sex Chances of having a boy or girl are always 50% Pedigrees Method of tracking traits within a family. Squares = Males Circles = Females Colored = Trait Pedigree Example A circle represents a female. A horizontal line connecting a male and female represents a marriage. A half-shaded circle or square indicates that a person is a carrier of the trait. A completely shaded circle or square indicates that a person expresses the trait. A square represents a male. A vertical line and a bracket connect the parents to their children. A circle or square that is not shaded indicates that a person neither expresses the trait nor is a carrier of the trait. Tay-Sachs Pedigree • 1. How many generations are there in this pedigree? • 2. Who died in Generation 2? • 3. How many kids were produced from generation 1? Tay-Sacs Pedigree • 4. Who got married in generation 3? • 5. How many kids lived in generation 4? It’s in the blood Your blood cells have protein coats that make them unique to other people’s blood cells. The alleles for blood types are both multiple allelic and codominant. Human Blood Groups Phenotype (Blood Type) Antigen on Genotype Red Blood Cell Safe Transfusions To From Genetic Disorders Recessive Disorders Albinism- no pigment Cystic Fibrosis- mucus in lungs PKU – inability to break down phenylalanine Tay-Sachs- breakdown of nervous system Genetic Disorders Dominant Allele Disorders Huntington’s Disease- lose muscle control & mental function Achondroplasia- dwarfism Genetic Disorders Codominant Disorders Sickle Cell Disease- abnormal shaped blood cells causing blood clots Sickle Cell Anemia • Found mainly among African-Americans. • The Hemoglobin that traps oxygen is deformed so it can’t catch oxygen. • Deformed cells can also clog small blood vessels. • Caused by a point mutation. Cystic Fibrosis • This is caused when 3-bases of your DNA are deleted. • RESULTS: • Wrong protein is made. • Heavy mucus forms in the lungs making it difficult to breathe. Cause of Cystic Fibrosis Chromosome # 7 CFTR gene The most common allele that causes cystic fibrosis is missing 3 DNA bases. As a result, the amino acid phenylalanine is missing from the CFTR protein. Normal CFTR is a chloride ion channel in cell membranes. Abnormal CFTR cannot be transported to the cell membrane. The cells in the person’s airways are unable to transport chloride ions. As a result, the airways become clogged with a thick mucus. Sex linked traits A trait controlled by an allele on the sex chromosomes. - most found on the X-chromosome - males more likely to express these traits Color Blindness • Located on the X-chromosome (sex-linked). • The most common form is red-green colorblindness. • You can’t distinguish between colors. • More common among males. Figure 14-13 Colorblindness Section 14-2 Father (normal vision) Colorblind Normal vision Male Female Daughter (normal vision) Son (normal vision) Daughter (carrier) Son (colorblind) Mother (carrier) Section 14-2 Figure 14-13 Colorblindness Father (normal vision) Colorblind Normal vision Male Female Daughter (normal vision) Son (normal vision) Daughter (carrier) Son (colorblind) Mother (carrier) Hemophilia Located on the X-chromosome (sex-linked). Protein for normal blood clotting is missing. Causes an inability of blood to clot. Sex linked traits examples If a male cardinal is red and female is brown, which chromosome is the allele for red feathers found? Chromosomal Disorders • Mutations with chromosomes. • Mostly occur during meiosis(nondisjunction) • Examples: Down syndrome Sex Chromosome Disorder. Nondisjunction in meiosis I Nondisjunction in meiosis II Meiosis I Nondisjunction Meiosis II Nondisjunction Gametes n+1 n+1 n-1 n-1 n+1 n-1 n n Number of chromosomes Figure 8.21 Down’s Syndrome • Nondisjunction leads to 3 copies of chromosome #21. • No clear understanding on why the extra chromosome causes the birth defect. Sex Chromosome Disorders Turner’s syndrome • Nondisjunction leads to only one X chromosome being inherited. • Causes females to be sterile. Klinefelter’s syndrome • Nondisjunction leads to an extra X chromosme being inherited. • Causes males to be sterile. Determining Genetic Disorders • Doctors look at Karyotypes