* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Female
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
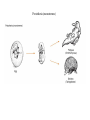
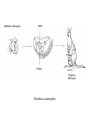
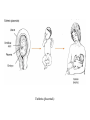
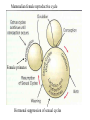
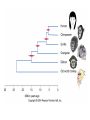
Mammalian Reproductive Strategies Prototheria (monotremes) Metatheria (marsupials) Eutheria (placentals) Patterns of Social Behavior Sociability: important characteristic for most primates Continuous interactions among a group of individuals Advantages of Group Living • 1. Observational learning. – Reduces necessity of individual trial-anderror learning. • 2. Possibile genetic resistance to disease and parasites. • 3. Efficient location of food resources • 4. Increases the reproductive fitness of group members. Social groupings What kind of social grouping? Polygyny: one reproductively mature (RM) male, several RM females Gelada baboon Lip retraction: threat display • • • • • Individuals are solitary Males are intolerant of one another. Single male establishes a large territory. Contains several females Each female has her own separate home range • Polygyny • Extensive home ranges Multi-male; multi-female groups Overlapping territories • Multi-male, multi-female groups • Non-aggressive • Human societies extremely diverse • Monogamy • Polygamy – polygyny and polyandry • For most of human evolution - and for most women in the world today, menstruation is a rare occurrence • Repetitive pregnancies and long periods of lactation Fundamental intersexual reproductive strategies • Female. • Maximize resources available to her and her offspring. • Female primates spend most of their adult lives pregnant, lactating, and caring for offspring. • High energy demands. • Male. • Produce many offspring and make sure they are yours. • Non-human primates: androgen levels fluctuate in response to female receptivity. Mammalian female reproductive cycle Female primates Hormonal suppression of sexual cycles Nonhuman Cultural Behavior • • • • • Learned behavior shared between generations. t Chimpanzees: tool use Spearing of bushbabies Termite fishing with modified stems and twigs. Have a preconceived idea of what the finished tool needs to be in order to be useful. • May make the tool in advance of the opportunity for use. • Preparing for the future. Requires planning and forethought. Meat component of chimpanzee diet Bone review Genetic similarities and differences Human and ape chromosomes A phyletic classification of families mtDNA 4,700 base sequence Genes for 11 tRNAs 6 proteins Human-chimpanzee relationship 1023 more likely than Chimpanzee-gorilla relationship Y DNA Base sequence for Testis-specific protein Y Autosomal DNA Base sequence of Beta-globin gene cluster A cladistic classification of families