* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Agent-Based Hybrid Intelligent Systems and Their Dynamic
Affective computing wikipedia , lookup
Pattern recognition wikipedia , lookup
Knowledge representation and reasoning wikipedia , lookup
Expert system wikipedia , lookup
Gene prediction wikipedia , lookup
Self-reconfiguring modular robot wikipedia , lookup
Incomplete Nature wikipedia , lookup
Ecological interface design wikipedia , lookup
Agent-based model in biology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
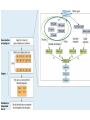
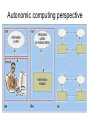
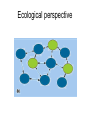
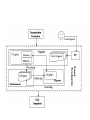
Agent-Based Hybrid Intelligent Systems and Their Dynamic Reconfiguration Zili Zhang Faculty of Computer and Information Science Southwest University [email protected] Acknowledgement: Pengyi Yang, Li Tao Roadmap • Background and Motivation • The Genetic Ensemble (GE) Hybrid System – – – – Problem Definition Overview of the GE System Experimental Results Advantages of the GE System • Dynamic Reconfiguration – Dynamic Reconfiguration Model – The Algorithm for Dynamic Reconfiguration – Experiments and Evaluation • Conclusions Background and Motivation • A few years ago, we proposed an agentbased framework for complex problem solving (Z. Zhang & C. Zhang, Agent-Based Hybrid Intelligent Systems: An Agent-Based Framework for Complex Problem Solving, LNAI2938, Springer, 2004.) • This framework was applied to: – Financial Investment Planning (PRICAI’02) – Data Mining etc (Applied AI, 2003) Our Understanding • Hybrid approaches are required for many complex problems • Better results can be achieved when these techniques are combined in hybrid intelligent systems • Agent technology is well suited to model the manifold interactions among the many different components of hybrid intelligent systems In Bioinformatics • Hybrid algorithms can be used to solve a variety of problems in bioinformatics • The hybrid algorithm often improves on either a single algorithm, in terms of performance, or in the transparency of its results • There are numerous ways in which algorithms can be combined (E. Keedwell and A. Narayannan: Intelligent Bioinformatics – The application of AI techniques to bioinformatics problems, Wiley, 2005 [Ch. 11]) The GE Hybrid System • Z. Zhang. P. Yang, X. Wu, and C. Zhang, An Agent-based Hybrid System for Microarray Data Analysis, IEEE Intelligent Systems, Sept./Oct. 2009. Problem Definition • To identify biologically important genes and to improve data classification accuracy, we need to develop effective gene selection measures. • Currently, there are a lot of gene selection strategies available. Several studies set out to compare the strength and the weakness of each method. The comparison results tell us that with different datasets different methods often perform unevenly. • Instead of choosing one method for one situation, we combine different methods to create a more accurate and general hybrid system—the GE system. Classifiers • Integrated classifiers: – – – – – Decision Tree (DT) Random Forest (RF) 7-Nearest Neighbors (7NN) Naïve Bayes (NB) 3-Nearest Neighbors (3NN) Blocking Committee • Suppose a total of n classifiers each creates a different hypothesis denoted as hi (s),(i 1, , n) while classifying the data using gene subset s. The fitness function derived from blocking integration strategy can be defined as follows: n fitnessb ( s ) arg min C (hi ( s), y ) yY i 1 Where y is the class label and C(.) is the accuracy Evaluation function which can be calculated by cross Validation etc. Voting Committee • Suppose a total of n classifiers each creates a different hypothesis denoted as hi (s),(i 1, , n) while classifying the data using gene subset s. The fitness function derived from voting integration strategy can be defined as follows: k fitnessv ( s ) arg max V (hi ( s), y ) yY i 1 Where y is the class label, k is the number of classifier in voting, and V(.) is the voting function of a given classifier. Filters • Gain Ratio d Gain( g j ) j 1 Split ( g j ) fitnessg ( s ) • ReliefF d fitnessr (s) ReliefF ( g j ) j 1 where d denotes the number of genes in subset s, and g j is the jth gene in subset s. Why Choosing these algorithms? • We based the selection of classifiers for GE hybrids on their sample classification accuracy and diversity from other classifiers. • For the filter components, we favored those that are consistent with classifier components. • By Implementing different algorithms in terms of agents, we can test different combinations by forming different multiagent systems at runtime rather than at design time. • We no longer need to modify the code each time we test a new combination. • Therefore, in a given time frame we can investigate many more algorithm combinations than we could using traditional methods. Experimental Results • Datasets • Gene Subset Size Determination • Classification Results • Reproducibility Advantages of the GE System • Evaluate gene subsets from multiple aspects. • Select better generalization gene profiles. • Avoid selection bias of certain feature evaluation method. • Allow different selection and evaluation methods to be integrated at ease. • Achieve higher classification accuracy while also obtain better selection stability Dynamic Reconfiguration • Given the scale and complexity of real-world applications, it is increasingly important that complex software systems operating in dynamic operational environments call for dynamic reconfiguration (self-configuration, selforganization) property. • Such software systems should reorganise automatically with environments and tasks changes as we can not pre-define everything at the design time. Observations • Today’s complex problem solving systems often fail because of the wrong configuration or static organization. • In this context, to fail means to produce incorrect solutions, solutions of unacceptable bad quality or to spend unreasonable time and resources. How to Model Dynamic Configuration • Autonomic computing perspective • Self-organization perspective • Ecological perspective (F. Zambonelli, Self-Management and Many Facets of “Nonself”, IEEE IS, March/April, 2006, pp. 53-55.) Autonomic computing perspective Self-organization perspective Ecological perspective Using AOC to Model Dynamic Reconfiguration • Autonomy-Oriented Computing (AOC) is an emerging computational paradigm that draws on the principles of self-organization and complex systems [Jiming Liu et al] • A formal framework of AOC consists of a population of autonomous entities and the rest of the system referred to as the environment. • An autonomous entity consists of a detector (or a set of such), an effector (again, there can be a set of such) and a repository of local behavior rules. • Specifically, using AOC framework to model dynamic reconfiguration of agentbased systems, we need to clearly describe what are the environment, primitive behaviors and behavioral rules of autonomous entities (here agents), and the interactions between agents and their environment. • Once we have done these, the dynamic reconfiguration of agent-based systems is then reduced to the self-organization of AOC systems. • A heuristic algorithm (HIERA) has been developed to support the organization formation behavior in dynamic reconfiguration. The HIERA algorithm • Initialization: initialize the parameters of CAgents, including searching steps, primitive behaviors probability, and so on. • Search: use local-searching algorithm to search appropriate MAgent. • Behavior Selection: use Roulette method to select primitive behaviors according to different behavior probability, and use heuristic rules to modify behavior probabilities • Based on the experiments conducted, HIERA algorithm can converge in an acceptable time • It can change its searching strategy adaptively according to different environments. Conclusions • Hybrid approaches are required for many complex problems • Agent-based approaches are suitable for building hybrid systems in general, and that a genetic ensemble system is appropriate for microarray data analysis in particular. • Dynamic reconfiguration is crucial for complex software systems Future Work • Trustworthiness of agent-based systems with dynamic reconfiguration capability – Trusted computing initiative – Trusted Software initiative in China • Questions and Comments?