* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
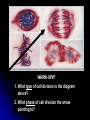
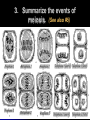
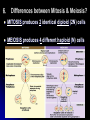
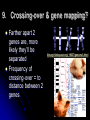
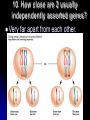
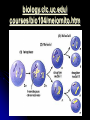
WARM-UP#7 1. What type of cell division is the diagram above? 2. What phase of cell division the arrow pointing to? REMEMBER THE… Characteristics of living things Living things are made up of cells Unicellular – one celled organisms Multicellular – many celled organisms Characteristics of living things Living things reproduce to make offspring of the same species Asexual reproduction Sexual reproduction Characteristics of living things Living things grow and develop MEIOSIS PROCESS OF REDUCTION DIVISION (CHOROMOSOME # IS CUT IN ½ BY SEPERATION OF HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES IN DIPLOID CELLS) 2. Chromosome number in body cells vs. gametes? Body Cells: Diploid (2N) - have 2 sets Gametes: Haploid (N) - have 1 set 3. Summarize the events of meiosis. (See also #5) 3. Summarize the events of meiosis. (See also #5) 4. What are the results of meiosis? 4 haploid (N) cells Genetically different from each other & the original cell 6. Differences between Mitosis & Meiosis? MITOSIS produces 2 identical diploid (2N) cells MEIOSIS produces 4 different haploid (N) cells 7. Human cells 2N=46. How many chromosomes are in a…? Sperm Cell? 23 chromosomes Gamete is haploid (N) Egg Cell? 23 chromosomes Gamete is haploid (N) White Blood Cell? 46 chromosomes Body cell is diploid (2N) 8. How does independent assortment apply to chromosomes? The “chromosomes” assort independently, not individual “genes” 9. Crossing-over & gene mapping? Farther apart 2 genes are, more likely they’ll be separated Frequency of crossing-over = to distance between 2 genes library.thinkquest.org/ 19037/genome3.html 10. How close are 2 usually independently assorted genes? Very far apart from each other. biology.clc.uc.edu/ courses/bio104/meiomito.htm MEIOSIS FOLDABLE