* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Punnett Squares
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
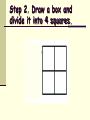
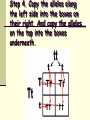
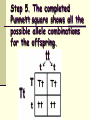
Punnett Square Notes Reginald Punnett What is probability? A number that describes how likely it is that a certain event will occur If you toss a coin, what is the probability that it will land on heads? 1 in 2 = ½ = 50% Punnett Squares A chart used to visualize all the possible combinations of alleles from a genetic cross In a genetic cross, the allele that each parent will pass on to its offspring is based on probability. We use Punnett squares to help us visualize the results. Alleles Dominant alleles are symbolized with capital letters (B, X, C) Recessive alleles are symbolized with lowercase letters (b, x c) Key Terms Phenotype: physical characterisitic/appearance Genotype: genetic makeup (allele combinations, letters) Homozygous: Homo = same Same alleles- TT, bb, DD Heterozygous: Hetero = different Different alleles- Tt, Bb, Dd Hybrid Step 1: Read the problem and write out the parental cross. Problem: A cross between a hybrid tall plant (Tt) and a short plant (tt) Parental Cross: Tt x tt Step 2. Draw a box and divide it into 4 squares. Step 3. Write one parent’s alleles along the top, and the other parent’s along the left side Step 4. Copy the alleles along the left side into the boxes on their right. And copy the alleles on the top into the boxes underneath. Tt Tt tt tt Step 5. The completed Punnett square shows all the possible allele combinations for the offspring. Tt Tt tt tt Step 6. List the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Genotype (allele combination) 2 Tt 2 tt Phenotype = = (visible trait) 2 tall 2 short Step 7. Find the genotype and phenotype frequencies. The frequency is the % probability (likelihood) of the offspring having that particular genotype or phenotype. Genotypes: Tt: # of Tt X 100 = 2 X 100 = 50 % chance Total 4 tt: # of tt X 100 = 2 X 100 = 50 % chance Total 4 Phenotypes: Tall: # Tall X 100 = 2 X 100 = 50 % chance Total 4 short: # short X 100 = 2 X 100 = 50 % chance Total 4