* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DD - Montville.net
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA paternity testing wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
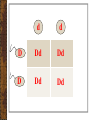
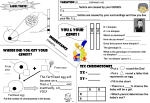
5 Steps to Solving Monohybrid Crosses First, analyze the problem and highlight important information PROBLEM: Dimples are dominant over no dimples. A father is homozygous dominant for dimples and a mother is homozygous recessive for dimples. What are the chances that their child will have dimples? Step 1: Choose a letter to represent a trait. Dimples = D No Dimples = d Step 2: Write down the genotype of the parents. Remember that each parent has 2 alleles. Mom Dad d d DD Step 3: Write the genetic cross. dd x DD Step 4: Set up the Punnett Square. A Punnett Square is a chart scientists use to show all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross. Remember, the Punnett Square shows all the possible outcomes that any 1 child may inherit. Then next time mom and dad have another child it is a new roll of the genetic dice. d d D Dd Dd D Dd Dd Step 5: Determine the phenotypes and genotypes of the offspring. Remember to label the ratios. 0 0 Genotype Ratio 0 DD : 4 Dd : dd express in % 0 % DD : 100 % Dd : % dd Phenotype Ratio: 4 Dimples : 0 No dimples express in % 100% Dimples : 0 % No dimples Independent Practice PROBLEM: In humans, freckles are dominant over no freckles. A man heterozygous for freckles reproduces with a woman also heterozygous for freckles. What chance does their child have for no freckles? **Show your work for Steps 1-5 below: 1. freckles = F no freckles = f 2. Mom = Ff Dad = Ff 3. Ff x Ff F f 4. F FF Ff f Ff ff 5. Genotypic Ratio Genotypic Percent Phenotypic Ratio Phenotypic Percent 1 FF : 2 Ff : 1 ff 25%FF : 50% Ff : 25% ff 3 freckles : 1 no freckles 75% freckles: 25% no freckles