* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NCRR Animal Model Resources
Survey
Document related concepts
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Human–animal hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
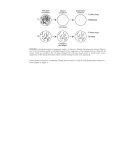
Linking Translational Research to Animal and Bio-Materials Resources Animal and Bio-Materials Resources 1. The problem with resources 2. Limitations of current informatics support 3. Examples of solutions • • Ontologies to describe resources Using ontologies to link resources with human disease NCRR Comparative Medicine Biological Resources Invertebrate Resources • Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center • Caenorhabditis Genetics Center • National Resource for Aplysia • National Resource for Cephalopods Non-human Primate Resources • National Primate Research Centers (8) • Baboon and Monkey Research Resources (3) • Chimpanzee Biomedical Research Resources (6) • Specific-Pathogen-Free Macaque Resources (4) Zebrafish International Resource Center Rodent Resources • Mutant Mouse Regional Resource Centers (4) • Induced Mutant Resource • Special Mouse Strains Resource • Peromyscus Genetic Stock Center • Rat Resource and Research Center • Transgenic Mice With Altered Calcium Handling Resource Biological Materials Resources • Adult Mesenchymal Stem Cell Resource • National Cell Culture Center • National Stem Cell Resource • Viper Resource Center • Yeast Genetic Stock Center How can researchers find appropriate models for human disease research? Human diseases ? Biological models Search: Retinal degeneration Problems that impede finding animals & biological materials as models for human disease 1. Lack of centralized “one stop shopping” • Heterogeneous information • Multiple sites 2. Inconsistent search mechanisms 3. Inconsistent use of descriptive terms 4. Lack of support for synonyms Linking Translational Research to Animal and Bio-Materials Resources Animal and Bio-Materials Resources 1. The problem with resources 2. Limitations of current informatics support 3. Examples of solutions • • Ontologies to describe resources Using ontologies to link resources with human disease QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ZFIN: FlyBase: Melissa Haendel Michael Ashburner Doug Howe Rachel Drysdale Erik Segerdell George Gkoutos Sierra Taylor Animal disease models: Animal models Mutant Gene Mutant or missing Protein Mutant Phenotype (disease model) Animal disease models: Humans Animal models Mutant Gene Mutant Gene Mutant or missing Protein Mutant or missing Protein Mutant Phenotype (disease) Mutant Phenotype (disease model) Animal disease models: Humans Animal models Mutant Gene Mutant Gene Mutant or missing Protein Mutant or missing Protein Mutant Phenotype (disease) Mutant Phenotype (disease model) Animal disease models: Humans Animal models Mutant Gene Mutant Gene Mutant or missing Protein Mutant or missing Protein Mutant Phenotype (disease) Mutant Phenotype (disease model) Vocabulary Animal Central nervous system Diencephalon Nervous system Photoreceptor Retina Ontology Animal Nervous system Central nervous system Diencephalon Retina Photoreceptor Ontology Nervous system Ectoderm D P CNS Neural plate P D Diencephalon Ontology Nervous system Ectoderm D P CNS Neural plate P D Diencephalon Linking Translational Research to Animal and Bio-Materials Resources Animal and Bio-Materials Resources 1. The problem with resources 2. Limitations of current informatics support 3. Examples of solutions • • Ontologies to describe resources Using ontologies to link resources with human disease SHH-/+ SHH-/- shh-/+ shh-/- Phenotype (clinical sign) = entity + attribute shh-/- + value Phenotype (clinical sign) = P1 entity = eye + attribute + value + placement + hypoteloric shh-/- Phenotype (clinical sign) = entity + attribute + value + placement + hypoteloric P1 = eye P2 = midface + development + hypoplastic shh-/- Phenotype (clinical sign) = entity + attribute + value + placement + hypoteloric P1 = eye P2 P3 = midface + development + hypoplastic + hypertrophied = kidney + size shh-/- Phenotype (clinical sign) = entity + attribute + value + placement + hypoteloric P1 = eye P2 P3 = midface + development + hypoplastic + hypertrophied = kidney + size ZFIN: eye PATO: placement hypoteloric midface development hypoplastic kidney size hypertrophied Phenotype (clinical sign) = entity + attribute + value Anatomical ontology Cell & tissue ontology Developmental ontology Gene ontology biological process molecular function cellular component + PATO (phenotype and trait ontology) Phenotype (clinical sign) = entity + attribute + value + placement + hypoteloric P1 = eye P2 P3 = midface + development + hypoplastic + hypertrophied = kidney + size Syndrome = P1 + P2 + P3 (disease) = holoprosencephaly Human holoprosencephaly Zebrafish shh Zebrafish oep Human holoprosencephaly Zebrafish shh Zebrafish oep Linking Translational Research to Animal and Bio-Materials Resources Animal and Bio-Materials Resources 1. The problem with resources 2. Limitations of current informatics support 3. Examples of solutions • • Ontologies to describe resources Using ontologies to link resources with human disease QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture.