* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alkylating agents
Development of analogs of thalidomide wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
DNA-encoded chemical library wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
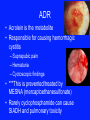
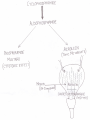
Alkylating agents: Nitrogen Mustards Platinum analogs 1)Bendamustine 7)Carboplatin 2)Cyclophosphamide 8)Cisplatin 9)Oxaliplatin 3)Estramustine Triazenes 4)Ifosfamide 10) Dacarbazine 5)Mechlorethamine 11) Procarbazine 6)Melphalan 12) Temozolomide Miscellaneous 13) Busulfan 14) Chlorambucil 15) Lomustine Alkylating agents -Transfer alkyl group to cellular elements -Alkylation of DNA -Drug – Cyclization – ethyleimonium ion – transfer alkyl group to DNA Nitrosoureas -Carbamoylation of lysine of proteins -Single strand or both strands – BIFUNCTIONAL -DNA Strand breakage -Cross linking of DNA -CCNS. -Mostly in late G1 & S Pharmacological effects : - Dose related ADR. On rapidly growing tissue -Carinogenic – Secondary esp. AML -VESICANT CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE NITROSOUREAS: -Not cross resistant with other alkylating agents -Enter BBB- lipid soluble – Brain tumors -Oral administration -STREPTOZOCIN ADR • Acrolein is the metabolite • Responsible for causing hemorrhagic cystitis – Suprapubic pain – Hematuria – Cyctoscopic findings • ***This is prevented/treated by MESNA (mercaptoethanesulfonate) • Rarely cyclophosphamide can cause SIADH and pulmonary toxicity NON CLASSICAL ALKYLATING AGENTS: PROCARBAZINE: Hodgkin's, Non – Hodgkin's, Brain -Microsomal enzymes – azoprocarbazine + H2O2 -One metabolite – weak MAOI -Increase risk of secondary cancer DACARBAZINE -Activation in liver monomethyl derivative diazomethane, methyl Carbonium ion cytotoxic -Malignant melanoma, HL, Soft tissue sarcomas, neuroblastoma. -Potent vesicant BENDAMUSTINE: -Bi functional PLATINUM ANALOGS: Cisplatin Carboplatin Oxatiplatin -Kill cells in all stage of cell cycle -Synergism with alkylating agents, fluoropyrimidines & taxanes. -vigorous hydration – Renal toxicity. -Oxaliplatin + 5-FU + leucovorin – FOLFOX regimen – metastatic colorectal cancer - Severe nausea & vomiting Neurotoxicity- dose limiting. Antimetabolites Folic Acid Analogs Purine Analogs Pyrimidine Analogs Methotrexate Mercaptoguanine Fluorouracil Trimetrexate Pemetrexed Thioguanine Fludarabine Phosphate Cladribine Cytarabine Gemcitabine Capecitabine Anti metabolites: Folate antag:1)Methotrexate 2)Pemetrexed Punine analogs:- 3) Cladribine 4) Clofarabine 5) Fludarabine 6) Mercaptopurine 7) Pentostatin Pyramiding analogs. 8) Azacitidine 9) Capecitabine 10) Cytarabine 11) Decitabine 12) Fluorouracil 13) Gemcitabine Antimetabolits: sites of drug action Methotrexate (MTX) • MTX is a folic acid analog that binds with high affinity to the active catalytic site of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) • Thus it interferes with the synthesis of tetrahydrofolate (THF) • THF serves as the key one-carbon carrier for enzymatic processes involved in de novo synthesis of thymidylate, purine nucleotides, and the amino acids serine and methionine. • Inhibition of these various metabolic processes thereby interferes with the formation of DNA, RNA, and key cellular proteins. Mechanism of Resistance 1. Decreased drug transport 2. Altered DHFR 3. Decreased polyglutamate formation 4. Increased levels of DHFR Contd.. • Most commonly used anticancer drug. • Cell cycle specific (CCS) drug and acts during S phase of the cell cycle. • Antineoplastic, immunosuppressant and antiinflammatory • Used in RA, psoriasis • Well absorbed orally; can also be given IM, IV or intrathecally**. • It is bound to plasma proteins, does not cross the BBB and most of the drug is excreted unchanged in urine. • It is a weak acid and so is excreted better at high urine pH. Appropriate hydration and alkalinizing the urine is important to prevent renal tox with MTX Leucovorin Rescue Mechanism of action of methotrexate and the effect of administration of leucovorin. • FH2 = dihydrofolate • FH4 = tetrahydrofolate • dTMP = deoxythymidine monophosphate • dUMP = deoxyuridine mono phosphate. Anti-metabolites:1)Methotrexate:- Mechanism of action Leucovorin rescue Resistance:- Uses:- ALL, Choric cancer , Burkitt's, breast cancer, Head & Neck Cancer Inflammatory diseases PR:- Intrathecal – Pharmacological sanctuary ADR:- Renal damage, Cirrhosis, Pulmonary infiltrates 2) 6 – MP:- Azathioprine – 6MP PK:- DI MOA Allopurinol 3) 6 – TG – Purine Analog Acute nonlymhocytic leukemia + daunorubicin + Cytarbine 6 – TG HGPRT TGMP di & tri PO4 Θ Biosynthesis of Purines Cancer abc admin by allopurinol 4) Fludarabime:- CLL, hairy cell leukemia, indolent NHL high doses – encephalopathy, blindness and death. 5) Hairy cell leukemia, CLL, NHL Enzyme inhibitors Topoismerase inhibitors Anthracy clines 6) Etoposide 1) Damorubicin 7) Irinotecarn 2) Doxorubicin 8) Topotecam 3) Epirubicin 4) Idraubicin 5) Mitoxantrone Anthracy clines Inhibit topoisornerase High –affinity binding to DNA through intercalation – blockade of synthesis of DNA & RNA, & DNA strand scission Generation of Seniquinone & O2 free radicals though Fe dependent process Binding to cellular membranes to alter fluidity & non tram sport Doxorubicin - Used in Many Cancer Carditoxi city - Acute Chronic DEXRAZOXANE “ Radiation recall reaction”