* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HEMOSTASIS
Survey
Document related concepts
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
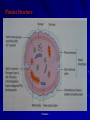
PLATELETS OBJECTIVES Platelets Production Platelet Structure Peripheral Zone Sol-Gel Zone Organelle Zone Platelet Function Platelet Function Tests drmsaiem Platelets Production Are produced in the B.M. by fragmentation of the Cytoplasm of Megakaryocytes. Each Megakaryocytes is responsible for the production of 4000 platelets. The time interval from differentiation of the stem cell to the production of platelets averages about 10 days. drmsaiem Platelets production Platelets production is under the control of humeral agents known as Thrombopoietin. The normal platelet count is about 250 x 109/l (150-400 x 109/l). The mean platelet diameter is 1-2 µm and the mean cell volume 5.8 fl. drmsaiem Platelet Structure drmsaiem Platelet Structure Though platelets are anuclear cytoplasmic fragments, they contain a number of organelles, such as mitochondria, microtubules, Dense Body, etc. These organelles can be divided into three defined zones that possess a unique function. Peripheral Zone Glycocalyx surround the platelet and is considered an important component of the platelet membrane. Platelet membrane, represents a fluid lipid bilayer composed of glycoprotein, glycolipids, and lipoproteins. drmsaiem Platelet Structure (Peripheral Zone) A number of GPs present in this area are responsible for blood group specificity (ABO), tissue compatibility (HLA), and platelet antigenicity. Platelet membrane glyco-proteins serve as a receptor and facilitate transmission of stimuli across the platelet membrane. Platelet membrane GPIb appears to be a primary receptor for vWF, which serves to mediate the initial adhesion of platelets to subendothelium. drmsaiem Platelet Structure Platelet membrane GPIIb/IIIa functions as a receptor for substance such as fibrinogen, fibronectin, and vWF, thereby mediating platelet aggregation. The platelet membrane also includes receptors for substance such as ADP, thrombin, epinephrin, and serotonin, which play a role in platelet aggregation. drmsaiem Platelet Structure Sol-Gel Zone The term Cytoskeleton is often used to describe this zone. Microtubules and microfilaments are found within this zone. Microtubules encase the entire platelet, maintaining its discoid shape. drmsaiem Platelet Structure Microfilaments are present in the cytoplasm of the platelet and are composed of actin and myosin-link contractile protein. Actin is the major contractile protein in the platelet cytosol, accounting for 20-30% of the total platelet protein, where as myosin composes 2-5% of the total platelet protein. drmsaiem Platelet Structure Organelle Zone It is responsible for the metabolic activities of the platelet. Platelets contain three morphologically distinct types of storage granules; Alpha granules, dense granules, lysosomes containing acid hydrolases. Alpha granules are more numerous (20-200 per platelet) and contain a number of different proteins. Dense bodies are fewer in number (2-10 per platelet) and represent densely opaque granules in transmission electron microscope (TEM) preparations. drmsaiem Platelet Structure The contents of the dense body granules are; Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Calcium Catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine) Serotonin Pyrophosphate Magnesium. The contents of both the alpha and dense granules are released during the energy- dependent release reaction. drmsaiem Platelet Structure Dense Tubular System (DTS) Important structure present in the cytoplasm of the organelle zone of the platelets. DTS is derived from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of immature Megakaryocytes. The DTS is the site of prostaglandin and thromboxane synthesis and sequestration of calcium. drmsaiem Platelet Structure It is primarily the release of calcium from the DTS that triggers platelet contraction and subsequent internal activation of platelets. Platelet activation is an energy- dependent process that relies on the metabolic function of mitochondria. There are about 10 to 60 mitochondria per platelet require glycogen as their source of energy for metabolism. Resting platelet ATP (energy) production is generated by glycolysis and the oxidative Kerbs cycle. drmsaiem