* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Loop Diuretics
Discovery and development of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Oral rehydration therapy wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Spironolactone wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
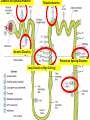
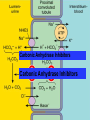
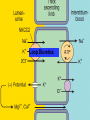
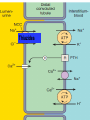
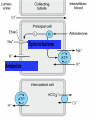
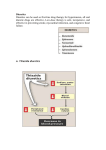
DIURETICS Prof. R. K. Dixit Pharmacology K.G.M.U. Lucknow [email protected] Objectives of today’s Lecture After completion of this lecture you will be able to know – Diuretics • • • • • • • • Definition Classification Names of members in classes Mechanism of action Major indications Major side effects and Precautions Major drug interactions MCQs related to Diuretics Facts of Renal Physiology • Kidney- – Weight- 0.5% of Body, – Receive 25% of cardiac output (50 times) • Kidney functions – Balance of electrolytes, Plasma volume, Acid Base – Activation of Vitamin D – Synthesis of Erythropoietin, Urokinase – Excretion of Urea, Uric acid, Creatinine etc. • Transport types – Passive • Simple, channel mediated and facilitated diffusion, solvent drag – Active • Primary and Secondary (Symports and Secondary Counter transport) Facts related to Renal Physiology • Pressure difference at Bowman’s Capsule20mm Hg • Filter= Plasma-Proteins • Volume of – Filter- 180 liters – Urine- 1.5 liters (1%) • Kidneys – Renal Blood Flow- 1200ml/min – Renal Plasma Flow- 650 ml/min – GFR- 120 ml/min – Reabsorb – Sodium, Chloride and Bicarbonates > 99% while Potassium about 85% Terminology • Natriuresis- increased sodium excretion • Kaliuresis- Increased Potassium excretion • Diuretics- Drugs which cause a net loss of Na+ and water in urine. (Exception- Osmotic diuretics (Mannitol) don't cause natriuresis but produce diuresis Nephron Parts and Characters Proximal Tubule • Leaky- Freely permeable to water, solutes • Active absorption of – Sodium Chloride, – Sodium Bicarbonate – Glucose – Amino Acids – Organic Solutes • Followed by passive absorption of water Loop Of Henle • Descending limb– Permeable to water • Thick ascending limb – – Impermeable to water but – Permeable to sodium by Na+K+2Cl- Co transport – About 25% of filtered sodium is absorbed here Macula Densa and Juxtaglomerular Apparatus • Contact between Ascending limb with afferent arterioles – by specialized columnar epithelial cells Macula Densa • Macula Densa sense NaCl conc. in filtrate • Give signal to J.G. Cells present in afferent arterioles • J.G. Cells of afferent arterioles secrete Renin RAAS in response to low BP, or Low Na Renin– Angiotensinogen - Angiotensin I ACE– Angiotensin II– Sympathetic, Aldosterone Vasoconstriction, Sodium and water retention, Early Distal Tubule • Active transport of sodium by NaCl symport • Calcium excretion is regulated (Parathomone and Calcitriol, increase absorption of calcium) Collecting Tubule and Collecting Duct • Aldosterone- On membrane receptor and cause sodium absorption by Na+/H+/ K+ Exchange • ADH- Collecting tubular epithelium permeable to water (Water enters through aquaporin-2) Nephron parts and their functions SEGMENT FUNCTION Glomerulus Formation of glomerular filtrate Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) Reabsorption of 65% of filtered Na+/K+/ Ca2+, and Mg2+; 85% of NaHCO3, (activity of Carbonic an-hydrase enzyme) and nearly, 100% of glucose and amino acids. Iso-osmotic reabsorption of water., Secretion and reabsorption of organic acids and bases, including uric acid and most diuretics Thin descending limb of Henle’s loop Passive reabsorption of water Thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop (TAL) Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Active reabsorption of 25% of filtered re-absorption of Ca2+ and Mg2+ Na+/K+/2Cl− Active reabsorption of 4–8% of filtered under parathyroid hormone control ; , secondary Na+ Cl− Ca2+ reabsorption ; Cortical collecting tubule (CCT) Na+ reabsorption (2–5%) coupled to K+ and H+ secretion (under Medullary collecting duct Water reabsorption under Vasopressin control Aldosterone) The relative magnitudes of Na+ reabsorption at sites • PT - 65% • Asc LH - 25% • DT - 9% • CD - 1%. • • • • Control of Renal Function Sympathetic- Increase Na reabsorption, Renin RAAS- Renin in response to Low sodium, Low BP ADH – Water reabsorption at collecting duct Atrial Natriuretic Peptide/Factor- Released when atrial pressure is high and causes solute and water diuresis and reduces blood volume and BP. Inhibits synthesis of Renin, Aldosterone, ADH and overcomes the long term persistent effect of aldosterone (Opposite of RAAS) • Prostaglandins- maintain renal circulation Breath for a minute Pharmacology copy by student Diuretics • Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (Site I) – Brinzolamide, Acetazolamide, Dorzolamide • Osmotic Diuretic (Site II) – Glycerine, Urea, Mannitol, Isosorbide • Loop Diuretics (Site III)- TALH – Frusemide/ Furosemide, Bumetanide, Torasemide, Ethacrynic acid • Thiazide Diuretics (Site IV) – Hydrochlorothiazide, Clopamide, Benzthiazide, Chlorthalidone, Metolazone, Xipamide, Indapamide • Potassium Sparing Diuretics (Site V) – Aldosterone Antagonist • Spironolactone, Canrenone, Eplerone – Direct Acting (Inhibition of renal epithelial Nq+ channel • Triamterene, Amiloride (more potent) Carbonic An-hydrase Inhibitors Thiazide diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Potassium Sparing Diuretics Loop Diuretics (High Ceiling) Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Loop Diuretics Thiazides Spironolactone Amiloride A GMBrings FruTECuts MIXs with Big HandsAnd Starts Taking- A GMBrings FruTEAcetazolamide Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (Site I) Glycerine, Mannitol Osmotic Diuretics (Site I, II and…) Torasemide, Ethacrynic acid Bumetanide, Furosemide, Loop Diuretics (Site III) Cuts MIXs with Big HandsClopamide, Chlorthalidone, Metolazone, Indapamide, Xipamide, Benzthiazide, Hydrochlorthiazide, Thiazide Diuretics (Site IV) And Starts TakingSpironolactone, Triamterene Amiloride, Potassium Sparing Diuretics (Site V) Diuretic Site of Action Adverse Effects Special points Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors PTC (inhibition of CAE) Metabolic Acidosis Weak, Used in Glaucoma, Petit mal epilepsy, Acute mountain sickness, to alkaline the urine Osmotic Diuretics PTC, LOH, DCT (Osmotic retention of water, Dilates Afferent arterioles, Increased hydrostatic pressure in glomerulus Shifting of fluid from intracellular to extracellular, Hyponatremia, Pulmonary edema Potent Used in Glaucoma, Poisoning, Increased ICT, impending ARF Loop Diuretics Thick Ascending Limb of Henle (NaK2Cl inhibition) Weak CAI action Hyponatremia Hypomagnesaemia Hypocalcaemia Hyperuricemia Hyperglycemia Hyperlipidemia Hyperuricemia Ototoxic (ECA) Most potent, Most Potent is Bumetanide, Effective even in low GFR, All except Ethacrynic acid are sulphonamide related, Venodilatation, Decrease Left Ventricle Pressure, Used in Acute LVF, Pulmonary Edema, Nephrotic syndrome, ARF, NSAIDS blunt effect, Cerebral edema, short term tt of Hypertension, to reduce volume overload during transfusion, Thiazide Diuretics DCT (NaCl) Hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis (Gitelman’s Syndrome) Hypercalcemia Moderate, Chlorthalidone is Longest acting, Paradoxical effect in Diabetes Insipidus First line in Hypertension, Potassium Sparing Diuretics CD HyperKalemia Antiandrogenic effect Weak, As supplement to other to counter the hypokalemia, Canrenone is active metabolite, used in Conn’s syndrome (Primary Hyperaldosteronism) cirrhotic edema, polycystic ovary Breathing Please…………….. Pharmacology teacher grfom where you passed Special mention • Don’t use diuretics overenthusiastically. (dehydration, hypotension) • Brisk diuresis in cirrhosis may precipitate hepatic coma. (hypokalemia, alkalosis and increased NH3 levels) • Diuretics not used in Toxaemia of Pregnancy. (Blood volume is low despite edema. Diuretics will compromise placental circulation) • Most of Loop and Thiazide diuretics are sulphonamide derivatives. (Think of allergic manifestations) • Hypokalemia by diureitcs precipates digitalis, quinidine side effects • Hypokalemia by diuretics decrease sulfonylurea action (reduced insulin release due to reduced action of ATP dependent potassium channel) • High ceiling not given with Amino-glycosides • ACE inhibitors with Thiazides reduce the chances of hypokalaemia (FDC) • Probenicid inhibits tubular secretion of Frusemide and Thiazides and reduce action • Potency of producing hypokalaemia CAsI>Thiazides>Loop • NSAIDS reduce diuretic action due to PG inhibition and affecting glomerular blood flow • CAsE is present in PT, gastric mucosa, exocrine pancreas, ciliary body, arachnoid plexus & RBC • Acetazolamide action is self limiting • Spironolactone breaks the Thiazide resistance • Aspirin blocks Spironolactone action by inhibiting tubular secretion of canrenone • Spironolactone can produce dangerous hyperkalaemia when used along with ACEI and ARBs • Spironolactone has antiandrogenic side effects • Eplirenone is new potassium sparing diuretics with less antiandrogenic effects • Osmotic diuretics indicated in impending ARF. (Don’t use if ARF has set in) Acetazolamide, CAIs, Alkaline urine, S/E Acidosis Clopamide, Metolazone, Indapamide, Xipamide, Benzthiazide, Hydrochlorthiazide, Hypercalcaemia A GM Brings FruTE Cuts MIXs with Big Hands And Starts Taking Amiloride, Spironolactone, Triamterene Bumetanide, Frusemide, Torasemide, Ethacrynic acid- Loop, Most potent, Hypocalcimia Glycerine, Mannitol, Osmotic, Hyponatremia, Not when ARF already sets in MCQs on Diuretics • Reabsorption of which of the following is affected maximum by action of vasopressin? – Water – Chloride – Potassium – Hydrogen A • Bumetanide belongs to which of the following class of diuretics? – Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor – Aldosterone antagonist – Thiazide diuretics – Loop diuretics D • All of the following compounds produce diuretic action by acting on thick ascending part of loop of henle EXCEPT – Ethacrynic acid – Torasemide – Furosemide – Clopamide D • Which of the following is thiazide like diuretics? – Spironolactone – Triameterene – Metolazone – Acetazolamide C • Which of the following is carbonic anhydrase inhibitor? – Acetazolamide – Spironolactone – Benzthiazide – Clopamide A • Which of the following is NOT an aldosterone antagonist? – Spironolactone – Canrenone – Eplerenone – Triameterene D • Among all of the following which is most potent? – Frusemide – Bumetanide – Torasemide – Ethracrynic acid B • Spirnolactone may be beneficial in all of the following clinical conditions EXCEPT – Nephrotic edema – Hypertension – Congestive heart failure – Hyperkalaemia D • Among following which is most ototoxic? – Metolazone – Clopamide – Ethacrynic acid – Chlorthalidone C • Which of the following is not an adverse effect of Furosemide? – Hyperuricaemia – Hyperglycaemia – Hyperlipidemia – Hypermagnesaemia D • Which of the following drugs can precipitate hypercalcaemia? – Spironolactone – Hydrochlorthiazide – Furosemide – Mannitol B • Thiazides induced hyperuricaemia may be prevented by administration of which of the following? – Allopurinol – Probenecid – Mannitol – Furosemide A • Which of the following condition is contraindication for Mannitol administration? – Acute congestive glaucoma – Head injury – Impending acute renal failure – Acute Pulmonary Edema D • Among following which compound has maximum potency? – Chlorthiazide – Chlorthalidone – Hydroflumethozide – Clopamide B • Which of the following is most appropriate mechanism of action of Triametrene – Inhibition of Miniralocorticoid receptors – Inhibition of Na+K+2Cl- channels – Inhibition of Na+Cl– channels of DCT – Inhibition of renal epithelial Na+ channels D • Which of the following drug is used in acute mountain sickness – Acetazolamide – Spironolactone – Domperidone – Ethacrynic acid A • Site of action of spironolactone is – Proximal Convoluted Tubule – Descending limb of Loop of Henle – Collecting Duct – Ascedning limb of loop of henle C • Which of the following is converted by Angiotensin Converting Enzyme – Angiotensinogen to Angiotensin I – Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II – Angiotensin II to Angiotensin III – Inactivation of Angiotensin III B • Renin is secreted from – Macula Densa cells – Juxta Glomerular Cells – Specialized cells of Ascending limb of henle – Specialized cells of efferent arterioles B • Which of the follwing is NOT an indication of Acetazolamide – Petit mal epilepsy – Periodic Paralysis – To acidfy urine – To alkalinise urine C • In loop of henle what percentage of sodium is reabsorbed – 65% – 25% – 9% – 1% B • Which of the following diuretics is not a sulphonamide derivative – Ethacrynic acid – Furosemide – Bumetanide – Torasemide A • Which of the follwing diuretic is active even when GFR is less than 20ml/min – Chlorthiazide – Chlorthalidone – Metolazone – Clopamide C • Which of the following drug does not produce hypokalaemic metabolic alkalosis – Furosemide – Hydrochlorthiazide – Acetazolamide – Indapamide C • Which of the following is NOT indicated in Diabetes Insipidus? – Desmopressin – Hydrochlorthiazide – Chlorpropamide – Mannitol D Thanks