* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PIG Excretion - Mrs Miller's Blog | Science Revision
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
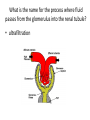
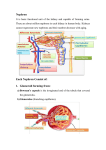
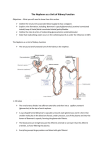
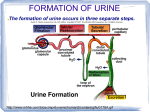
PIG Excretion What are the cells lining the Proximal convoluted tubule called? (1) What is are the cells lining the Proximal convoluted tubule called? • Epithelial cells How are substances reabsorbed in the Proximal convoluted tubule? (5) How are substances reabsorbed in the Proximal convoluted tubule? • • • • Selective reabsorption Of glucose and amino acids By co-transporter proteins Microvilli provide a large surface area for uptake • Water moves out by osmosis How is pressure maintained in the glomerulus? (2) How is pressure maintained in the glomerulus? • Afferent arteriole is wider than the efferent arteriole leading to • High hydrostatic pressure in glomerulus Why would happen if someone ate loads of protein in their diet? (4) Why would happen if someone ate loads of protein in their diet? • • • • • • More urea produced More protein broken into amino acids Increased deamination More ammonia formed More ammonia converted to urea Called the ornithine cycle (ornithine is a name for one of the products and a catalyst that helps in this process) Why do you need anti-coagulant in dialysis? (2) Why do you need anti-coagulant in dialysis? • So that clots don’t form • While blood is in the machine Why is no anti-coagulant added to the blood at the end of dialysis? (1) Why is no anti-coagulant added to the blood at the end of dialysis? • So blood can clot normally after treatment How do molecules and ions move from the blood into the dialysis fluid? (1) How do molecules and ions move from the blood into the dialysis fluid? • diffusion Why does the blood flow in the opposite direction of the dialysis fluid in the machine? (2) Why does the blood flow in the opposite direction of the dialysis fluid in the machine? • Maintain a diffusion gradient • Allowing maximum removal of waste Describe the barrier between the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule? (3) Describe the barrier between the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule? • Endothelium: narrow gaps for plasma to pass through • Basement membrane: collagen fibre and glycoprotein mesh • Podocytes: epithelial cells with major processes (finger like projections) and gaps o fluid can pass through What is filtered out of the blood? (5) What is filtered out of the blood? • • • • • Water Amino acids Glucose Urea Inorganic ions How is the permeability of the collecting duct controlled? (5) How is the permeability of the collecting duct controlled? • Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus lose water by osmosis • They shrink and release ADH • ADH binds to receptors in cells of collecting duct • Aquaporins fuse with cell membrane • More water is reabsorbed What is the name for the process where fluid passes from the glomerulus into the renal tubule? (1) What is the name for the process where fluid passes from the glomerulus into the renal tubule? • ultrafiltration What is the product of glycolysis? (1) What is the product of glycolysis • pyruvate Name 2 co-enzymes involved in respiration (2) Name 2 co-enzymes involved in respiration • NAD and FAD What are the 4 stages of respiration? (4) What are the 4 stages of respiration? • • • • Glycolysis Link reaction Krebs cycle Electron transport chain (oxidative phosphorylation) Where do the 4 stages of respiration take place? (4) Where do the 4 stages of respiration take place? • • • • Glycolysis- cytoplasm Link reaction- mitochondrial matrix Krebs cycle- mitochondrial matrix Electron transport chain- across inner mitochondrial membrane