* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TED
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Plateau principle wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct Xa inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct thrombin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
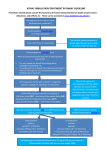
By: Hadeel Al-Kofide MS.c Warfarin interactions: Drug-drug interactions Herb-drug interaction Bridge therapy: Bridge therapy during invasive procedures Bridge therapy during dental procedures Patient education CJ is a 48 y.o. male, s/p cadaveric renal transplant, developed embolic CVA On chronic anticoagulation for 4 years Presented to the primary care clinic with painful, discolored, cracking of great toe Treated with itraconazole 100 mg po qd Presents to AC clinic INR 18.5 (repeated and verified) Hgb/Hct: 7.5/22 Guiac: + When he was asked why he took it: Neither my doctor nor the pharmacist that filled the prescription thought it would be a problem Three day admission 4 units PRBC’s transfused Cost to the health care system of $5000-7000 Cost in lost productivity, work time, etc.?????? Could this have been avoided? 1. Warfarin + NSAIDs 2. Warfarin + Sulfa drugs 3. Warfarin + Macrolides 4. Warfarin + Quinolones 5. Warfarin + Phenytoin 6. ACE inhibitors + Potassium supplements 7. ACE inhibitors + Spironolactone 8. Digoxin + Amiodarone 9. Digoxin + Verapamil 10. Theophylline + Quinolones Pharmacokinetic interactions Alteration in: Absorption Pharmacodynamic interactions Affect tendency for bleeding or clotting through: Antiplatelet effects Protein binding Hepatic metabolism Increases or decreases in vitamin K catabolism Interference with platelet function: Platelet aggregation is a crucial first step in primary hemostasis Drugs that impair platelet function increase the risk of hemorrhage in patients on warfarin They do so without elevating the INR ASA & clopidogrel INR = International Normalized Ratio Injury to gastrointestinal mucosa: NSAIDs NSAIDs cause dose- & duration-dependent gastrointestinal erosions The risk of hemorrhage is high by the concomitant use of warfarin, even in patients whose INR lies within the desired range NSAIDs = Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Reduced synthesis of vitamin K by intestinal flora Vitamin K is partly dependent on the synthesis of vitamin K2 by intestinal microflora Many antibiotics alter the balance of gut flora, thereby enhancing the effect of warfarin Some antibiotics also inhibit the hepatic metabolism of warfarin. These antibiotics include co-trimoxazole, metronidazole, macrolides & fluoroquinolones Interference with warfarin metabolism: Warfarin is metabolized through cytochrome P450 Drugs that inhibit this enzyme (e.g., amiodarone, cotrimoxazole, metronidazole and fluvoxamine) potentiate the effect of warfarin Other drugs that induce CYP 2C9 activity (e.g., rifampin) will do the converse Interruption of the vitamin K cycle: The most important drug in this category is acetaminophen One of acetaminophen metabolites inhibits vitamin Kdependent carboxylase, a key enzyme in the vitamin K cycle Some patients may have rapid & dramatic rise in the INR Drug Estrogen Vitamin K Risk on hemorrhage (INR) Mechanism ↓ Increase synthesis of clotting factors Separate dose 2-6 hrs Cholestyramine Thyroid Hormones ↓ Reduce absorption of warfarin ↑ Increase catabolism of clotting factors Drug Nafcillin Barbiturates Rifampin Phenytoin Macrolides Co-trimoxazole, Metronidazole, Fluoroquinolones Risk on hemorrhage (INR) Mechanism ↓ Induction of warfarin metabolism ↑ Inhibition of vitamin K synthesis by intestinal flora, inhibition of hepatic warfarin metabolism, or both Drug Fluconazole, miconazole Amiodarone Acetylsalicylic acid, Clopidogrel, Ticlopidine NSAID UFH LMH Risk on hemorrhage (INR) Mechanism ↑ Inhibition of warfarin metabolism ↑ Interference with primary hemostasis ↑ Additive anticoagulant response Drug Chinese wolfberry, Cranberry juice, grapefruit juice Garlic Ginger Ginkgo St. John’s wort Risk on hemorrhage (INR) Mechanism ↑ Inhibition of warfarin metabolism ↑ Inhibition of platelet aggregation ↓ Induction of warfarin metabolism Drug Risk on hemorrhage (INR) Mechanism Green tea ↓ Contain vitamin K Ginseng ↓ Unknown Patients taking warfarin are susceptible to numerous drug interactions Can we avoid them?? Close monitoring of INR Adjust warfarin dose according to INR Temporary use of intravenous UFH or LMWH for a patient on long-term anticoagulation who is about to undergo a surgical procedure is called bridge therapy Risk of thromboembolism Risk of bleeding 1. Management of anticoagulation around invasive procedures 2. Management of anticoagulation around dental procedures High Risk of Bleeding • Cardiac surgery • Neurosurgery, • Most cancer surgery • Bilateral knee replacement • Kidney biopsy GI = Gastro-Intestinal Low Risk of Bleeding • Coronary angiography • GI endoscopy • Colonoscopy • Bronchoscopy • Biopsy (thyroid, breast, lymph node, pancreas) Thrombosis Risk CrCl Bridge Therapy Pre-Procedure High Day 5 Day 3 Post-Procedure Day 1 12-24 hr 12-48 hr Resume enoxaparin Resume warfarin AF Stroke history Mechanical valve DVT/PE < 3 mo > 30 Enoxaparin Last dose 1 mg/kg q Last dose warfarin 12 hr enoxaparin Vitamin K 2.5 mg PO AF = Atrial Fibrillation; DVT = Deep Vein Thrombosis PE = Pulmonary Embolism Thrombosis Risk CrCl Bridge Therapy Pre-Procedure High Day 3 Day 2 Day 1 12-24 hr 12-48 hr Vitamin K 2.5 mg PO Admit; IV UFH LD 70 U/kg MD 15 U/kg If INR >1.5 give vitamin K 1 mg IV Stop UFH 6 hrs preprocedure Resume UFH Resume warfarin AF Stroke history Mechanical valve ≤ 30 Last dose warfarin DVT/PE < 3 mo UFH = Un-Fractionated Heparin IV = IntraVenous Post-Procedure Thrombosis Risk CrCl Pre-Procedure Low Cardiomegally with no history of thrombosis DVT/PE > 3 mo Bridge Therapy All Post-Procedure Day 4 Day 2 Day 1 12-24 hr 12-48 hr Last dose warfarin Vitamin K 2.5 mg PO ----- ----- Resume warfarin Bleeding Risk Low Procedure 1. 2. 3. Surgical scalling Simple restoration Local anesthetic injection Recommendations 1. 2. Do not interrupt warfarin treatment Use local measures to prevent or control bleeding Bleeding Risk Procedure 1. 2. Moderate 3. 4. 5. Subgingival scalling Restoration with subgingival preparations Standard root canal therapy Simple extraction Regional injection of local anesthetics Recommendations 1. 2. Interruption of warfarin treatment is not necessary Use local measures to prevent or control bleeding Bleeding Risk Procedure 1. 2. High 3. 4. Extensive surgery Apicoectomy (root removal) Alveolar surgery (bone removal) Multiple extractions Recommendations 1. 2. Need to reduce INR or even return to normal hemostasis Follow bridge therapy guideline for invasive procedures based on risk of thromboembolism Group Discussion