* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psychology - Cloudfront.net
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
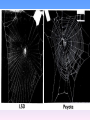
Hypnosis Hypnosis • A social interaction in which a hypnotist makes suggestions about perceptions, feelings, thoughts, or behaviors, and the subject follows those suggestions Social Influence Theory • Theory that powerful social influences produce a state of hypnosis. • This theory notes that a person’s physiological state does not change under hypnosis. • Social factors influence people to believe hypnosis will work. What is Hypnosis?: Divided Consciousness Theory Divided Consciousness Theory • Theory that during hypnosis our consciousness splits so that one aspect of consciousness is not aware of the role that other parts are playing. • Promoted by Ernest Hilgard (1904-2001) Hypnotic Techniques Hypnotic Induction • The process by which a hypnotist creates a state of hypnosis in a subject • Usually done by voicing a series of suggestions • Voice is usually calm and of a rhythmic tone Hypnotizability • Differences in the ability of people to become hypnotized • Varies from person to person • Varies from situation to situation Hypnotizability Limits to Hypnotic Suggestions • Suggestions usually involve sensations, thoughts, emotions, and a wide variety of behaviors. • Hypnosis does not cause behaviors. • Hypnosis can lead people to certain behaviors but so can ordinary suggestions. Posthypnotic Suggestions • Hypnotic suggestion that the subject will carry out after the hypnosis session has ended • Technique can be used to encourage helpful behavior changes, such as stopping smoking or losing weight. Hypnotic Amnesia • Inability to remember what happened during hypnosis because the hypnotist suggests that the subject will have no memory of that period of time Applications of Hypnosis: Hypnosis and Pain Control Pain and Hypnosis • Hypnosis does work as a means to control pain. • Has a number of practical applications Drugs Psychoactive Drug • Chemical substance that alters perceptions, mood, or behavior • Three common psychoactive drugs: – Caffeine – Alcohol – Nicotine • Induce an altered state of consciousness Dependence • State of physiological, psychological or both types of need to take more of a drug after continued use. • Withdrawal follows if the drug is discontinued Withdrawal • Discomfort and distress that follow when a person who is dependent on a drug discontinues the use of that drug • Withdrawal symptoms are usually the reverse of the drug’s effects. Tolerance • Reduced responsiveness to a drug, prompting the user to larger dosages to achieve the same pleasurable effects previously obtained by lower doses Tolerance Alcohol: A Depressant Depressants • Drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body functioning • Includes alcohol and sedatives Alcohol (ethyl alcohol) • Found in beer, wine, and liquor • The second most used psychoactive drug (caffeine first) • Slows thinking, and impairs physical activity Blood Alcohol Content (BAC) • A measure of how much alcohol is in a person’s bloodstream • BAC of .08 considered legal intoxication in most states Euphoric Affects of Alcohol • Alcohol impairs the parts of the brain responsible for controlling inhibitions and making judgments Alcohol, Memory, and Sleep • Studies have shown that alcohol impairs memory by suppressing the processing of events into long term memory. • Alcohol impairs REM sleep, further disrupting memory storage. Alcoholism Stimulants Stimulants • Drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions • Include: caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, and cocaine Caffeine • Stimulant found in coffee, chocolate, tea, and some soft drinks • Provides user with a sense of increased energy, mental alertness, and forced wakefulness • Blocks neurological receptor sites that, if activated, sedate the central nervous system Nicotine • Stimulant found in tobacco • Effects similar to those of caffeine • Very addictive and does not stay in the body very long Cocaine • Stimulant derived from leaves of the coca plant • Crack – cocaine crystals • Blocks the reuptake of certain neurotransmitters • Dependency is quick and severe; places extreme strain on cardiovascular system Amphetamines • Drugs that stimulate neural activity, speeding up body functions • Include increased energy and mood changes • Includes: speed, uppers, and methamphetamines • Mimic adrenaline • Can cause irreversible changes in mood Hallucinogens Hallucinogens • Psychedelic drugs that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input • Include: LSD and ecstasy • Sometimes called “psychedelics” meaning mind-manifesting Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD) • • • • Powerful hallucinogenic drug Also known as “acid” The effects vary from person to person Users can be dangerous to themselves and others. Ecstasy • Hallucinogenic drug that produces lower inhibitions, pleasant feelings, and greater acceptance of others • Also called MDMA • Even moderate users may experience permanent brain damage. Marijuana Marijuana • Leaves, stems, resin, and flowers form the hemp plant that, when smoked, lower inhibitions and produce feelings of relaxation and mild euphoria • THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) is the active ingredient • Disrupts memory; lung damage from smoke 10 mg of Caffeine