* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download rights of correct drug administration
Pharmaceutical marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Medical prescription wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
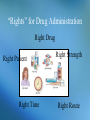
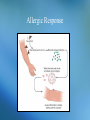
Chapter 3 Dispensing of Pharmacologic Agents Chapter 3 Topics • • • • • The Prescription “Rights” for Correct Drug Administration Dosage Forms and Routes of Administration Factors that Influence Drug Action Endogenous Chemicals that Affect Drug Action and Response • Teaching Patients Medication Management Learning Objectives • Know the components of the prescription, including the commonly used abbreviations. • Understand the rights of correct drug administration. • Recognize common dosage forms. • Know the routes of administration. • Recognize factors that influence the effects of drugs, particularly in the elderly and pediatric populations. • Know the effects natural chemicals have on drug action and response. • Understand the immunization process. The Prescription The Prescription Abbreviation ac bid c cap DAW D/C g Translation before meals twice a day with capsule dispense as written discontinue gram The Prescription Abbreviation gr gtt hs IM IV L mcg Translation grain drop at bedtime intramuscular intravenously liter microgram The Prescription Abbreviation mEq mL NKA NKDA npo pc PO Translation milliequivalent milliliter no known allergy no known drug allergy nothing by mouth after meals by mouth The Prescription Abbreviation prn q qh q2h qid qs stat Translation as needed every every hour every two hours four times a day a sufficient quantity immediately The Prescription Abbreviation tab tid ud wk Translation tablet three times daily as directed week Problematic Abbreviations Dangerous Abbreviation µg qd qod U MgSO4 MSO4 .2 2.0 Correct Form to Use Microgram or mcg every day every other day units magnesium sulfate morphine sulfate 0.2 2 Problematic Abbreviations • Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP) – Lists dangerous abbreviations and other safety tips. – Check out the site at www.ismp.org. – Review Appendix B in the textbook for additional safety tips. Discussion What makes an abbreviation dangerous? What is the role of the pharmacy technician when a prescription arrives with a dangerous abbreviation? “Rights” for Drug Administration Right Drug Right Patient Right Time Right Strength Right Route Discussion How do the “rights” for correct drug administration help avoid dispensing errors? What other things should a pharmacy technician check when dispensing a medication? Mediation Label Dosage Forms and Routes of Administration • Peroral (PO, by mouth) Dosage Route – Oral (swallowed) – Sublingual (under the tongue) – Buccal (dissolves in the check) Dosage Forms and Routes of Administration • Parenteral Dosage Route – – – – – Intravenous (vein) Intra-arterial (artery) Intracardiac (heart) Subcutaneous (beneath the skin) Intramuscular (muscle) Dosage Forms and Routes of Administration • Topical Dosage Route – – – – – – – – Transdermal (skin surface) Conjunctival (conjunctiva) or Intraocular (eye) Intranasal (nose) Aural (ear) Intrarespiratory (lung) Rectal Vaginal Urethral Dosage Forms and Routes of Administration • Peroral (PO, by mouth) Dosage Forms tablets, capsules, solutions, syrups, elixers, suspensions, magmas, gels, powders, trouches/lozenges Dosage Forms and Routes of Administration • Parenteral Dosage Forms – Solutions – Suspensions Dosage Forms and Routes of Administration • Topical Dosage Forms ointments, creams, pastes, powders, aerosols, lotions, transdermal patches, sprays, inhalants, suppositories, enemas, emulsions, sponges, gels Factors that Influence Drug Action • Review: What are the four phases of the pharmacokinetic process? Absorption Distribution Metabolism Elimination Factors that Influence Drug Action • Age Pediatric patients and elderly patients may need a reduced dose because of smaller size or inability of liver to metabolize medication • Disease Specific diseases may hinder the pharmacokinetic process of some drugs • Mental State, Genes, Gender Considerations for Elderly Patients Physiologic Function Changes – – – – – – – – Optic Auditory Gastrointestinal Pulmonary Cardiovascular Urinary Hormonal Composition of the body Considerations for Elderly Patients • • • • Altered Drug Responses Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) Polypharmacy Noncompliance Considerations for Pediatric Patients • Wide variation between age and degree of organ-system development • Reevaluate all doses at regular intervals. • Be sure the dosage is appropriate for the child’s age. • Always double-check all computations. Discussion What should a pharmacy technician do when a parent is struggling to determine the best dose of an OTC medication for a pediatric patient? Discussion What should a pharmacy technician do when a parent is struggling to determine the best dose of an OTC medication for a pediatric patient? Answer: Ask the pharmacist to determine the child’s dose for the caretaker if the dose information is not provided. Immunization What are the two types of immunity? Immunization What are the two types of immunity? – Active immunity – Passive immunity Immunization What are the two types of immunity? – Active immunity Coming in contact with an infectious agent or an inactivated part of an infectious agent through a vaccine – Passive immunity Receiving antibodies that were formed by another person or animal that developed them in response to being infected Immunization Schedule Endogenous Chemicals that Affect Drug Action and Response Two types of receptors that histamine acts on: – H1 receptors mediate the contraction of smooth muscle of the bronchi and intestine – H2 receptors mediate the action of histamine on gastric secretion and cardiac acceleration Endogenous Chemicals that Affect Drug Action and Response Two types of drugs that block the histamine receptors: – Antihistamines block H1 receptors – H2 blockers • cimetidine (Tagamet) • ranitidine (Zantac) • famotidine (Pepcid) • nizatidine (Axid) Allergic Response Allergic Diseases • • • • • Allergic rhinitis Hay fever Allergic dermatitis, eczema Contact dermatitis Urticaria (hives) Drug Therapy for Allergies • Free environment of allergens (if possible) • Corticosteroids • Short-term relief of symptoms with antihistamines • Long-term desensitization programs Prostaglandins • Mediators of several physiologic processes • Include PGA, PGB, PGE, and PGF • Actions – – – – – Endocrine system Cardiovascular system Gastrointestinal system Pulmonary system Inflammatory Teaching Patients Medication Management Goal: Compliance A patients’ adherence to the dose schedule and other particular requirements of the specific drug regimen Discussion What kinds of information help improve patient compliance? Discussion What kinds of information help improve patient compliance? Answer: – – – – Methods of administration How to make swallowing easier Times and time intervals for administration If medication should be taken with food or not – Possible side effects – How long the medication should be taken Discussion What can the pharmacy technician do to help patients manage their medications properly? Teaching Patients Medication Management Teaching Patients Medication Management