* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4 - CindiLamb.com
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Wilson's disease wikipedia , lookup
Alcoholic polyneuropathy wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of binge drinking wikipedia , lookup
Drug rehabilitation wikipedia , lookup
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol and cancer wikipedia , lookup
Long-term effects of alcohol consumption wikipedia , lookup
The Natural History of Alcoholism Revisited wikipedia , lookup
Effects of alcohol on memory wikipedia , lookup
Disease theory of alcoholism wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Alcoholism in family systems wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol abuse wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol and health wikipedia , lookup
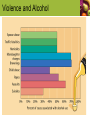
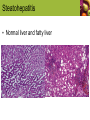
Judith E. Brown www.cengage.com/nutrition/brown Alcohol: The Positives and Negatives Unit 14 Prof. Albia Dugger • Miami-Dade College Alcohol Facts • Alcohol is a food • Contains carbohydrates (energy) • Alcohol is a drug • Alcohol (ethanol) modifies body functions • Harmful in high doses Fermentation • Alcohol is produced from carbohydrates in grains and other foods by fermentation • Fermentation • The process by which carbohydrates are converted to ethanol by the action of enzymes produced by yeast The Positive • Moderate alcohol consumption • Men: 2 drinks/day, women:1 drink /day • Reduces risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, stroke, dementia • Increases HDL cholesterol • Improves glucose utilization • Decreases chronic inflammation • Improves cognitive function One Drink Key Terms • Chronic inflammation • Low-grade inflammation that lasts weeks to years • Inflammation • The immune system’s first response to infection or irritation; triggers release of biologically-active substances that promote oxidation and other harmful reactions Positive Effects of Phytochemicals • Phytochemicals • Act as antioxidants • Reduce plaque in arteries • Decrease inflammation • Decreased inflammation: • Helps prevent plaque formation in arteries • Improves circulatory function • Improves maintenance of normal cell health The Negative • Heavy drinking • 5 or more drinks/day • Increases risks of high blood pressure, stroke, dementia, some cancers, central nervous system disorders, vitamin and mineral deficiencies The Negative • Alcohol abuse is associated with: • A high proportion of deaths from homicide, drowning, fires, traffic accidents, and suicide • Rapes and assaults • Alcohol poisoning • Steatohepatitis • Cirrhosis Key Terms • Alcoholism • Illness characterized by dependence on alcohol and a level of alcohol intake that interferes with health, family, social relationships, and job performance Key Terms • Alcohol poisoning • Life-threatening condition due to excess alcohol consumption; a medical emergency • Characterized by mental confusion, vomiting, seizures, slow or irregular breathing, and low body temperature Key Terms • Steatohepatitis • Disease characterized by fat accumulation in the liver and liver inflammation • Associated with alcoholism, obesity, and diabetes • May progress to cirrhosis Key Terms • Cirrhosis • Disease of the liver characterized by widespread fibrous tissue buildup and disruption of normal liver structure and function • Can be caused by a number of chronic conditions that affect the liver Violence and Alcohol Steatohepatitis • Normal liver and fatty liver Drinking During Pregnancy • Fetal alcohol syndrome causes long-term mental and growth retardation • There is no safe level of alcohol intake during pregnancy Alcohol, Diet, and Nutrients • “Empty calories” • Alcohol contains 7 calories/gram, but few nutrients • Heavy drinkers may be vitamin deficient How the Body Handles Alcohol • Alcohol is: • Absorbed through stomach and small intestine • Circulated to body tissues • Broken down and used for energy or fat storage • Blood alcohol builds up • Mild intoxication, about 0.03% • Legal limit, typically 0.08% • 0.6% or more can cause death Blood Alcohol Levels Increased Effects of Alcohol • Blood alcohol levels increase faster in women than in men • Over 150 medications interact harmfully with alcohol (sleeping pills, pain killers) • Combining alcohol and pain relievers may cause stomach ulcers or liver damage Drinking Responsibly • Do NOT drink: • • • • • If you are or could become pregnant On an empty stomach Quickly Until you lose control Before or during driving, hunting, or operating heavy equipment What Causes Alcoholism? • Alcoholism: • Tends to run in families • Has a genetic component • Is influenced by environmental factors • Risk increases: • When drinking begins at a young age • Around peers who drink • With stress Alcohol and Adolescents • Underage drinking accounts for 20% of all alcohol consumed in the US • Average age when drinking begins: 14 years • Four times more likely to become alcohol dependent than 21-year-olds Help for Alcohol Dependence • Alcoholism is managed, not cured • Behavioral therapy is successful in about 1/3 of people with alcoholism • Medications treat people with genetic predispositions toward alcoholism Drink Responsibly