* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. dia
Plateau principle wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
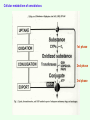
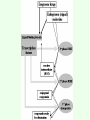
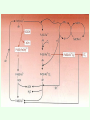
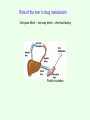
BIOTRANSFORMATION, Drug metabolism, detoxification netversion Fate of Xenobiotics • Enzymatic conversion • Elimination without any chemical reaction • Spontaneous chemical conversion • Accumulation without conversion Cellular metabolism of xenobiotocs 1st phase 2nd phase 3rd phase phase I metabolism – purpose: „function groups” are formed • • • • Oxidation Reduction Hydrolysis Hydratation Formation of a more polar metabolite than the original substrate, better chance for excretion, lipid soluble → water soluble Cytochrome P450 system flavoprotein lipid – (membrane – SER) hemoprotein Flavoprotein: NADPH – P450 oxidoreductase Lipid: phosphatidyl choline Hemoprotein: Cytochrome b5 Cytochrome P450 Reductase – P450 ratio: 1 : 10 1 : 100 Role of the liver in drug metabolism -first pass effect – one way street – chemical factory Portal circulation Cytochrome P450 gene superfamily • In mammals 8 families, in drug metabolism 4: CYP1, CYP2, CYP3, CYP4 • Expressed mainly in liver, but also in lungs, intestines, skin and kidneys • Gene evolution, protein filogenesis – natural selection – survival value • Ancestor gene 3,5 bilion yrs (22 exon), 1,5 bilion yrs ago: plant ↔ animal separation, 400 million yrs ago: surface ↔ ocean 1.5 billion yrs 400 million yrs today Figure 3. Contribution of major human P450s to the Phase I metabolism of all drugs currently marketed (25). The compilation is intended to be approximate and will vary with changes in drugs. For tables of raw data see Rendic (22). The non-P450 enzymes include alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenases, flavin-containing monooxygenases, etc. CYP 1 2 genes even 100 fold inducibility Inducers: metilcholantrene dioxin derivatives industrial technologies environmental pollution cigarette smoke Inducibility incidence of bronchial arcinoma Substrates: Policyclic aromatic carbohydrates (PAH): benzpyrene, benzanthracene etc. Medicines: teophyllin, phenacetin etc. CYP 2 (A – H) Inducers: phenobarbital Ethanol Aceton Diazepam derivatives CYP 2A steroids, testosteron CYP 2B progesteron, D3 vitamin, antiepileptics CYP 2C mephenytoin - antiepileptics CYP 2D antidepressants, beta blockers, antihypertensive agents, debrisoquine metabolism PM poor metabolizer EM extensive metabolizer Inducibility gastrointestinal tract carcinomas, bronchial carcinoma incidence CYP 2E etanol, aceton diabetes mellitus, starvation Figure 1. Relative rates of CYP2D6 activity in a Caucasian population (4). CYP2D6 activity is represented as the ratio of unmetabolized drug (here, debrisoquine) to drug metabolite (4hydroxydebrisoquine) collected from the urine following a single dose. The distribution is the result of the existence of more than seventy alleles in the population (see http://www.imm.ki.se/CYPalleles/). Early research labeled individuals as "extensive metabolizers" (green) and "poor metabolizers" (blue) (5). The "ultrarapid metabolizer" phenotype (red) can result from inherited gene amplification Figure 4. Significance of unexpectedly low metabolism of a drug by P450s. The typical pattern seen with the majority of the population (extensive metabolizers) is shown in the upper panel, where the plasma level of the drug is maintained in a certain range over the period of several consecutive doses (arrows indicate multiple doses). Unusually slow metabolism (lower panel) occurs when a poor metabolizer (without previous knowledge of phenotype) receives the same dose, resulting in an elevated plasma level of the drug. Adapted from CYP 3 Inducers: steroids Oral contraceptives PCN – pregnenolon carbonitril Substrates: Antibiotics nifedipin cyclosporin CYP 4 Inducer: clofibrate – antihyperlipemic agent Substrates: Fatty acids eicosanoids
















![[4-20-14]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003097962_1-ebde125da461f4ec8842add52a5c4386-150x150.png)