* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Anatomy of Language Sydney Lamb Rice University, Houston
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia wikipedia , lookup
Neurodegeneration wikipedia , lookup
Wilson's disease wikipedia , lookup
Hemiparesis wikipedia , lookup
Hyperkinesia wikipedia , lookup
Management of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
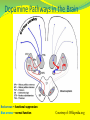
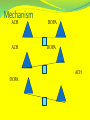
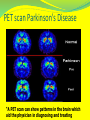
Famous Faces of Parkinson Michael J. Fox Katharine Hepburn Muhammad Ali Mao Tse Tung Pope John Paul II Johnny Cash PARKINSON’S DISEASE WHAT IS IT? WHAT ARE THE CAUSES? WHAT AFFECTS DOES IT HAVE ON THE BODY? ARE THERE ANY TREATMENTS AVAILABLE? WHO IS AT RISK OF DEVELOPING THE DISEASE? These questions, and more, will be answered in this presentation… WHAT IS IT? Parkinson’s Disease (PD) affects the brain’s ability to produce dopamine. Dopamine is a chemical messenger responsible for transmitting signals within the brain. Loss (or low levels) of Dopamine causes the Brain’s critical nerve cells (in the substantia niagra) to fire out of control. This is why patients have sporadic muscle movements. Dopamine Pathways in the Brain Red arrows – functional suppression Blue arrows – normal function Courtesy of: Wikipedia.org Mechanism . ACH DOPA ACH DOPA ACH DOPA What causes PD? The exact cause of PD is not known, but most researchers believe that it is a combination of both environment and genetic factors. Environmental toxins: Incidences seem to vary by geographical locations. For example, more cases are reported in locations where certain pesticides and transition-series metals are present. –Wikipedia.org What causes PD? Other risk factors: Head trauma sufferers are 4 times more likely to develop PD than those without head traumas. (J.H. Bower study) Antipsychotic medications can induce symptoms of PD by lowering dopamine levels. SYMPTOMS OF PD MOST-COMMON SYMPTOMS: Tremors Rigidity Slowness of Movement Postural Instability **It should be noted that symptoms usually increase in severity over time. SYMPTOMS OF PD TREMORS: Maximal during muscular rest Minimal during muscular movement Uncontrollable Sporatic SYMPTOMS OF PD RIGIDITY: Increased muscular tone, which leads to stiffness. The muscles become inflexible, or rigid SYMPTOMS OF PD POSTURAL INSTABILITY Muscular rigidity leads to inflexibility, which leads to the body having difficulty maintaining a fully-erect posture. This impaired posture leads to balance problems, and an increase in falls. Photo courtesy of Wikipedia LESS–COMMON SYMPTOMS OF PD The following symptoms have been reportedly linked with Parkinson’s Disease. However, they seem to occur with less frequency as the ones listed prior. Shuffling gait (short, quick steps, with the feet barely lifting from the ground) Decreased arm swing Speech problems Swallowing & Chewing disturbances Mood disturbances (Depression) Sleep disturbances (possibly due to muscle movements during REM sleep) Skin Problems Urinary & Intestinal disturbances DIAGNOSIS OF PD Diagnosing PD can be difficult due to the nature of the disease. Blood tests currently are not available for diagnosis. Advanced testing needs to be performed for accurate evaluation of symptoms. One such test is known as the PET. PET scan Parkinson's Disease “A PET scan can show patterns in the brain which aid the physician in diagnosing and treating TREATMENT OF PD Unfortunately, there isn’t currently a cure for PD. Although, several organizations are working diligently to provide a medical breakthrough. (thru stem cell research) Consequently, drug therapy is the only current therapy available to PD sufferers. TREATMENT OF PD 1.L dopa 2-anticholinergic 3-amantadin 4-selegeline 5-dopamin agonists PD TREATMENT 1-LEVODOPA – is the most-widely used form of treatment for PD. Levodopa is transformed into Dopamine in the affected neurons. While this treatment is good in some ways, it also has a variety of side affects. Not all of the Dopamine is taken in by the affected area. Consequently, it is delivered to other areas of the body. PD TREATMENT CARBIDOPA – Is another drug that is used in PD treatment. Works by slowing the body’s conversion of Levodopa to Dopamine. This helps aid the uptake of Dopamine to affected cells, thus decreasing the amount of Dopamine secreted to other areas of the body. Consequently, this process usually leads to a decrease in side affects. 2-Amantadin Available:Cap 100 mg Mechanism: Dopami. Agonist-anti.cholin Doseage; one to 2 Cap daily Adventage;first line drug-decres dose of L Dopa Disadventages:Livedo reticularis-Vomiting-nausea 3-Anticholinergics Available:Bipiridine-artan 2 mg Mechanism: anti.cholinergic Doseage; one to 2 Tab daily maximum 8 mg Adventage;reduce tremor Disadventages:Hypotension/glaucoma/reduce memory/BPH/salivation Never use after 70 yers Antidepressant what 4-Selegeline Available:Tab 5 mg Mechanism: MAO inhibitor Doseage; one to 2 Tab daily Adventage;Preventsa progress of PD Disadventages:Arythmia/dizziness/vomiting 5-Dopamine agonists Available: 1-bromocrip tine 5mg 2-pramipexoloe.18-.7 mg 3-requipe.25-1 mg Mechanism: Dop agonist Doseage; one to 2 Tab daily Adventage;Lowering dose of l dopa/reduce Dyskinesia Disadventages:vomiting/lower BP 6-Others 1-Never use D2 Antagonists 2-Cisapride for constipation 3-Ssris and tricyclics 4-low meat 5-Falling 6- Eff tab Vitc PD TREATMENT THALAMOTOMY – Surgical destruction of the thalamus.