* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - Circle of Docs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
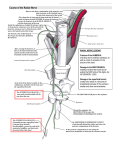
Spinal Anatomy 1. greater wing of sphenoid bone and the petrous portion of the temporal bone make up the middle cranial fossa 2. sd 3. paresthesias and pain over the 1st, 2nd, and ½ of the 3rd fingers could be from muscle spasm of the pronator muscle 4. if a cervical rib is noted on x-ray, which nerve root levels could be affected: C8, T1 5. sd 6. largest portion of cord is located at the C5-C6 level 7. an obstruction of the interventricular foramen would produce its greatest build up of pressure in the lateral ventricle 8. cutaneous sensation over the dorsal aspect of foot of 2nd, 3rd, and 4th metatarsals is from superficial fibular nerve 9. cranial nerve that originates from the posterior aspect of the brain stem: CN4 10. orientation of the inferior articular facets in the lumbar spine: anterior and lateral (AIL/AIM/AIL) 11. termination of the spinal cord and emergence of the filum terminale occurs at L2 12. ligament that separates the greater and lesser sciatic foramens: sacrospinous sacrotuberous ligament creates the lesser sciatic foramen 13. ligament that attaches to the anterior aspect of the foramen magnum and the anterior aspect of C1: anterior atlantoccipital membrane 14. ligament that prevents hyperextension of lumbar spine: anterior longitudinal 15. ligament that connects the apex of one spinous to the apex of another: supraspinous 16. ligament that connects lamina to lamina: ligamentum flavum 17. protrusion of the meninges and spinal cord: spina bifida meningomyelocele 18. transverse sinus is contained in: tentorium cerebelli 19. confluence of sinuses is found on occipital bone 20. arachnoid villi is located in superior sagittal sinus 21. paresthesia in the mandibular region could be caused by a lesion of a nerve that goes through which foramen: foramen ovale (rotate the max, spin the middle, oval man) 22. superior articulating factes in the lumbar spine are orientated posterior and medial 23. lesion of the ciliary ganglion can result in ptosis, dilation of pupil, loss of sweat to face 24. orientation of the cervical transverse processes: 30-40 degrees anterior and lateral 25. to prevent neural tube defects in pregnant female, folic acid is recommended 26. in the thoracic spine, what helps form the anterior border of the intervertebral foramen: rib heads 27. formed from intramembranous ossification: frontal bone 28. olfactory nerve goes through cribriform plate 29. axons of supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei end in the posterior pituitary 30. involved in smell: amygdaloid body 31. lesion in Brocas area 17 may involve this artery: middle cerebral artery 32. blood supply to the pituitary gland is by way of: internal carotid 33. weakest fibers located b/w L5 and S1: posterolateral 34. globus pallidus and putamen will send fibers to thalamus 35. nerve that innervates the levator palpebrae superioris muscle: oculomotor nerve 36. CN6 innervates the lateral rectus 37. most superior nerve that can be affected in a disc herniation is C3 (no discs above) 38. lateral sacral crest is derived from transverse processes 39. fracture of odontoid and avulsion of the cord above C3 would cause death w/i minutes 40. recurrent meningeal nerve innervates all except a. ALL b. Meninges c. PLL d. Posterior aspect of disc 41. make up the choroid plexus: ependymal cells 42. responsible for myelination in CNS: oligodendrocytes 43. responsible for myelination in PNS: Schwann cells 44. gap b/w 2 schwann cells: node of ranvier 45. process on the posterior aspect of the transverse process in the lumbar spine: accessory process (mammilary process is off of superior facet) 46. type of joint b/w the anterior arch of atlas and dens: pivot 47. not part of erector spinae muscle group a. semispinalis b. spinalis c. iliocostalis d. longissimus 48. connects amygdaloid to hypothalamus: stria terminalis 49. radial nerve comes off of posterior cord of brachial plexus 50. floculonodular lobe of the cerebellum is from archicerebellum 51. involves both the visual and auditory tracts: tectospinal pathway 52. cranial nerve that does not contain parasympathetic fibers: hypoglossal (III, VII, IX, X have parasympathetic) 53. supplies the gracillus muscle: obturator 54. supplied by the deef fibular nerve a. extensor hallicus longus b. peroneus longus c. peroneus brevis d. soleus 55. lamina that surrounds the central canal of the spinal cord: 10 56. what lamina is substantia gelatinosa: 2 (pain) 57. part of visual pathway: lateral geniculate body 58. largest taste bud: vallate 59. dorsal root ganglion is derived from: neural crest cells (neural tissue outside of spinal cord; spinal cord proper is neuroectoderm) 60. cornea of eye is an extension of surface ectoderm 61. posterior disc protrusion into the intervertebral foramen b/w the C7 and T1 vertebrae will affect which nerve level: C8 62. neural tube becomes the a. spinous process b. spinal cord c. lamina d. transverse process nucleus pulposus – notochord 63. drains into the inferior nasal meatus: nasolacrimal duct (maxillary sinus goes into medial nasal meatus) 64. m/c clinical manifestation of a congenital hemivertebrae in the thoraco-lumbar junction is scoliosis 65. forms the floor of the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle: head of caudate nucleus 66. preganglionic sympathetic fibers arise from interomediolateral cell column 67. if articulation b/w L5-S1 is altered so that the right joint can be visualized, but the left one cannot be seen, it indicates: facet tropism 68. ligament that forms part of the neural canal: posterior longitudinal ligament 69. cranial nerve supplies taste to the anterior 2/3 of tongue: CN7 70. nerve that contains taste fibers a. chorda tympani b. inferior olivary c. nasopalatine d. greater petrosol 71. lateral lemniscus, part of the hearing pathway, and the hair cells is where the lateral lemniscus originates; which is in b/w: cochlear nerve 72. most medial of the erector spinae muscles a. iliocostalis b. longissimus c. semispinalis d. spinalis 73. CN that innervates the superior oblique muscle of eye: trochlear 74. segmental level that comprises the phrenic nerve: C3, C4, C5 75. preganglionic parasympathetic fibers of the occulomotor nerve synapse at the ciliary ganglion 76. dorsal spinocerebellar tract has its origin in the dorsal column of Clark 77. all are supplied by the inferior laryngeal nerve EXCEPT a. cricothyroid b. posterior cricoarytenoid c. lateral cricoarytenoid d. transverse arytenoids 78. originates from the C2 dorsal primary rami: greater occipital nerve 79. avulsion of the posterior cerebral artery in the Circle of Willis will drain into the interpeduncular cistern 80. lesion of L5 prevents big toe from extending 81. foramen next to the internal auditory meatus: jugular foramen 82. most numerous in the CNS a. neuron b. astrocytes c. ependymal cells d. oligodendrocytes cerebellum – 10% of brain mass, 50% of neurons 83. innervates skin over the popliteal fossa: posterior femoral cutaneous nerve 84. cranial nerve that innervates the carotid sinus: IX 85. cremaster muscle is derived from internal oblique muscle 86. inguinal ligament is derived from external oblique muscle 87. m/c cervical vertebrae injured in a whiplash type injury: C5-C6 88. attaches to the anterior aspect of sacrum: piriformis 89. dorsal scapular nerve does not innervate a. levator scapulae b. rhomboid major c. rhomboid minor d. serratus posterior superior 90. sd