* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CNS Infections
Surround optical-fiber immunoassay wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Management of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
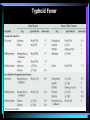
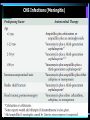
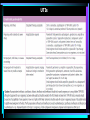
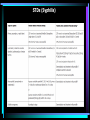
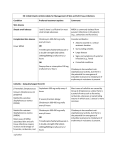
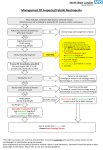
Impetigo The best topical agent is mupirocin; other agents, such as bacitracin and neomycin, are less effective. Patients who have numerous lesions or who are not responding to topical agents should receive oral antimicrobials effective against both S. aureus and S. pyogenes. Impetigo Folliculitis Local measures such as saline compresses and topical antibacterials (e.g., mupirocin) are usually sufficient to control the infection. Furuncles and Carbuncles Most furuncles: moist heat. carbuncle, a furuncle with surrounding cellulitis or fever, or a furuncle located about the midface: an antistaphylococcal antibiotic (e.g., dicloxacillin). In a penicillin-allergic adult: clindamycin, or co-trimoxazole. Patients with moderate to severe disease are best treated with initial parenteral therapy (e.g., vancomycin, linezolid, or daptomycin) Erysipelas Mild early cases of erysipelas in an adult may be treated with oral penicillin V (500 mg every 6 hours) or initial IM procaine penicillin (600,000 units once or twice daily). Erythromycin (250 to 500 mg orally every 6 hours) or other macrolides are suitable alternatives. More extensive erysipelas, hospitalization and parenteral aqueous penicillin G (2,000,000 units every 6 hours). If differentiation from cellulitis is difficult: a PRP (nafcillin or oxacillin), a cephalo 1, or therapy against MRSA. cellulitis Outpatient: PRP (nafcillin or oxacillin), cephalo 1 MRSA is suspected: clindamycin, TMP-SMX, doxycycline or minocycline + B-lactam (eg, amoxicillin), linezolid. Inpatient: PRP, cephalo 1 MRSA is suspected: clindamycin vancomycin, linezolid, daptomycin, Diabetic Ulcers Mild: PO cephalexin, dicloxacillin, clindamycin Moderate to severe: IV clindamycin plus a cephalo 3, clindamycin plus a fluoroquinolone, piperacillin-tazobactam, carbapenem, ampicillin-sulbactam, ticarcillin-clavulanate. Diabetic Ulcers Gastroenteritis ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin and levofloxacin, norfloxacin Azithromycin Typhoid Fever Gastroenteritis (nosocomial) CNS Infections (Meningitis) CNS Infections (Brain Abscess) CNS Infections (Shunt Infection) vancomycin plus either cefepime, ceftazidime, or meropenem CNS Infections (Subdural Empyema, Epidural Abscess) vancomycin plus cefepime or ceftazidime + metronidazole or meropenem In spinal cases, anaerobic coverage is not required. CNS Infections (Suppurative Intracranial Thrombophlebitis) vancomycin plus cephalo 3 or 4 + metronidazole or meropenem UTIs (Cystitis) Fluoroquinolones, TMP/SMX, nitrofurantoin, amoxicillinclavulanate, cephalosporins, tetracyclines, and fosfomycin. Most women: 3 days women who have a history of previous UTI caused by antibiotic-resistant organisms or more than 7 days of symptoms, and in men: 7 days UTIs UTIs UTIs (HCA) Mild to moderate illness without alterations in mental status or hemodynamic status may be treated with a urinary fluoroquinolone, such as ciprofloxacin or levofloxacin, or a broad-spectrum cephalosporin such as cefepime. If the patient has evidence of pyelonephritis or urosepsis, one should consider a broader-spectrum drug such as piperacillintazobactam or a carbapenem for empiric treatment. If the urine Gram stain shows gram-positive cocci (most likely enterococci or staphylococci), treatment with vancomycin is reasonable. STDs (urethritis) Ceftriaxone, 250 mg IM; or Cefpodoxime, 400 mg PO; or Cefixime, 400 mg PO Plus Azithromycin, 1 g PO; or Doxycycline, 100 mg bid PO for 7 days All sex partners within the preceding 60 days should be referred for evaluation, testing, and empiric treatment with a drug regimen effective against chlamydia and gonorrhea. STDs (Chancroid) Partners: Rx if they had sexual contact with the patient during the 10 days preceding the patient’s onset of symptoms. STDs (Granuloma Inguinale (Donovanosis)) Persons who have had sexual contact with a patient who has granuloma inguinale within the 60 days before onset of the patient’s symptoms should be examined and offered therapy. STDs (Lymphogranuloma Venereum) Persons who have had sexual contact with a patient who has LGV within the 60 days before onset of the patient’s symptoms should be examined, tested for urethral or cervical chlamydial infection, and treated with a chlamydia regimen (azithromycin 1 gm orally single dose or doxycycline 100 mg orally twice a day for 7 days). STDs (Syphilis) STDs (Trichomoniasis) male partners should be evaluated and treated with either tinidazole in a single dose of 2 g orally or metronidazole twice a day at 500 mg orally for 7 days.