* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download I and D alone is sufficient for most small simple
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
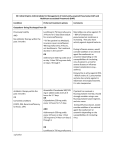
ED: Initial Empiric Antimicrobials for Management of Skin and Soft-Tissue Infections Condition Preferred treatment options Comments Simple small abscess I and D alone is sufficient for most small simple abscesses MRSA is commonly isolated from purulent infections in ED patients (e.g., carbuncles and furuncles). Complicated skin abscess Clindamycin 300-450 mg orally every 6 hours Consider antibiotics: Skin abscess Cover MRSA OR Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole 12 double-strength (DS) tablets (160mg/800mg) orally every 12 hours OR Doxycycline or minocycline 100 mg orally every 12 hours Abscess located in a critical anatomic location Surrounding cellulitis Large abscess Signs and symptoms of systemic infection (e.g., fever) Comorbid conditions Clindamycin has excellent antistaphylococcal activity, but there is the potential for emergence of inducible resistance to clindamycin if erythromycin resistance is present. Cellulitis – being discharged from ED -hemolytic Streptococcus Group A Streptococcus (S. pyogenes) Cephalexin 500 mg orally every 6 hours Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) If severe β-lactam allergy: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Clindamycin 300-450 mg orally every 6 hours Most cases of MRSA associated skin and soft tissue infections require incision and drainage of furuncles, carbuncles, and 11/17/10 Clindamycin 300-450 mg orally every 6 hours OR Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole 12 double-strength (DS) tablets (160mg/800mg) orally every 12 hours Most cases of cellulitis are caused by Group A Streptococcus unless there is a portal of entry such as furuncles, carbuncles, abscesses or penetrating trauma in which case S. aureus is more common. Clindamycin has excellent antistaphylococcal activity, but there is the potential for emergence of inducible resistance to clindamycin if erythromycin resistance is present. abscesses. OR Doxycycline or minocycline 100 mg orally every 12 hours Cellulitis – requiring IV therapy -hemolytic Streptococcus Cefazolin 1-2 g IV every 8 hours Group A Streptococcus OR Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) Nafcillin 500 mg – 1 g IV every 4 hours The current incidence of MRSA in cellulitis is not known Consider coverage for MRSA If severe β-lactam allergy: Consider drawing blood cultures Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV every 12 hours (rounded to nearest 250 mg) If there is purulence With systemic toxicity Critical anatomic location Comorbidities or immunocompromised host OR Clindamycin 600 – 900 mg IV every 8 hours Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV every 12 hours (rounded to nearest 250 mg) Consider drawing blood cultures Necrotizing Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (e.g., Necrotizing fasciitis) Community-acquired Infections Group A Streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes) remains the most common organism Gas gangrene can also be associated with Clostridium spp. especially in the setting of penetrating trauma Please draw 2 sets of blood cultures. 11/17/10 Ampicillin-sulbactam 3 g IV every 6 hours AND Clindamycin 600 – 900 mg IV every 8 hours If severe β-lactam allergy: Levofloxacin 750 mg IV every 24 hours AND Clindamycin 600 – 900 mg IV every 8 hours Surgical consultation recommended for necrotizing skin and soft tissue infections. In patients with a history of alcoholism and/or liver disease consider covering Vibrio vulnificus infections especially in the setting of recent water exposure or shellfish consumption. Please call infectious diseases consultation in these cases. MRSA is a rare cause of necrotizing skin and soft tissue infections. In the case of suspected MRSA infection addition of Vancomycin is appropriate. Mixed polymicrobial infections Risk factors: immunocompromised, recent surgical procedures, diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, and spontaneous mucosal tears of the gastrointestinal or genitourinary tract (i.e., Fournier’s gangrene) Please draw 2 sets of blood cultures Piperacillin-tazobactam 3.375 g IV every 6 hours Surgical consultation recommended. OR Imipenem-cilastatin 500 mg IV every 6 hours AND Clindamycin 600 - 900 mg IV every 8 hours AND Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV every 12 hours (rounded to nearest 250 mg) If severe β-lactam allergy : Levofloxacin 750 mg IV every 24 hours AND Clindamycin 600 - 900 mg IV every 8 hours AND Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV every 12 hours (rounded to nearest 250 mg) Animal and Human Bites Outpatient - (being discharged from ED) Amoxicillin-clavulanate 875/125 mg orally every 12 hours Pasteurella species are isolated from 50% of dog bite wounds and 75% of cat bite wounds. If severe β-lactam allergy: Doxycycline 100 mg every 12 hours OR Levofloxacin 500 mg orally every 24 hours or Ciprofloxacin 500 mg orally every 12 hours AND Clindamycin 300-450 mg orally 11/17/10 Human bites reflect oral flora of the biter and tend to be more serious: Streptococcus viridans, Eikenella corrodens, Fusobacterium species, Peptostreptococcus, and Prevotella. For bites involving hand and wrist please call covering hand surgical service for assessment. Please offer tetanus vaccination. every 6 hours Being admitted and requiring IV therapy Ampicillin-sulbactam 3 g IV every 6 hours Consider drawing blood cultures If severe β-lactam allergy: Please offer tetanus vaccination. Levofloxacin 750 mg IV every 24 hours AND Clindamycin 600 - 900 mg IV every 8 hours Diabetic Foot Infections Uninfected Ulcerations Avoid prescribing antibiotics Wound lacking purulence or any manifestations of inflammation Cellulitis without ulceration Please see above recommendations for cellulitis Ulceration with surrounding skin and soft tissue infection not requiring admission Cephalexin 500 mg orally every 6 hours for 7-14 days Evidence does not support the use of antibiotics for the management of clinically uninfected ulcerations, either to enhance wound healing or as prophylaxis against infection. OR Amoxicillin-clavulanate 875/125 mg orally every 12 hours for 7-14 days If β-lactam allergy: Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole 2 double-strength (DS) tablets (160mg/800mg) orally every 12 hours for 7-14 days OR Levofloxacin 750 mg orally every 24 hours for 7-14 days Being admitted for intravenous therapy 11/17/10 Ampicillin-sulbactam 3 g IV every 6 hours Low threshold to provide coverage for MRSA OR Please draw 2 sets of blood cultures Piperacillin-tazobactam 3.375 g IV every 6 hours Use previous culture data to choose empiric antibiotics (e.g., if patient has a history of ESBL E. coli or K. pneumoniae infections, consider Ertapenem 1 g every 24 hours) If severe β-lactam allergy: Severe: Necrotizing infection or gangrenous Please draw 2 sets of blood cultures Levofloxacin 750 mg IV every 24 hours AND Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV every 12 hours (rounded to nearest 250 mg) Piperacillin-tazobactam 3.375 g IV every 6 hours OR Imipenem-cilastatin 500 mg IV every 6 hours Seek surgical consultation. AND Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV every 12 hours (rounded to nearest 250 mg) If severe β-lactam allergy: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Levofloxacin 750 mg IV every 24 hours AND Metronidazole 500 mg IV every 8 hours AND Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV every 12 hours (rounded to nearest 250 mg) Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 41: 1373-406 Clin Infect Dis. 2004; 39: 885-910 N Engl J Med. 2007; 357: 380-390 Am Fam Physician. 2008; 78:71-82 NEJM 2006; 355: 666-674 www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dhqp/pdf/ar/CAMRSA_expmtgstrategies.pdf Inf Dis Clinics NA. 2008; 1:89-116 Emerg Med Clinics NA. 2008; 26:431-455 11/17/10