* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Is it a spider bite or an infection?
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
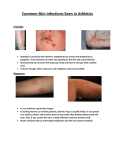
Is it a spider bite or an infection? Brian M. Bourgeois, M.D., F.A.C.S. Westbank Industrial Medicine Cellulitis Infection of the skin and its appendages Progresses through the layers of skin Involves transgression of epidermis by external source Introduction of native or foreign bacteria Cellulitis Recognition Treatment – first line vs. second line Surgical drainage Outpatient vs. inpatient Antibiotics Pathogens aka. offenders Staph. Strep. Vibrio Tetanus MRSA MRSA Methicillin resistant Staph. Aureus Appropriate treatment Carrier state Prevention Damage control Spider Bite Brown recluse Frequency Recognition Treatment Prevention Brown Recluse What’s the Hubbub? Necrosis Secondary Tissue loss Outcome infection Skin Care/Barrier Protection Mechanical agent Soaps Chemicals Surveillance MYTHS and FACTS All infectons are due to spider bites All spider bites cause infections These infections are resistant to antibiotics Infections are contagious Patients require significant operations