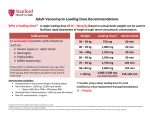
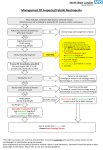
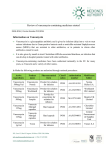
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section: 2-1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript