* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Barbiturates
Effects of long-term benzodiazepine use wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
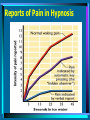
General Psych 2 States of Consciousness: Hypnosis – Module 18 Drugs and Consciousness – Module 19 April 6-13, 2004 Classes #19-21 Hypnosis • An altered state of consciousness brought on by special techniques and that produces responsiveness to suggestions for changes in experience and behavior • Probably around since antiquity, the rediscovery of hypnosis is commonly credited to Franz Anton Mesmer Franz Anton Mesmer (1734-1815) • Mesmer would pass magnets over the bodies of ailing people, some of who would lapse into a trancelike state and then awaken much improved – At the time many thought Mesmer’s work was linked to quackery… – Today skepticism remains as books on hypnosis is often grouped with those on parapsychology, ghosts, and witchcraft • Nevertheless, most psychologists believe it to be a respectable topic for scientific study Can hypnosis work on anyone? Can you be hypnotized against your will? • Hypnotic Susceptibility – Degree to which a person responds to hypnotic suggestions • Willingness to be hypnotized is most important factor • A key quality of hypnotically susceptible people is if they can become deeply absorbed in imaginative activities (Fantasy-prone personalities) • Stanford Hypnotic Suggestibility Scale Can hypnosis enhance the recall of forgotten events? • Can hypnosis help you to retrieve forgotten or suppressed details of a crime? • Can hypnosis help you to recall kindergarten classmates? • Can hypnosis alleviate pain? • There is some controversy surrounding these questions… 1976 Bus Kidnapping (Chowchilla, CA) • On July 15, 1976 a busload of children aged 5-14 and their school bus driver, Ed Ray (then 55 years of age) were abducted… – 19 girls and 7 boys were forced into two vans, driven around for 11 hours and then forced into a moving van buried in a nearby rock quarry – After 16 hours they dug themselves out – After the rescue, Ray mentioned that he had seen a license plate of one of the vans but couldn’t recall any of the numbers • Under hypnosis, he was able to recall all but one of the digits – with this crucial information the kidnappers were tracked down Unfortunately… • Most hypnotized witnesses respond with new but incorrect information • It appears that hypnosis can impair recall at least as often as it can improve it Can hypnosis force people to act against their will??? • Orne and Evans (1965) – 18 college students put randomly into one of three groups… • Group 1: Hypnotized • Group 2: Not hypnotized but asked to pretend • Group 3: Just asked to participate in experiment Orne and Evans (1965) • All three groups were asked to perform the following acts: – Pick up a poisonous snake – Put hands in fuming nitric acid – Throw acid in the face of one of the researchers • What do you think happened? Lets look at age regression… • Is it real? – True (1949): this researcher says yes – Orne (1982): this researcher says no Can hypnosis alleviate pain? • Yes – this has been clearly established in experiments… – Hypnotized subjects report far less pain than others when their arms are placed in ice water Why? • 2 Theories – Selective Attention Theory – Dissociation Theory Selective Attention Theory • We feel little or no pain because our thoughts are away from it – like an injured athlete who still completes the play… Dissociation Theory: A divided consciousness? • A dissociation or split between different levels of consciousness – dissociating the sensation of pain with our emotional suffering • Hilgard (1986) – “the hidden observer” Reports of Pain in Hypnosis Is hypnosis an altered state of consciousness? • Some psychologists say yes – It is a special state of consciousness characterized by a greatly increased suggestibility • Other psychologists say no – They emphasize similarities between a hypnotic state and a wakeful, conscious state – There is an awareness of surroundings and others • A social influence as well??? – If they like and trust hypnotist they feel motivated to do well • Some say the subjects are faking it and others say they are controlled by the hypnotist…you make the call Drugs and Consciousness: Altering consciousness with drugs • In this final section on states of consciousness, we will discuss some of the chemicals that alter consciousness by inducing changes in perception, mood, or behavior – Because of their ability to alter psychological processes, these chemicals are referred to as psychoactive drugs Altering consciousness with drugs… • Psychoactive drugs are taken to achieve a state of consciousness the user considers to be positive, pleasant, even euphoric – No reasonable person would take a drug because he or she expected to have a negative or unpleasant experience • Unfortunately, this is sometimes the case Psychoactive Drugs • Any substance that alters: – Mood – Awareness of the external environment – Awareness of the internal environment • Examples: – Marijuana, LSD, cocaine, heroine, alcohol, nicotine, codeine, caffeine, etc. Factors that influence the effects of drugs • Dose-dependent effects – The amount of the drug influences its effect • Its intensity • The kind of effect it has on the person • Tolerance • Refers to the lessened effect the drug will produce with continued usage – Cross-tolerance • Can sometimes occur when one takes a certain drug that then produces a tolerance in another drug of that type – Example: alcohol can produce a tolerance for antianxiety drugs Factors that influence the effects of drugs • Interaction effects – The effects of some drugs can be drastically altered if they are taken in combination with other drugs – The combination is often greater than what one might think the sum of the two drugs would be • Individual differences – Chemical, personality, and experience differences will often cause the same dosage of a drug to produce much different effects depending on the individual who is taking it • Expectations – Psychological factor is often present as individuals sometimes produce the effect that they expect the drug will produce Factors that influence the effects of drugs • Examples – People often get “drunk” on O’Douls – Saline solution often stops pain in those thinking they are receiving a pain killer – Subjects catch fewer colds because they believe they are receiving huge doses of vitamin C, when in fact they are getting only small amounts of powdered sugar. • When the research study ends and they no longer receive the placebo, the number of colds caught has been shown to go back up Types of Psychoactive Drugs • Depressants – Reduce physiological arousal and help individuals to relax • Opiates – Have the effect of dulling or numbing the senses – Can produce a sleeplike state • Stimulants – Increase arousal – Produce states of arousal • Hallucinogens – Distort sensory experience Depressants • Alcohol • Barbituates • Benzodiazephines Alcohol • Alcohol is a depressant yet we often feel lively after a couple of drinks… – It gives this feeling by slowing down the brain centers that control judgments and inhibitions Curious Effects • Memory • Sex • Hangover Alcoholism • Refers to one’s dependence on alcohol that seriously interferes with one’s life • Most common and costly form of drug abuse in U.S. • Aproximately 7% of adults 18 and over (10M people) • Traditionally more common (about 2 to 1) among males but recent research suggests that women are closing this gap Detrimental Effects • Life span of average alcoholic is 12 years shorter than the norm • Alcoholism ranks as the third leading cause of death in U.S. • More than one-third suffer at least one coexisting mental disorder • Organic impairment such as brain shrinkage occurs in a high proportion of alcoholics • About 20% attempt suicide • About 10% are successful Symptoms of Alcohol Dependence • Use alcohol to boost self-confidence and to relax around others • Drink to forget their problems or to relieve stress • Often are the ones who want “one more” drink even when their friends have stopped drinking • After friends have left they drink with new friends…often close the bar…stay past last call • Get drunk without planning to • Have blackouts Symptoms of Alcohol Dependence • Lie about their drinking, try to hide it, sneak drinks at work or school • Drink in the morning to cure a hangover • May begin to have financial, work, or family problems • Complete loss of control Treatments • Rehab Centers – Treatment centers where the addict is supervised 24/7 – Supervised detoxification period to eliminate drugs from our bodies system • Alcoholics Anonymous – Self-help group – Little research because of members anonymity but indications are most don’t stick to it – Need to go to regular meetings for it to work – 90 meetings in first 90 days and then at least once per week after that • Antabuse – A type of aversion therapy where usually a pill is taken that will cause the patient to become sick whenever they drink alcohol Barbiturates • Barbiturates are powerful depressants that slow down the central nervous system – Classified as sedative/hypnotics • Once a very commonly used tranquilizer but because they are highly habit-forming their usage decreased – They have effects similar to alcohol – They depress sympathetic nervous system activity – They have been used to induce sleep and reduce anxiety • In large doses, can lead to impaired memory and judgment Barbiturates • Barbiturates and other sedative/hypnotics are medically prescribed to treat sleeplessness, anxiety, and tension, and to help prevent or mitigate epileptic seizures – Certain barbiturates are also used to induce anesthesia for short surgical procedures or at the beginning of longer ones – Because of the risks associated with barbiturate abuse, and because new and safer drugs such as the benzodiazepines are now available, barbiturates are less frequently prescribed than in the past – Nonetheless, they are still available both on prescription and illegally • Other names: barbs, barbies, downers, goofballs Barbiturates • In low doses, barbiturates have a tranquilizing effect • Increased doses are hypnotic or sleepinducing • still larger doses act as anticonvulsants and anesthetics • Barbiturates have been widely used as sleeping pills…such use may lead to… – psychological dependency – physiological tolerance – death by overdose (often the drug of choice for those attempting suicide) • Barbiturates do not relieve pain Barbiturates • What it feels like… – Relaxation, peacefulness, sleepiness, pleasurable intoxication, dizziness, inactivity, withdrawal, interrupted thought processes, mood swing, excitement, increased pain, hostility, depression, anxiety, confusion, changed vision, intense emotions, hangover • Barbituates give a quick “high” but the effects drop off and persist for a low level for a longer duration Barbiturates • Besides having therapeutic uses, barbiturates are often used for their pleasurably intoxicating effects • Some people take them in addition to alcohol, or as a substitute • Heavy users of other drugs sometimes turn to them if their usual drugs are not available, or to counteract the effects of large doses of stimulants such as amphetamines or cocaine Barbiturates • Non-medical users often start taking barbiturates at doses within a safe therapeutic range – As tolerance develops, however, they progressively increase their daily dose to many times the original – It is extremely important to note that in spite of acquiring tolerance to the intoxicating effects of barbiturates, the user develops no tolerance to the lethal action of the drug • Therefore, high doses could produce fatal results even for tolerant abusers • Taking barbiturates with other CNS depressants… – e.g. alcohol; tranquillizers; such opioids as heroin, morphine, meperidine (Demerol), codeine, or methadone; and antihistamines (found in cold, cough, and allergy remedies) can be extremely dangerous, even lethal Benzodiazepines • Benzodiazepines (commonly referred to as benzos) are a more recent generation of tranquilizers – Some of the more common benzodiazepines are: ativan, librium, valium, and xanax – They are usually prescribed by doctors to treat anxiety and sleep problems, they can also, be used to treat panic disorders and muscle spasms, and occasionally used in the treatment of epilepsy and alcohol withdrawal Benzodiazepines • Heroin users tend to use benzos to help them sleep or when they're trying to get off heroin • Speed and ecstasy users use them to help them sleep or when they're 'coming down‘ • Some people use them as their drug of choice. • Benzodiazepines affect the central nervous system – Like alcohol and heroin they are depressants, and slowdown responses such as respiration, heart rate, etc. Short-Term Effects • • • • • Relaxation Drowsiness Dizziness Confusion Mood swings Common Long-term Effects • • • • • • Lethargy Irritability Nausea Loss of sexual interest Increased appetite Increased weight Opiates • Derived from opium these drugs depress CNS functioning • Include: opium, morphine, codeine, and heroin • Have the effect of dulling or numbing the senses… – Pupils constrict – Breathing slows – User becomes lethargic • For a few hours, such things as pain and anxiety are replaced by blissful pleasure But for bliss you pay the price… • Unfortunately, the bliss is eventually replaced by a gnawing craving for another fix • The need for progressively larger doses will lead to the physical anguish of withdrawal if use is discontinued – If the user has taken opiates regularly, the withdrawal symptoms may appear after only a few hours have passed since the last dose and peak after 2-3 days – The symptoms include aches, nausea, fever, trembling, convulsions, sweating and shivering. • For some…the ultimate price to pay is death by overdose But for bliss you pay the price… • The path to addiction is insidious… – When repeatedly flooded with these artificial opiates – the brain stops producing its own natural opiates (endorphins) – So, when the drug is withdrawn, the brain lacks the normal level of these painkilling neurotransmitters • The result is the raw agony of withdrawal Opiates • Opiates can be divided into natural and synthetic opiates • Natural opiates are derived from the opium poppy – Morphine and codeine are made from raw opium and can further be refined into heroin – Synthetic opiates include methadone and pethidine • Opiates have been used as medicines for a long time – Today, morphine is used as a pain relief • Example: for terminally ill cancer patients – Certain cough medicines and pain killers contain codeine On the street… • Opium is sold as dark brown lumps or powder – It is usually eaten or smoked • Heroin, when sold at street, is usually diluted with other powders (often with glucose) and its color varies from white to brown – The mixes contain a very varying amount of pure heroin – Heroin can be taken orally, intravenously or it can be smoked • Narcotic pain killers are sold as capsules, tablets, liquid or suppositories Its effects… • The effects of opiates, like those of other intoxicants, depend on: – The user's state of mind and on the company the user is in – Whether an opiate is used on its own or together with other intoxicants – Whether the user is a novice or an experienced user also has an influence on the effects of the drug Effects can be dangerous… • Immediately after taking the drug the user will experience a rush of euphoria • Feelings of hunger and pain are suppressed, along with sexual desire • Novice users may also feel nauseous and restless • Higher doses will make the user feel warm, his limbs feel heavy and his mouth dry • The user will feel alternately alert and drowsy… Effects can be dangerous… • At even higher doses the pupils become constricted and the skin feels cold and clammy and turns bluish • A fatal respiratory failure may develop • There is always a danger of an overdose when the drug is bought on the street as it is very difficult to determine how strong the mixture is Stimulants • Increase arousal and cause states of euphoria that are generally referred to as highs • The two most powerful that are abused: – Amphetamines – Cocaine Amphetamines • SLANG TERMS – – – – – – – – uppers ups wake ups bennies dexies black beauties jollies speed • An amphetamine is a drug that is a stimulant to the central nervous system Amphetamines • Amphetamines are colorless and may be inhaled, injected, or swallowed… – These drugs may be used medically to treat depression, obesity, and other conditions • Amphetamines are also used non-medically to: – Avoid sleep – Improve athletic performance – Counter the effects of depressant drugs IMMEDIATE EFFECTS • • • • • • • • • Increased talkativeness Increased aggressiveness Increased breathing rate Increased heart rate Increased blood pressure Reduced appetite Dilated pupils Visual hallucinations Auditory hallucinations EFFECTS OF LARGE DOSES • • • • • • • • • • Fever and sweating Dry mouth Headache Paleness Blurred vision Dizziness Irregular heartbeat Tremors Loss of coordination Collapse • Death may also occur due to burst blood vessels in the brain, heart failure, or very high fever LONG-TERM EFFECTS • Mental illness similar to paranoid schizophrenia… – Amphetamine Psychoses • Delusions like those seen in paranoid schizophrenia– the long-term effect of high doses cause an overproduction of dopamine • Malnutrition due to suppression of appetite • Increased susceptibility to illness due to poor diet, lack of sleep and unhealthy environment • Violence and aggression • Multiple drug users may use other drugs to counter unwanted side effects of amphetamines LONG-TERM EFFECTS • Infections resulting from IV injections • Blockage of blood vessels • Tolerance and dependence WITHDRAWAL SYMPTOMS • Amphetamines are addictive – Because of this, when the user discontinues use or reduces the amount he/she uses, withdrawal symptoms may occur WITHDRAWAL SYMPTOMS • • • • • • • Severe exhaustion Deep sleep lasting from 24 to 48 hours Psychotic reaction Extreme hunger Deep depression Anxiety reactions Long but disturbed sleep Cocaine • Effects are similar to amphetamines but the rush is much more intense… – SLANG TERMS • Coke • Crack • Dust • Snow • Blow • Flakes • Bloke • Bernice • Dream Cocaine • Cocaine is an addictive substance which comes from coca leaves or is made synthetically – This drug acts as a stimulant to the central nervous system – Cocaine appears as a white powder substance which is inhaled, injected, freebased (smoked), or applied directly to the nasal membrane or gums – Cocaine gives the user a tremendous "rush“ – These chemicals trick the brain into feeling it has experienced pleasure PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS • Increased – Heart Rate – Breathing – Blood pressure • Nausea • Weight loss • Tremors • Insomnia • Rapid breathing • Twitching • Fever • Paleness PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS • • • • • • • • • Sexual problems (impotence) Dilated pupils Cold sweats Fatigue Constipation Headaches Blurred vision Seizures Nasal congestion PERSONALITY EFFECTS • • • • • • • • Lying Stealing Superior attitude Less ambition Argumentativeness/short temper Job problems Denial of responsibility Depression PERSONALITY EFFECTS • • • • • • • • Confusion Increased number of accidents Hallucinations Anxiety Paranoia Poor concentration Loss of interest in sex Flattened and dulled emotions HEALTH PROBLEMS • • • • • Ulceration of the nasal membrane Cardiac arrest Respiratory arrest Physiological seizures Lung damage Addiction • The effects of cocaine occur within the first few minutes, peak in 15-20 minutes and disappear in about 1 hour • The immediate effects are what make cocaine so addicting • The user is willing to endure the lows in order to experience the highs. • Cocaine is highly addictive • Every use of the drug makes the addiction stronger Addiction • This addiction can begin almost immediately following the first use • The addiction to cocaine is very strong, therefore, withdrawal symptoms are likely to occur when a person is not using the drug… – Extreme irritability – Sluggishness – Nausea – Disorganized thinking – Extreme irritability – Sluggishness – Nausea – Disorganized thinking Hallucinogens • Marijuana • LSD • PCP Marijuana • About 1 in 3 Americans has used marijuana at least once and approximately 10% of the population uses it on a regular basis • Next to tobacco and alcohol, marijuana is the most popular substance chosen by young people for regular use Marijuana • Triggers a mixture of effects that makes this drug difficult to classify… – Like alcohol it has a depressant effect… • It relaxes, disinhibits, impairs motor coordination – It is also a mild hallucinogen • It can slow the passage of time and amplify one’s sensitivity to colors, sounds, tastes, and smells Marijuana • Dried leaves of the cannabis plant • Usually smoked, but can be eaten in cookies, candy or brownies • Marijuana’s effects vary widely from person to person – Mood swings from “placid dreaminess to euphoric gaiety” – Negative mood swings are rare Marijuana • Effects cognition… – Users believe that things are more interesting, more profound, that they are more creative • Research has shown this is not the case – Increased distractibility – Decline in short term memory Marijuana • Very quickly absorbed into the bloodstream when smoked • Takes longer when eaten, but the effects last longer as well • Effects physical coordination and perceptual abilities – Not much different than alcohol when it comes to driving…probably should stay away from heavy equipment too… LSD (Lysergic acid diethylamide) • Causes a disruption of serotonin brain receptors and this leads to hallucinations • It comes in a variety of forms but is virtually always taken orally Effects • Onset – Generally 20-60 min. • Duration – Primary effects last 6-8 hrs. • Experience – Beginning is a sort of anticipation, then a slight energy surge, something is different feeling, lights may seem to have an extra twinkle, then effects get stronger – feelings of insight, confusion, paranoia, and quickly changes emotions (happiness to fear to joy to irritation, etc) Problems • Although a euphoric state is often achieved, LSD users must be prepared for a “bad trip”… – Recent experiences such as unsettling events during the day can blossom into more serious distress and trauma while tripping – A “bad trip” can produce vividly, terrifying images…so much so that its possible for someone to jump out of a window in order to get away from these images – Very important for these drug users to take precautions so that tragedies can be averted Problems • Post-hallucinogen perceptual disorder – At least 5% of LSD users experience LSD flashbacks… – Sudden, uncontrollable recurrences of perceptual distortions like those experienced on a “trip” – Person “freaks out” because they have no clue what is happening to them – May become chronically anxious because of this – Seems that the drug is stored somewhere in the body and later released • Using LSD can result in chromosomal damage Problems • Some people become psychologically dependent on LSD – Not usually physiologically addictive though PCP (Phencyclidine) • Commonly referred to as “angel dust” this substance is often sprinkled over dried parsley, oregano, or marijuana leaves, it can be smoked and effects noted within 2 to 5 minutes, then peaking at 15 to 30 minutes • Taken orally, in the pill form or mixed with food or beverages, PCP's effects are usually noted within 30 minutes and tend to peak at about 2 to 5 hours Angel Dust • Lower doses of PCP typically produce euphoria and decreased inhibition as may be seen with drunkenness • Mid-range doses cause body wide anesthetic with enhanced sensations and impaired perceptions which may result in panic reactions and violent defensive behaviors • Large doses may produce paranoia, auditory hallucinations, psychosis similar to schizophrenia • Massive doses, more commonly associated with ingesting the drug, may cause cardiac arrhythmias, seizures, muscle rigidity, acute renal failure, and death – Because of the analgesic properties of PCP, users who incur significant injuries may not feel any pain Near-Death Experiences…do we really have them??? • Gallup (1982) – Huge nationwide survey – 15% reported having a close brush with death – One-third of these (8 million people) reported having a mystical experience in connection with it Siegel (1977) • Many similarities between “near-death” experiences and typical hallucinogenic experiences – Visions of tunnels or funnels – Bright lights – Beings of light – Replay of old memories – Out-of-body sensations Near-Death Experiences • Often, oxygen deprivation is occurring during injuries to the brain – these are known to produce hallucinations • Since reports are always of a positive nature… • Interesting note: – Some researchers have interviewed people who have experienced both and say that these people deny their similarities – In addition, those in the near-death experience are permanently changed by the experience which is not the case with hallucinations – They usually become kinder, more spiritual people