* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacovigilance wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
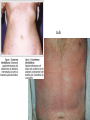
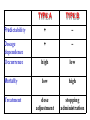
3. cvičenie ADR. EBM. • Each pharmacotherapy means risk akceptation, each drug can have potential risk for patient benefit • Risk of pharmacotherapy should never exceed risks of not treating particular disease!!! risk Pharmacovigilance Includes all aspects of postmarketing development: - monitoring of clinical safety - identification of new threats - estimation of risk and contribution - action and communication Goal: to prove product safety Pharmacovigilance • We take into consideration during drug selection: – – – – EFFICACY SAFETY PRICE SUITABILITY • in 60th after talidomid scandal, WHO established monitoring focused to early detection of ADR • WHO created system of spontanneous ADR monitoring with center in Uppsala (Sweden) TALIDOMID • 1959-1961: sedative, hypnotic drug for pregnant women (marketed in Germany, England, Canada..., never in USA) • Born were > 12 000 children with phocomelia • Now: new indications – imunomodulatory, antiangiogenic and antiinflammatory properties: – skin lupus erythematodes – skin form of lepra – Kaposi´s sarcoma at AIDS ... ADVANTAGES of pharmacovigilance at worldwide cooperation • Large number of treated patients • Detection of possible race variations • Detection of rare ADR • Possibility of soon warning of particular drug risk all over the world SIDE EFFECT Each unintend drug effect, occuring at normal doses used for patients, which is in relation to pharmacologic properties of drug. (antihypertensive effect of minoxidil + hypertrichosis) ADVERSE EVENT Each noxious health event, which can occur during therapy, but doesn´t have to have relation with this therapy. (patient takes ATB and breaks his leg) ADVERSE DRUG REACTION = ADR • Reaction to drug which is noxious and unintended and occurs at doses of drugs normally used for prophylaxis, diagnosis or treatment of disease or to modify physiologic functions • Detection of ADR at targeted monitoring 10-30%. • At spontanneous monitoring < than 1%. • Intoxications and mistakes in therapy don´t belong here UNEXPECTED ADVERSE REACTION Adverse reaction whose character or intensity isn´t in concordance with domestic informations about drug or isn´t expected according to drug characteristic. SIGNAL Reported information about possible causal relationship between adverse event and, this relationship was yet unknown or incompletely documented. Usually more than 1 report is required for signal. Risk factors of ADR Drug Pacient • nonselective and nonspecific • with narrow therapeutics range • lipophilic Prescription • Wrong selection of drug, drug combination, dose, route of administration, therapy length • polymorbidity • diseases of organs of elimination • age, women • pharmacokinetic variability (etnic group, genetic polymorphism) • compliance Number of drugs 0-5 6-10 11-15 > 16 ADR 4% 10% 28% 54% I. ADR according to mechanism of origin 1. Type A („augmented“) • these ADR are expected • they can be predicted on the base of pharmacodynamic properties of drug • they depend on drug dose, they appear at higher doses • frequency is high > than 1% • mortality is low • therapy consists in dose adjustment • e.g.: cough after ACEI, bleeding from GIT after NSA, aspirin, corticoids ... rash 2. Type B („bizard“) • idiosyncratic reactions • these ADR are not expected • they can be hardly predicted • doesn´t depend on dose • frequency is low < than 0,1% • mortality is high • treatment consists in stopping drug administration • e.g.: haemolytic anaemia after metyldopa, hepatitis induced by isoniazid, allergic reaction after PNC ... TYPE A TYPE B Predictability + – Dosage dependence Occurrence + – high low Mortality low high dose adjustment stopping administration Treatment 1 drug – different types of ADR DRUG Type A reaction Type B reaction Ampicillin Pseudomembr. colitis Intersticial nephritis, allergy Chlorpropamid Sedation Hepatotoxicity Naproxen GIT haemorrhage Agranulocytosis Warfarin Bleeding Breast necrosis 3. Type C („continous“) • this type of ADR increases number of “spontanneous“ diseases • they occur usually after long-lasting administration • they are often serious and persistant • mechanism of genesis is unclear • they are unexpected, not predictable • they can´t be verified experimentally • e.g.: oral contraceptives and increased occurrence of thromboembolia, analgetic nephropaty 4. Type D („delayed“) • • • • • late ADR (years resp. generations) teratogenity carcinogenity mutagenity e.g.: ca. of vagina at daughters of mothers treated with dietylstilbestrol 5. Type E („End of use“) • after therapy ending (syndrom from omitting) • rebound phenomenon • e.g.: beta blockers, opioids, corticosteroids, nitrates ... II. ADR according to intensity • mild – don´t require to stop or to change treatment • moderate – require to change therapy, but don´t threat life of the patient • serious – death, hospitalization, invalidization, teratogenity III. ADR according to frequency Frequency • frequent >1,0 % (sedative effect after promethazin) • seldom >0,1% (rhabdomyolysis after statins) • rare > 0,01% (agranulocytosis after metamizol) Determination of causality Basic categories: A. High probability of causality B. No sufficient proof of causality 0. Isn´t possible to evaluate causality ACTIONS AT PROOF OF CAUSALITY • • • • • warning methodic direction limitation of indication change of dose deregistration of the drug Deregistered drugs • • • • • • • troglitazon benaxoprofen terfenadin mibefradil cerivastatin – 2001-2002 rofekoxib, vadekoxib – 2004-2005 group with the highest risk NSA (> 30% of deregistrations) • % of ADR reported at active monitoring : 10-30% (mostly done by pharmaceutical companies during clinical trials) at pasive monitoring < 1% • Type A ADR: - 80% • Treatment of ADR represents 13-15% of therapy costs • ADR occurs mostly between 1-10 day from beginning of therapy EBM (Evidence based medicine ) • EBM brings proofs about efficacy and safety from large clinical studies • Applied are relevant statistic methods, metaanalysis • These results are used for creating recommandations for therapy (guidelines) P R E D P Í Š T E R E C E P T