* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tina said you all learned ALOT last week
Discovery and development of non-nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Specialty drugs in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical marketing wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Plateau principle wikipedia , lookup
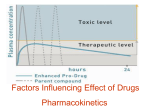
You learned a LOT last week Who can tell me what you learned? Let’s add to your vocabulary Neuron Neurotransmitter (NT) Enzyme DNA/RNA Vesticles Receptors A few extra facts to throw in No single reproducible abnormality in any NT, enzyme, receptor or gene has been found to cause Psychopathology (but they can contribute to the risk) Virtually all Psychotropic drugs have been found thru serendipity or by guessing And we know… Drugs effect the body (Pharmacodynamics) That the body effects the drugs absorption, distribution, biotransformation, and excretion (Pharmacokinetics) Absorption Occurs in the stomach and small intestines for oral medications Bioavailability- How much of the drug is available in the bloodstream – Taken with or without food – Blood/Brain Barrier – Introvenious drugs (100% bioavailable) Why is this necessary to know? Distribution After the drug is absorbed and reaches the blood stream (absorption)…. Then it must be distributed to various organs or body sites – High blood flow 1st (liver, kidney, heart, brain) – Muscles and fat tissues 2nd Each medication has a particular distribution pattern. – For example, TCAs are distributed in the fat and muscle cells. What are the implications for the prescribing physician? – Why might a patient not become depressed for days or weeks after discontinuing medications? Biotransformation (Metabolism) Toxicity Issues Metabolizes primarily in the Liver via enzymes, so that Kidneys can secrete more easily Different people have different enzymes in the liver, thus one may metabolize Zoloft well, but not Prozac. What are the implications for prescribing physicians? Biotransformation What do you think are the cultural implications in Biotransformation? Biotransformation 5-10% of Caucasians are poor metabolizers via the enzyme CYP450 2D6, so they must metabolize drugs that require this enzyme in an alternate manner, which might not be as efficient 20% of Japanese and Chinese individuals have reduced activity in enzyme CYP450 2C19 How does this make you feel about the clinical studies that have been done with little attention to race/ethnicity? Excretion Drugs are eliminated from the body thru the Kidneys, Intestines, Respiratory, Sweat, Saliva, and Breast Milk Adequate excretion is dependent on Kidney functioning What should physicians take into consideration prior to prescribing a medication? Half-Life is an important factor in Excretion Half-life: The period of time required for the concentration or amount of drug in the body to be reduced by one-half 4-5 X half-life=Steady State – As repeated doses of a drug are administered its plasma concentration builds up and reaches what is known as a steady state. This is when the amount of drug in the plasma has built up to a concentration level that is therapeutically effective and as long as regular doses are administered to balance the amount of drug being cleared the drug will continue to be active. The time taken to reach the steady state is about five times the half life of a drug. Steady State does not = onset of drug action Half-life example Some drugs like ibuprofen have very short half lives, others take much longer to eliminate from the plasma resulting in a long half life. So drugs like ibuprofen that are cleared from the blood more rapidly than others need to be given in regular doses to build up and maintain a high enough concentration in the blood to be therapeutically effective. Which would be more addictive? A drug with a long or short half life? Now that we understand Pharmacokinetics, we want to know more about Pharmacodynamics-how the drugs effect the body. This will be the focus of the rest of the class