* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Case Study - Cal State LA
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
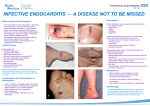
CASE STUDY PATHOGENIC BACTERIOLOGY 2009 Edmund Yeo Case # 52 Team Members: Tania Guevara Anthony Obisesan CASE SUMMARY Age: 39 Intravenous Drug User Cellulitis of right arm after several weeks of fevers Used outpatient antibiotics without relief 1-cm vegetation on ventral surface of the aortic valve 2 sets of blood cultures obtained with microorganism present “needle track” marks on upper and lower extremities Cardiac exam showed a grade II/VI systolic murmur Spleen tip was palpable DIAGNOSIS/ ISOLATION/ IDENTIFICATION OF ENTEROCOCCUS Gram stain Growth in CO2 rich environment on a variety of media, including blood agar Able to survive in oxygen rich environments Growth in high salt concentration environment Hydrolization of esculin in the presence of bile Catalase negative CLASSIFICATION, GRAM STAIN RESULTS, AND MICROSCOPIC APPEARANCE OF ENTEROCOCCUS Enterococcus species Gram positive cocci in chains Growth in broth containing 6.5% NaCl Hydrolyzed esculin in the presence of bile Catalase negative KEY INFORMATION POINTING TO DIAGNOSIS Intravenous Drug Usage Opens up body to infections from blood infecting organisms because of needle usage and open wounds Antibiotic use without relief 1-cm vegetation on aortic valve Gram stain Growth in high salt concentration broth Esculin hydrolyzation with bile present THE DIAGNOSIS FOR CASE # 52 Endocarditis Caused by: Enterococcus species (IVDU) HACEK organisms (IVDU) Candida albicans (IVDU, immunocompromised) S. aureus (IVDU, contaminated surgery, catheterisation) Pseudomonas species (contaminated water or drugs) S. bovis, Clostridium septicum (breakdown of barrier between gut lumen and blood vessels that drain the bowel) Alpha hemolytic strep species (Dental work) DISEASES AND PATHOGENESIS OF DISEASE CAUSED BY ENTEROCOCCUS Diseases Endocarditis Bladder infection Prostrate infection Epididymal infection Pathogensis Adherance Platelet aggregation Causes swelling and inflammation due to cell aggregation Tissue factor-dependant fibrin production THERAPY, PREVENTION AND PROGNOSIS OF PATIENT INFECTED WITH ENTEROCOCCUS Therapy Vancomycin should be tested before administered Vancomycin resistant strains should be treated with Linezolid Prevention Be careful with contaminated hospital equipment Stay away from street drugs, may be contaminated Don’t share needles, might have been used by infected person Prognosis High doses of antibiotic should be administered through IV to maximize the diffusion of the antibiotic into the bloodstream. PRIMARY RESEARCH ARTICLE CONTRIBUTING TO THE UNDERSTANDING OF THE DISEASE CAUSED BY PATHOGEN X Ulrich Sagel, Berit Schulte, Peter Heeg, Stefan Borgmann, 2008, “Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci Outbreak, Germany, and Calculation of Outbreak Start”, Emerging Infectious Diseases, vol 14: 317-319. They observed incoming and outgoing patients with infections from organism and set up a method to be able to calculate when an outbreak would occur. They found that their model of predicting outbreaks was accurate and could be used to alert hospitals to increase their preparations in admitting infected patients and to double check to make sure they do not have or use contaminated tools. This relates to the case because the patient in this case had been to the hospital many times and was given antibiotics that had no effect on relief. This would show that he might have a resistant strain of some kind of bacterial infection that should have been checked up on. TAKE HOME MESSAGE Endocarditis involves inflammation of the inner layer of the heart due to vegation of platelets, fibrin, microorganisms, and inflammatory cells. Typical symptoms are chills, cough, fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, weight loss, sweating, muscle aches, and joint pains Pathogen is Enterococcus Diagnostics: Blood test for organism presence Gram stain Biochemical tests Therapy is based on the strain of organism, which can have different resistances to different antibiotics Antibiotic sensitivity testing should be done on the organism, then once an effective antibiotic is found, the patient should be treated with it. To prevent infections of this type, avoid contaminated needles or drugs which give the organism easy access to your bloodstream. Also double check hospital equipment for cleanliness. This pathogen can be transmitted in a variety of ways because it is able to live in oxygen rich areas. It can be transmitted through any contact with infected blood with open wounds. Threat is medium to high dependant on the strain. Chance of microbial resistance is high and increasing more and more, so it is getting harder to treat. REFERENCES "Endocarditis - cardiologychannel." Cardiologychannel, Your Cardiology Community - Physician-Developed - Cardiovascular Health Info cardiologychannel. 12 Mar. 2009 <http://www.cardiologychannel.com/endocarditis/index.shtml>. "Enterococcus faecalis -." Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. 12 Mar. 2009 <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enterococcus_faecalis>. "Infective endocarditis -." Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. 12 Mar. 2009 <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bacterial_endocarditis>. Leboffe, Michael J., and Burton E. Pierce. A Photographic Atlas for the Microbiology Laboratory. Null: Not Avail, 2004. "The pathogenicity of enterococci -- Johnson 33 (6): 1083 -- Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy." Oxford Journals | Medicine | Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 12 Mar. 2009 <http://jac.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/33/6/1083>. Sagel, Ulrich, Berit Schulte, Peter Heeg, and Stefan Borgmann. "Vancomycin-Reistant Enterococci Outbreak, Germany, and Calculation of Outbreak Start." Emerging Infectious Diseases 14 (2008): 317-19.