* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS – A DISEASE NOT TO BE MISSED At
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
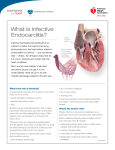
INFECTIVE ENDOCARDITIS – A DISEASE NOT TO BE MISSED . What is Infective Endocarditis? • • • • • A microbial infection of the endocardium ( the hearts inner lining) which also affects the heart valves Common causative organism are mainly bacteria (Staph. aureus, Staph. epidermis, Strep viridians , Enterococci) but can include fungi (candida albicans ) Microorganisms adhere and multiply on the heart valves leading to vegetation growth This vegetation can break off and cause emboli to occlude blood vessels within the body. Infective endocarditis is life threatening if not recognised and treated early. Presentation Initially symptoms may be vague and non specific such as • Low grade fever/chills • Night sweats • Fatigue • Arthralgia • Weight loss 1 2 At Risk Groups Include people with • Prosthetic heart valves • Congenital heart defects • Degenerative heart disease • Implanted cardiac devices, pacemaker/ICD • Long term indwelling vascular catheters • Previous history of endocarditis • Body piercings • Poor dental hygiene • Immunocompromised states • Intravenous drug use 3 4 Infective Endocarditis can manifest with varied & diverse clinical presentation often the result of major vessel emboli from rupture of vegetation & abscess formation on valves. • Stroke - confusion, hemiplegia, sensory dysfunction Pulmonary Embolism- breathlessness, tachycardia Splenic infarction- pain on splenic palpation Renal infarction- loin pain , haematuria, glomerulonephritis Retinal haemorrhages - Roth spots -seen on fundoscopy Dermatological signs- result of small emboli travelling to peripheral vessels include • Nail fold infarct (No.1) • Splinter haemorrhage- thin linear haemorrhages under nail beds (No.2) . • Oslers nodes- small, tender red / purple nodules found on distal digits on fingers and toes (No.3) • Petechial rash, on body, inside eyelids & oral mucosa (No. 4& 6) • Janeway leisons- Small painless, macular lesions on palms and soles of feet (No.5) Management • Early recognition and investigation is crucial • Blood cultures (ideally pre antibiotic therapy) • Early Echo (Transoesophageal ) Complications and Clinical Signs of Embolization • • • • As the disease progresses damage to the heart valves occurs and cardiac signs may be seen such as • New heart murmur or change in existing murmur • ↓ Cardiac out put • Heart failure • Conduction disorders (mainly) AV Blocks • Myocardial infarction • Treatment is with lengthy iv antibiotic therapy +/valve surgery • Team approach involve Cardiologist, ID, Microbiology Key Message 5 6 Infective Endocarditis is diverse and can masquerade as other illnesses. Vigilance and suspicion are key to its recognition. Consider infective endocarditis in at risk patients who present with fever of unknown origin.