* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GOUT
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of tubulin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
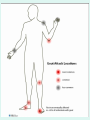
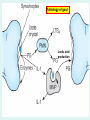
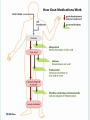
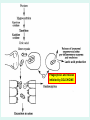
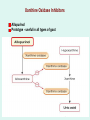
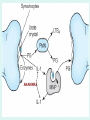
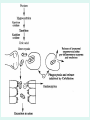
GOUT Dr.B.V.Venkataraman Professor in Pharmacology Faculti Perubatan, International Medical School, New BEL Road, Bangalore-560054 [email protected] GOUT Gout is a disorder of purine metabolism. Excess production or slow excretion (3.5-7.5mg/dl normal) Uric acid has low solubility in acidic urine Common in big toe, mid foot, ankle, knee Pathology of gout Lactic acid production Reasons for Gout Genetic factor – Men get more than females Excessive alcohol consumption, Diet rich in purine (meat preparations) Lead poisoning kidney disease Anticancer drugs, diuretics, Management of acute gout NSAIDs Corticosteroids Colchicine Management of Chronic gout Allopurinol Uricosurics – probenecid, sulfinpyrazole Newer drugs Anakinra Urate reasbsorbtion blocker (presently called RDEA594) COLCHICINE Source: colchicum autumnale It binds to tubulin, and causes its depolymerisation. This decreases the mobility of granulocytes into the affected area. decreases lactic acid production thereby reducing the deposition of urate crystals that perpetuates the inflammatory response Lactic acid production Phagocytosis and release Inhibited by COLCHICINE Colchicine (contd) Lack - analgesic, anti pyretic and uricosuric rapidly absorbed orally recycled in the bile excreted unchanged in the faeces and urine Indications of Colchicine prevention of acute attack and prophylaxis of intermittent attacks. replaced by NSAIDs and steroids in acute attack treatment, as it requires very high dose. IV dose does not produce diarrhoea. Diarrhoea occurs with oral route. Side effects of Colchicine diarrhea (not on iv route) occasionally cause nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. On chronic use rarely cause hair loss and bone marrow depression peripheral neuritis and myopathy. NSAIDs: Indomethacin is potent Relief is quick Minimal side effects during acute treatment 25-50 mg every 4 hr. Other NSAIDs (except salicylates) are also effective. NSAIDs CORTICOSTEROIDS: Effective and rapid in action Prednisone or methyl prednisone better than long acting anti inflammatory steroids Combined with indomethacin or colchicine. 40 mg/day till the attack subsides steroids should be tapered after acute phase. Local injections possible if one or two joint swellings CORTICOSTEROIDS CHRONIC GOUT Aim of the treatment Decrease uric acid synthesis (xanthine oxidase inhibitors) Increase the uric acid excretion (uricosuric drugs) Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors Allopurinol Prototype - useful in all types of gout Pharmacokinetics of allopurinol well absorbed orally metabolised into alloxanthine Both allopurinol and alloxanthine inhibit the uric acid synthesis has longer duration of action single dose is enough to maintain the inhibitory effect. Dose: 100 mg single dose after food. Side effects of allopurinol Most frequent treatment-related - liver function abnormalities, diarrhea, headache, and nausea Not used in acute attack, as it flares up the attack in some people Even in chronic treatment initial administration precipitate acute attack. So combine with colchicine or NSAIDs. Therapy should be always with plenty of fluid to avoid renal calculi. Febuxostat - well tolerated in patientsof allopurinol intolerance. Allopurinol interactions Inhibits metabolism of mercaptopurine, azothioprine and other xanthine alkaloids (theophylline) - doses should be reduced. Higher incidence of hypersensitivity reaction with ampicillin Inhibits metabolism of the oral anti coagulants prolongs bleeding URICOSURIC DRUGS increase the excretion of uric acid in the urine Probenecid and sulfinpyrazone - standard uricosurics. Competes with uric acid for tubular reabsorption Side effects Hypersensitivity reaction gastric irritation Use Chronic gout URICOSURIC DRUGS (Contd) Drug interaction Uricosuric drugs decrease the excretion of oral hypoglycaemic agents, sulphonamides, penicillin group of antibiotics, indomethacin Precaution Not suitable for acute attack Not used in high uric acid level ANAKINRA block the receptor, interleukin 1-beta - an important inflammatory chemical (cytokine) Urate reabsorbtion blocker a direct blocker of URAT1 - transporter of uric acid from the urine back into the body Decrease uric acid level even in acid urine RDEA594 (coded drug) ANAKINRA


























![06Gout_-_Copy[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008245674_1-77a6cc1563138f1c466036163f773b56-150x150.png)

