* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Dextropropoxyphene wikipedia , lookup
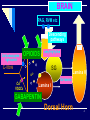
OPIOIDS - Pharmacology 1 Opioids Transmitters: Endogenous opioid peptides Enkephalins (m & d receptors) Dynorphins (κ receptors) Endorphins Actions Opioids stimulate axons of inhibitory interneurons Peripheral inflammation: Sensitivity to opioids in spinal cord is increased Peripheral neuropathic pain: Sensitivity to opioids is greatly reduced 2 Pain Modulation: Central mechanisms Gate control Aβ axons stimulate inhibitory interneuron Activity in central projection neuron is reduced Opiate-induced analgesia μ Receptor :Agonists: Morphine; Antagonist: CTAP Reduces acute pain & hyperalgesia in most models δ Receptor :Agonist: SNC80 , Antagonist: Naltrindole Reduces acute pain & hyperalgesia in inflam. pain models May have fewer side effects (Constipation, respiratory depression, physical dependence) than μ-agonists κ Receptor : Agonist: U50,488 No effect on chronic muscle pain Locations: PAGM, Ventral medulla, Dorsal horn 3 BRAIN PAG, RVM etc Descending pathways Carbamazapine, lignocaine C-fibre OPIOIDS amytriptyline Glutamate SG sP Ca2+ VDCCs Lamina V Ketamine Lamina I GABAPENTIN Dorsal Horn 4 Weak opioids Codeine Weak m agonist, methbolize to morphine (30%) Dose 30-60 mg oral q 4-6 hrs Side effects : constipation/ itching/ nausea/ vomiting Available as: TWC(15) TWC(30) Codeine (15, 30 mg) 5 Weak opioids (cont.) Tramadol Weak µ agonist Amine uptake inhibiting action:NE and serotonin Dose 50-100 mg oral q 6 hrs Anticholinergic side effects: tachycardia, nausea, vomiting,voiding difficulty, sweating Available as IR, ER (Tramal) and combination ( Ultracet® (Tramadol& paracetamol) 6 Strong Opioids agonists: morphine, pethidine,fentanyl, methadone partial agonists :-buprenorphine, pentazocine agonist-antagonist :- nalbuphine 7 Morphine Pethidine Only parenteral route in TH Bioavailability: 30-60%, to1st Faster onset, short duration (2- due part metabolism 3 hr) Immediate release: 3-4 hr No more effective than Extended release:12-24 h morphine at treating biliary or renal pain Metabolize to M6G (agonist), M3G High addictive potential (rush (neurotoxicity), may and stimulant effect) accumulate in renal failure More CNS toxicity (i.e. seizures, delirium due to norpethidine metabolite Should not be used any more 8 MST, MS Contin (10, 30, 60 mg) 9 Kapanol (20, 50, 100 mg) 10 Immediate release opioid Oral morphine solution Rama, Siriraj, Songkhla 2mg/ml -stability, convenience, dosage Fentanyl lollipop Fentanyl buccal tablet 11 Methadone Cheap and available for opioid maintenance Racemic of L and R –isoform, theoretically support NMDA and mu-receptor mechanism Variable half life, extended with long term use Use as third line, for switching in refractory case Start at lower dose, then slowly titrate Study recommends to switch from morphine to methadone in 3-day (one third reduction and substitution with equianalgesic dose (4 to 1- 6 to 1 ratio), followed by a one week titration Fredheim OM, Eur J Pain. 2007 ;11:599-604. 12 Narcotic Type 2 13 Transdermal narcotics Fentanyl TTS ( Durogesic®/ D-Trans® ) •12, 25, 50, 100 µgm/patch •onset : 6-12 hrs, change patch q 3 days •Should not use for acute pain due to delay onset •Indications Terminal cancer pts. who are not able to eat Cancer of the head and neck region Pts. who develop severe side effects of oral narcotics Pts. who consume very high dose oral narcotics 14 15 16 Opioid Therapy and Chemical Dependency • Risk of addiction: Evolving view Acute pain: Very unlikely Cancer pain: Very unlikely Chronic noncancer pain: Surveys of patients without abuse or psychopathology show rare addiction Surveys that include patients with abuse or psychopathology show mixed results 17 Opioid Therapy: Drug Selection • Immediate-release preparations Used mainly For acute pain For dose finding during initial treatment of chronic pain For “rescue” dosing Can be used for long-term management in select patients 18 Opioid Therapy: Drug Selection Immediate-release preparations Combination products Acetaminophen, aspirin, or ibuprofen combined with codeine, hydrocodone, dihydrocodeine Single-entity drugs, eg, morphine Tramadol 19 Opioid Therapy: Drug Selection Extended-release preparations Preferred because of improved treatment adherence and the likelihood of reduced risk in those with addictive disease Morphine, oxycodone, fentanyl, hydromorphone, codeine, tramadol, buprenorphine Adjust dose q 2–3 d 20 Opioid Therapy: Drug Selection Role of methadone Another useful long-acting drug Unique pharmacology when commercially available as the racemic mixture Potency greater than expected based on single-dose studies When used for pain: multiple daily doses, steadystate in 1 to several weeks 21 Opioid Selection: Poor Choices for Chronic Pain Meperidine Poor absorption and toxic metabolite Propoxyphene Poor efficacy and toxic metabolite Mixed agonist-antagonists (pentazocine, butorphanol, nalbuphine, dezocine) Compete with agonists withdrawal Analgesic ceiling effect 22 Opioid Therapy: Routes of Administration Oral and transdermal—preferred Oral transmucosal—available for fentanyl and used for breakthrough pain Rectal route—limited use Parenteral—SQ and IV preferred and feasible for long-term therapy Intraspinal—intrathecal generally preferred for long-term use 23 Opioid Therapy: Guidelines Consider use of a long-acting drug and a “rescue” drug—usually 5%–15% of the total daily dose Baseline dose increases: 25%–100% or equal to “rescue” dose use Increase “rescue” dose as baseline dose increases Treat side effects 24 Opioid Therapy: Side Effects Common Constipation Somnolence, mental clouding Less common Nausea Myoclonus Itch Urinary retention – Sweating – Amenorrhea – Sexual dysfunction – Headache 25 Opioid Responsiveness • Opioid dose titration over time is critical to successful opioid therapy • Goal: Increase dose until pain relief is adequate or intolerable and unmanageable side effects occur • No maximal or “correct” dose • Responsiveness of an individual patient to a specific drug cannot be determined unless dose was increased to treatment-limiting toxicity 26 Poor Opioid Responsiveness If dose escalation adverse effects Better side-effect management Pharmacologic strategy to lower opioid requirement Spinal route of administration Add nonopioid or adjuvant analgesic “Opioid rotation” Nonpharmacologic strategy to lower opioid requirement 27 Opioid Rotation Based on large intraindividual variation in response to different opioids Reduce equianalgesic dose by 25%–50% with provisos: Reduce less if pain severe Reduce more if medically frail Reduce less if same drug by different route Reduce fentanyl less Reduce methadone more: 75%–90% 28 Equianalgesic Table PO/PR (mg) Analgesic SC/IV/IM (mg) 30 Morphine 10 4–8 Hydromorphone 1.5 20 Oxycodone 20 Methadone 10 29 Acknowledgement Assoc. Professor Chutamanee Suttisisang Assoc. Professor Pongparadee Chaudakestrin Assist. Professor Penkae Ketuman Professor Anthony Dickenson 30