* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A Year in Review: Top New Drugs for 2010
Discovery and development of direct Xa inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Dydrogesterone wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct thrombin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
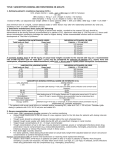
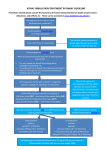
Angela Finney M.S.N., A.C.N.P.-B.C. Approximately 25 new drugs approved annually. Approvals this year include many different classes and cover a wide range of disease management. New clinical indications New routes of administration FDA website provides information about all new approvals. Actemra: RA Amturnide: Hypertension Bromday: post-op ocular inflammation Cuvposa: Chronic drooling in children Egrifta: Lipodystrophy in HIV pts. Glassia: Alpha-1 Proteinase Inhibitor Deficiency Kombiglyze XL: Type II DM Halaven: Breast Cancer Lastacaft: Allergic conjunctivitis Latuda: Schizophrenia Livalo: Dyslipidemia Moxeza: Bacterial conjunctivitis Nucynta: Analgesic Pradexa: Direct thrombin inhibitor Safyral: Oral contraceptive Tekamlo: Hypertension Teflaro: Antibiotic Tribenzor: Hypertension Victoza: GLP-1 receptor agonist for DM Vimovo: OA, RA, NSAID induced ulcer prevention Vyvanase: ADHD Xgeva: Osteolytic bone metastases solid tumors Class: Direct Thrombin Inhibitor. Indications: Prevention of stroke and Systemic emboli in non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Other indications: None at this time, in U.S. currently under investigation for DVT tx. and prevention. Intrinsic XII Extrinsic XI Injectable AT UFH Injectable LMWH AT Pentasaccharide Xa inhibitors UFH = unfractionated heparin. AT = antithrombin. DTI = Direct thrombin Inhibitor Hirsh. Chest. 2001;119:64S-94S. Tissue Factor IX VII VIII X V II Fibrinogen Fibrin Clot Oral Warfarin Oral and injectable DTIs RE-LY study established clinical efficacy. Conclusions: 1. Significantly more effective than warfarin. 2. Risk of major bleeding was significantly less. 3. Risk of hemorrhagic stroke was less. 4. All cause mortality was reduced. Dosing: 150mg BID 75mg CrCl 15-30 Not recommended < 15 Cost estimated at $230/mo. No known antidote. If necessary PRC, FFP or cryoprecipitate. PTT best estimate anticoagulation effect. Pre-op discontinuation 1-5 days and cover with Heparin/LMH. Specific instruction for conversion from warfarin to Pradaxa. ADR; dyspepsia, abd. pain, diarrhea, GI bleed. Bleeding risk: NSAIDA, other antiplatelets. Doesn’t affect P450 system. Minimal drug interactions. Avoid Rifampin, St. John’s wart. Caution with bleeding risk and contraindicated in active bleeding. Absorption: not affected by food. Achieves effective levels within 1-2 hrs, steady state in 2-3 days. Do not open, crush or chew tablets. Half life: 12-17 hrs. Excretion: primary renal. Pregnancy Category C. Breastfeeding: Unknown. Open pill container only good for 30 days. Conversion from warfarin → dabigatran Discontinue warfarin. Start dabigatran when INR < 2.0 Conversion from dabigatran → warfarin CrCl > 50 ml/min: Start warfarin 3 days prior to stopping dabigatran CrCl 31-50 ml/min: Start warfarin 2 days prior to stopping dabigatran CrCl 15-30 ml/min: Start warfarin 1 day prior to stopping dabigatran CrCl < 15 or on dialysis: no recommendations can be given **Since dabigatran contributes to INR elevation, warfarin’s effect on the INR will be better reflected after dabigatran has been stopped for ≥2 days Conversion from parenteral anticoagulants Start dabigatran at the time the next dose of the parenteral drug would be administered or at the discontinuance of a continuously administered parenteral drug (e.g. UFH) Conversion to parenteral anticoagulants CrCl ≥ 30 ml/min: Wait 12 hours after the last dose of dabigatran CrCl < 30 ml/min: Wait 24 hours after the last dose of dabigatran Invasive or surgical procedures If possible, discontinue dabigatran 1-2 days (Clcr ≥50 mL/minute) or 3-5 days (Clcr <50 mL/minute) before invasive or surgical procedures due to the risk of bleeding; consider longer times for patients undergoing major surgery, spinal puncture, or insertion of a spinal or epidural catheter or port. If surgery cannot be delayed, the risk of bleeding is elevated; weigh risk of bleeding with urgency of procedure. Bleeding risk can be assessed by the ecarin clotting time (ECT) if available; if ECT is not available, use of aPTT may provide an approximation of dabigatran’s anticoagulant activity. Class: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. Indications: treatment of primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia. Pharmacology: Block synthesis of cholesterol in the liver; inhibiting HMG-CoA, first enzyme in the cholesterol cascade. DRUG Percent LDL Reductions Dose Range Rosuvastatin 52-63% 10-40 mg Atovastatin 38-54% 10-80 mg Lovastatin 29-48% 20-80 mg Pitavastatin 31-41% 1-4 mg Pravastatin 19-40% 10-40 mg Fluvastatin 17-33% 20-80% Reference: Up to Date “Comparisons of Statins” 2011 Dosing: 1, 2, 4 mg. Start at 2 mg, increase to 4 mg after 4 weeks. Renal impairment: CrCl 30-60 1-2 mg. Precautions: Avoid with severe renal, hepatic dysfunction. Monitor warfarin. Reduce dose with erythromycin, cyclosporine. Lopid, niacin, fenofibrates increase risk of myopathy. Pregnancy category: X; presumed unsafe for lactation. Selectively distributed to liver, excreted in bile; avoids CYP450. Half life: 12 hrs. Can give anytime of day, regardless of food. Contraindicated: active liver disease, persistent transaminitis, heavy ETOH use, severe renal impairment. ADR: back pain, constipation myalgia, diarrhea. 1.Increase insulin secretion 2.Decrease glucagon secretion 3.Improve beta-cell function 4.Delays gastric emptying 5.Reduces hunger 6.Contributes to weight loss. Class: Long acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist. ( GLP-1). Incretin mimic. Indications: Adults; type II DM. Mono-therapy or combination. Not for IDDM. Pharmacology: GLP-1 stimulated pancreas increase insulin production and decrease glucagon production. Suppresses appetite, expect 6 # weight loss. Dosing: Initiate at 0.6mg SQ daily. Cost: $300/ 2 (3ml) pens, After one week increased to 1.2mg daily. Dose can be increased to 1.8mg if required. Expect 1.1% HgbA1c reduction with combo tx. Pregnancy Category C. Lactation: possibly unsafe. Half life: 13 hrs. Common ADR: nausea, vomiting, headache and diarrhea. Delays gastric emptying and may impair absorption of oral medications. May need to reduce dose of sulfonylurea to reduce risk of hypoglycemia. No studies establishing reduction of DM induced complications. Rare side effect: anti-liraglutide antibodies. Rare cases pancreatitis. Black Box Warning: risk of thyroid c-cell tumors. Contraindicated: family or personal hx of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasm Syndrome and medullary thyroid carcinoma. Combination of saxigliptin and metformin XR Onglyza: DDP-4 inhibitor Indications: Type II DM; adults Dosing: 5/500 mg. 2.5/1000 mg. 5/1000 mg. Once a day dosing with evening meal Confirm renal function before starting CrCl < 50: 2.5/500mg daily. Pregnancy Category B. Lactation: possibly unsafe Metabolism: extensive liver Risk for lactic acidosis. Cost: $110/mo. Class: 5th generation cephalosporin; broad spectrum. Indications: acute bacterial skin infections and CAP in adults >18 yrs. Effective in gram neg. and multi-drug resistant gram positive organism. Limited use in ICU; no pseudomonas, enterococcus, or actinetobacter coverage. Spectrum of Activity CAP SS Strep pneumoniae MSSA Klebsiella pneumoniae MRSA H-influenza Strep pyogenes E-coli Strep agalactiae K-octoca E-coli MSSA Reference: Pharmacist Letter Dosing: 600mg q. 12 hr IV over 1 hr. SSSI infections 5-14 days. CAP infections 5-7 days. Renal impairment: > 50 CrCl No adjustment > 30 < 50 400mg q. 12 hr. 15 - 30 300mg q. 12 hr. < 15/hemodialysis 200mg q. 12 h.r Pregnancy Category: B. Lactation: unknown. Metabolism: hydrolysis. No effect CYP450. Excretion: renal. Half life: 2.6 hrs. Microbiological cure rate 96%. No significant drug interactions. Most common ADR: diarrhea, nausea, rash. Indications: Moderate to severe acute pain. Class: Mu-opioid agonist. (Schedule II), Pharmacology: centrally acting analgesic; dual mode of action. Agonist of the u-opioid receptor & norepinephrine re-uptake inhibitor. Dosing 50-100mg every 4-6 hours. Maximum daily dose 700mg day one, 600mg/day subsequent day. Available in 50, 75, 100mg tabs. No renal adjustment in mild to moderate renal disease. Moderate hepatic disease: dose at 50mg q. 8 hrs. ADR: Dizziness, somnolence, nausea, vomiting, fatigue. Precautions: CNS & respiratory depression, head injury, liver impairment, seizure disorder. Contraindicated: Impaired pulmonary function. Drug interactions: Avoid with SSRI, SSNI, MAO inhibitors due to risk for serotonin syndrome. Primarily metabolized by liver including first pass metabolism. Half life 4 hrs. Primarily excreted in urine. Pregnancy Category: C Lactation: probably unsafe. Class: Non-opioid pain reliever; intravenous form of acetaminophen. Indications: Mild to moderate pain. Fever reduction. IV route reduces liver exposure by ½. Not for use in children under 2 yrs. Studies evaluating opioid sparing effects in post-op pts. Dosing similar to oral. Tribenzor Amturnide Tekamlo Twynsta Combination of olmesartan, amlodipine, HCTZ. Indications: Failed dual treatment. Dosing: 20/5/12.5 40/5/12.5 40/5/25 40/10/25 Cost: $135/mo. Combination of aliskiren, amlodipine, HCTZ Dosing: 150/5/12.5 mg. 300/5/12.5 mg. 300/5/25 mg. Costs: $105/mo Aliskiren and amlodipine combination Available dosing: 150/5 mg. 150/10 mg. 300/5 mg. 300/10mg. Cost: $130/mo. Telmisartan and amlodipine combination Available dosing: 40/10 mg. 80/5 mg. 80/10 mg. Cost: $165/mo Dulera®: mometasone/formoterol Available in 100mcg/5mcg & 200/5mcg Vimovo®: Naproxen/esomeprazole Available in 375/20mg or 500/20mg. Jalyn®: Dutasteride/tamsulosin Antithrombotic Therapy to Prevent Embolization in Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation. Up to Date. 2011. www.uptodate.com.. DeFronza, Ralph, et al. The efficacy and safety of Ssxagliptin when added to metformin therapy in patients with uncontrolled Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. http://www.diabetesjournals.org/content/32/9/1649.long Drusanom George. Pharmocodynamics of ceftaroline fosamil for complicated skin and skin structure infections. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy: Volume 65; pg. 33-39. Gotto, A., Moon. J. Pitavastatin for the treatment of primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia. Expert Reviewed Cardiovascular Therapy. Aug. 2010: 8 (8) 1079-90. Hatrick,C., Van Hove, I Efficacy and Tolerability of Tapentadol and oxycodone in patients awaiting primary joint replacement. Clinical Therapy. Feb. 2009: 31 (2) 260-71. Nucynta Package Insert. June 2010. PriCare. Pradaxa Package Insert. April 2010. Boehringer Ingelheim. Unger, Jeff. Clinical Efficacy of GLP-1 Agonist and their place in the diabetes treatment algorithm. Journal of American Osteopathic Association. Feb 2011: 111 (2) 2-9. Victoza Package Insert. Jan 2010. Novo Nordisk.