* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Four Phases of the Business Cycle
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
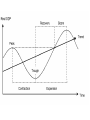
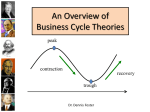
Four Phases of Business Cycle Business Cycle (or Trade Cycle) is divided into the following four phases Prosperity Phase : Expansion or Boom or Upswing of economy. Recession Phase : from prosperity to recession (upper turning point). Depression Phase : Contraction or Downswing of economy. Recovery Phase : from depression to prosperity (lower turning Point). Peak—A high point at which the economy is at its strongest and most prosperous. Trough—The final stage in the business cycle; demand, production, and employment reach their lowest levels. Prosperity phase • Prosperity phase - expansion of output, income, employment, prices and profits, there is also a rise in the standard of living - full employment of resources - high level of economic activity, it causes a rise in prices and profit - Boom Period. • The features of prosperity are: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 High level of output and trade. High level of effective demand. High level of income and employment. Rising interest rates. Inflation. Large expansion of bank credit. Overall business optimism. Recession Phase • Recession Phase - turning point from prosperity to depression • economic activities slow down • when demand starts falling, the overproduction and future investment plans are also given up • steady decline in the output, income, employment, prices and profit • businessmen lose confidence and become pessimistic (Negative) • reduces investment • expansion of business stops, stock market falls • orders are canceled and people start losing their jobs • increase in unemployment causes a sharp decline in income and aggregate demand. • Generally, recession lasts for a short period. Depression Phase • Depression Phase - a continuous decrease of output, income, employment, prices and profits, there is a fall in the standard of living and depression sets in. • The features of depression are : 1 Fall in volume of output and trade. 2 Fall in income and rise in unemployment. 3 Decline in consumption and demand. 4 Fall in interest rate. 5 Deflation. 6 Contraction of bank credit. 7 Overall business pessimism. Recovery Phase turning point from depression to expansion expansions and rise in economic activities demand starts rising, production increases and this causes an increase in investment steady rise in output, income, employment, prices and profits revival slowly emerges into prosperity, and the business cycle is repeated. Influences on business cycle • Business investment—High levels promote expansion; low levels contribute to contractions. • Money and credit—When interest rates are low, businesses and individuals generally borrow more money.(Converse is also true). • Public Expectations—If consumers think economy is heading toward recession, then they will limit their spending. Influences on business cycle • External Factors—World economic and political climate affect the business cycle in the U.S. – High oil prices of 1973, 1984, 2007. – War affects the business cycle.