* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Investment Demand
Fund governance wikipedia , lookup
Corporate venture capital wikipedia , lookup
Negative gearing wikipedia , lookup
Foreign direct investment in Iran wikipedia , lookup
Private money investing wikipedia , lookup
Interbank lending market wikipedia , lookup
Socially responsible investing wikipedia , lookup
Internal rate of return wikipedia , lookup
Early history of private equity wikipedia , lookup
Investor-state dispute settlement wikipedia , lookup
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
International investment agreement wikipedia , lookup
Environmental, social and corporate governance wikipedia , lookup
Investment banking wikipedia , lookup
History of investment banking in the United States wikipedia , lookup
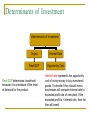
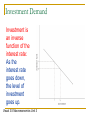
Investment Demand: Determinants of Investment AP Macroeconomics Review The Multiplier shows the total change in aggregate output (real GDP) due to/caused by an autonomous change in spending. 1/(1-MPC) Where are we going? In this lesson, you’ll learn about the determinants of investment, or spending by businesses to replace or increase the capital stock Investment spending in the US changes dramatically from year to year Keynes referred to this variability as “animal spirits of business” What is investment? To the economist, investment is spending on plant and equipment: the machinery and buildings that a firm uses to produce output. What is it not? Investment is not the purchase of stocks or bonds. It is the actual investment in the physical structure or equipment. Determinants of Investment Determinants of Investment Output Interest Rate Real GDP Opportunity Cost Real GDP determines investment because it is a measure of the level of demand for the product. Interest rate represents the opportunity cost of using money to buy investment goods. To decide if they should invest, businesses will compare interest rate to expected profit rate of new plant. If the expected profit is > interest rate, then the firm will invest. How to invest… In order to make an investment, business can do a few things: Use profits Use retained earnings Borrow Therefore, as interest rates go down, more investment opportunities will be available and firms will invest more! Investment Demand Investment is an inverse function of the interest rate: As the interest rate goes down, the level of investment goes up. Visual 3.5 Macroeconomics Unit 3 Increase in Investment This is what happens if businesses decide to spend more on investment goods – output, and therefore Real GDP, rises. Note: This is the multiplier process at work… Visual 3.4 Macroeconomics Unit 3 Upward shift in Keynesian model as interest rate goes down… But by how much will investment increase as the interest rate decreases? This sounds like a job for… Elasticity! Different Elasticities of Demand How much investment will increase as the interest rate decreases is dependent on elasticity of the investment function. Two investment functions: IA and IB. IA is more elastic than IB. Thus, the same decrease in the interest rate from r to r1 will result in two different levels of investment, I1 and I2. Visual 3.6 Macroeconomics Unit 3 And now… Some resources: http://www.reffonomics.com Works Cited Economics of Seinfeld. http://yadayadayadaecon.com/concept/ Krugman, Paul, and Robin Wells. Krugman’s Economics for AP. New York: Worth Publishers. Morton, John S. and Rae Jean B. Goodman. Advanced Placement Economics: Teacher Resource Manual. 3rd ed. New York: National Council on Economic Education, 2003. Print. Reffonomics. www.reffonomics.com.