* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 18
Development theory wikipedia , lookup
Currency war wikipedia , lookup
Financialization wikipedia , lookup
Heckscher–Ohlin model wikipedia , lookup
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
International monetary systems wikipedia , lookup
Economic globalization wikipedia , lookup
Internationalization wikipedia , lookup
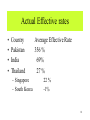
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
Exchange rate wikipedia , lookup
Fear of floating wikipedia , lookup
Lecture 18 Don DeVoretz Trade as an “Engine of Growth’ Some Best and Worst Practices? 1 Case for Free Trade • Empirical Evidence: 1990’s to present – China: trade related growth has reduced poverty – Asian Tigers, Trade as an “Engine of Growth” – India, Brazil and Russian • Trade, FDI plus Domestic markets 2 Case Against Free Trade • Empirical Evidence: Con 1990’s to present – Mexico: • NAFTA and collapse of Peso • Emigration and destabilization – Argentina: • Dollarized economy • Emigration and destabilization – Asian Tigers • Capital Flight and collapse of economies 3 Overvalued Exchange Rates • Why have most LDCs opted for Overvalued Exchange Rate ? – Overvalued exchange rates reduce price of Ms • hope to get capital goods cheaper • However, luxury items also cheaper – Consequence DUAL EXCHANGE RATES • Argentina : two exchange rates: – overvalued for capital goods – undervalued for consumer goods • Eventual devaluation 4 Some Indicators of Trouble • Balance of Trade – Income and Price terms of Trade • Balance of Payments – – – – Capital Flight Direction of FDI Size of remittances Aid 5 Strategy I: Devaluation • What are consequences of a 10% devaluation ? • • • • 1. real wages fall by 5% 2. GDP falls by 1 to 4 % 3. inflation 1 to 10% 4. need 15 % rise in foreign aid to most countries to offset effects of devaluation ? 6 Corruption and Overvaluation 7 Foreign Aid:Facts • 1960 to present : a. $1.6 trillion in foreign Aid b. 40 % of developing world gets about twice the aid as poorest. • 2. ODA from OECD has actually increased in early 1980s by .5% per annum. • 3. Case for Aid is close foreign exchange gap 8 Strategy II: Debt Repayment • Buy-back debt: – issue new Bonds to pay for old bonds which are at 40 % of ace value. a. at what price? – is it wise for LDCs to simply buy back debt ? 9 Strategy III: Political Struggles • Lobby DCs to a. lower effective rates of protection in DCs b. or supply special funds from IMF or multi-lateral banks c. debt forgiveness • Loans from IMF and others on concessionary terms 10 Strategy IV: Restructuring ? • Inward-looking commercial policies ? • Ingredients: • Low effective rate of protection – Nominal rate T= !(p’-p)/p! where p’ and p are unit prices with and without tariffs – Effective rate G=[(v’-v)/v](100) where v’ and v are value added with and without tariffs. – Effective rate can be positive or negative 11 Actual Effective rates • • • • Country Pakistan India Thailand – Singapore – South Korea Average Effective Rate 356 % 69% 27 % 22 % -1% 12 Perverse Effects of Effective Tariffs by Type of Good • Developing countries have - high effective rates on final goods - low effective rates on intermediate and capital goods – Implications: – backward linkages can not develop – no development of a capital-goods industries using labour intensive techniques 13 Arguments For Tariff Protection • • • • Tariff duties are major source of revenue Import restrictions rebalance payments Reduce economic dependence Encourage foreign firms to come behind tariff wall - How have these arguments panned out in history ? 14 Outward-looking Policies • • • • • Zero effective rates No quantity restrictions Convertible currencies Fluctuating exchange rates Membership in WTO: play by the rules ? 15 Trade Optimists • • • • • • Produces competition Increases efficiency, technical change Attracts foreign capital Generates foreign ex for food Ends rent-seeking and corruption Equal access to resources 16 Trade Pessimists • High effective rates in developed countries • Mfg. is oligopolistic • Low income elasticity of demand for LDC products • LDC exports grow slowly • LDC terms of trade declining 17 End of Show 18