* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
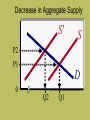
Chapter 11 Business Cycles These slides supplement the textbook, but should not replace reading the textbook What are the four phases of the business cycle? • Peak • Recession • Trough • Recovery 2 What causes unemployment? Excessive inventories 3 What causes inflation? MV/Q = P 4 What causes stagflation? A move to the left of the aggregate supply curve 5 Decrease in Aggregate Supply S' S P2 P1 D 0 Q2 Q1 6 What can cause a shift to the left of the aggregate supply curve? An increase in costs 7 What can cause an increase in costs? 8 • Monetizing the debt • > in the price of oil • > in public union benefits • Detailed laws • Emphasis on green technology • Unfunded liabilities • Interest on national debt • Taxes • Tariffs • Health care 9 What can cause deflation? 10 • Quantitative easing low interest rates • High corporate taxes • Double taxation on money earned in foreign countries • Interest earned on reserves held at the Fed • Large fines paid to Treasury by big banks • Interest on national debt • Expectation of lower prices • Lengthy and detailed laws 11 What was the Employment Act of 1946? Mandated the government to: 1) Balance the budget 2) Favorable balance of payments 3) Full employment 4) Coordinate monetary and fiscal policies 12 What is Keynesian Economics? If we can manage demand we can manage the economy 13 What did the 1970s teach us? A move to the left of the aggregate supply curve can only be solved by supply side remedies 14 What is the largest component of GDP? Consumption 15 What is investment? The purchase of new plants, equipment, buildings, and net additions to inventories 16 What is the acceleration principle? An increase in spending can lead to induced investments 17 Why is the investment sector so unstable? • Expectations can change • Inconsistent accelerator • A change in the rate of growth determines swings • Govt. policies can cause economic bubbles 18 What are pro-cyclical government polices? Policies that can accentuate the swings of the business cycle because of lag effects and emphasis of anti-growth policies 19 What is the Helmsman Dilemma? Brought on by the lag effects of discretionary fiscal policies 20 What is the Financial Stability Oversight Council? As part of the Financial Reform Bill of 2010 (DoddFrank Bill) the council decides which nonbank financial institutions might cause instability in the U.S. financial system 21 What is the significance of the FSOC? All banks with assets of more than $50 billion and any other financial businesses deemed large enough will be regulated by the Fed and protected with promise of bailouts if they get into financial trouble 22 What past examples of government protecting big business? • Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac • Bail out of banks in 2008-09 • General Motors and Chrysler 23 What affect does the foreign sector have on the economy? Can be pro-cyclical or counter-cyclical 24 How do we compare real GDP as a percent from year to year? We take the percent increase from year to year and compare 25 What is the percent increase as we go from 3 to 5? 2 / 3 = 67% 26 What is the percent decrease as we go from 5 to 3? 2 / 5 = 40% 27 What is the circular flow of income and expenditures? A model that shows the income and expenditures in the economy 28 What are leakages? Any diversion of money from the domestic spending stream 29 What are examples of leakages? Saving taxes imports 30 What are injections? Any payment of money into the economic stream 31 What are examples of injections? Investment government purchases transfer payments exports 32 At what point is equilibrium reached in the circular flow model? Where planned leakages equal planned injections 33 What are two examples of equilibrium in the circular flow of money? Internal - banks External – foreign exchange market 34 What happens when planned borrowing is greater than planned saving? Interest rates rise 35 What happens when planned saving is greater than planned borrowing? Interest rates fall 36 What happens when a country has a payments surplus? Its currency appreciates 37 What happens when a country has a payments deficit? Its currency depreciates 38 END