* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
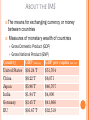
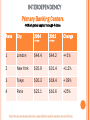
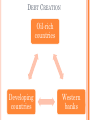
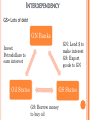
THE INTERNATIONAL MONETARY SYSTEM THE INTERNATIONAL MONETARY SYSTEM 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. About the IMS Brief History High Level of Interdependence Advantages of GN IMS Issues ABOUT THE IMS ABOUT THE IMS The means for exchanging currency or money between countries Measures of monetary wealth of countries Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Gross National Product (GNP) Country GDP (IMF 2012) GDP per capita (IMF 2012 United States $16.24 T China $8.22 T Japan $5.96 T $51,704 $6,071 $46,707 India Germany EU $4,000 $41,866 $32,518 $1.84 T $3.45 T $16.67 T ABOUT THE IMS Big Mac Index About it Tracks inflation Over/undervalued currency Shows purchasing power ¤ ABOUT THE IMS Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) Compares buying power from market to market GN currencies = more buying power Country Price Currency Exchange Rate U.S. Wooden baseball bat US $40 US $1 buys 10 MXN $ Mexico Wooden baseball bat MXN $15 US$ buys 2 2/3 bats in Mexico Effect: 1) Exchange US $ for MSX $, go to Mexico Peso increases in value relative to dollar 2) US demand drops; MX demand increases US price drops; MX price increases 3) Market should adjust over time ¤ Lose incentive to cross border ABOUT THE IMS About currency adjustments Devaluing a currency Strengthening it Buying up currency so less is in circulation Imports less expensive Exports less appealing Redenomination of a currency ¤ Intentionally make it weaker Imports more expensive Exports more appealing Russian 1998- ruble revalued ABOUT THE IMS Currency adjustment effects Weak yen= expensive luxury brands in Japan Weak euro= more investment in non-euros Denmark, Switzerland drop interest rates below 0% Strong Swiss franc = higher interest payments ¤ “Hermes Warned of Lower Profits under Abenomics” Mortgage borrowers in Poland suffer BRIEF HISTORY BASIS FOR MODERN SYSTEM European exploration, colonization British domination Gold Standard Gresham’s Law Clipping, altered alloy content Bad $ drives out good Significance Set equivalence Established fixed exchange rates •Provided stability Post-WWII-US ¤ hegemony POST WWII Why did the US assume hegemony after WWII? Democracy Trade partners Allies ¤ POST WWII How did the US promote economic hegemony? US Central banker Gold standard 1840 to ~WWI based on £ 1944 on $ •US$35=1 oz. gold Foreign Aid: IGOs, Bilateral Marshall Plan, Truman Plan, IBRD Rebuild WE and Japan; secure Turkey & Greece Military Aid Investment through MNCs ¤ END OF US GOLD STANDARD Why did the system end? US as central banker = Big strain Lots of US dollars held outside of US Large investment outflows by MNCs Declining exports Rising oil prices, cartel Vietnam War US civil rights movement New competition Japan, Germany = Nixon delinks $ Fixed to floating exchange rate ¤ END OF US GOLD STANDARD Effects Floating exchange rate system Hard on GS ¤ Peg to major currency Belize, Venezuela, Saudi Arabia-USD Former African colonies-euro •Morocco, Ivory Coast, Cameroon END OF US GOLD STANDARD Effects (cont.) o Adopt foreign currency Ecuador, Panama-USD European microstates euro o Accept/trade in foreign currencies ATM – Cambodia ¤ http://www.phnompenhpost.com/business/acleda-ups-security-measures END OF US GOLD STANDARD What is Zimbabwe’s situation? 100 T dollars- couldn’t buy bread Adopted $ in 2009 Use rands, dollars, pounds Problems Can’t print currency Coin shortage Affects SA Ecuador- mints centavos ¤ PEGGING CURRENCIES Post- Bretton Woods, common Benefits Stability Ties Ex-pats Common language Familial ties with émigrés Problems ¤ Former Caribbean, African colonies to Europeans LA to US Float at market rates If dollar, yen, euro, etc., too strong, need to adjust Domestic issues- can’t hold peg IMS INTERDEPENDENCY INTERDEPENDENCY Global Currency Flows Most traded currency? U.S. dollar- 81.01% of world’s trade http://www.reuters.com/article/2013/12/03/us-markets-offshore-yuan-idUSBRE9B204020131203?feedType=RSS&feedName=businessNews Second most traded currency? Yuan/remnimbi at 8.66% Global currency exchange http://www.economist.com/news/economic-and-financial-indicators/21586351-global-foreign-exchange-turnover INTERDEPENDENCY Primary Banking Centers -60% of global capital through 4 cities Rank City 2014 2013 In Billions In Billions Change 1 London $44.4 $44.2 +<1% 2 New York $35.9 $31.4 +1.2% 3 Tokyo $30.3 $18.4 + 39% 4 Paris $22.1 $16.6 +25% http://www.joneslanglasallesites.com/gcf/global-capital-markets-research/cities INTERDEPENDENCY How the GS became indebted ¤ Post WWII- colonies gained independence Reliance on primary resources Cash crops Raw materials Desire to industrialize Needed to borrow $ DEBT CREATION Oil-rich countries Developing countries Western banks INTERDEPENDENCY GS= Lots of debt GN Banks GN: Lend $ to make interest GS: Export goods to GN Invest Petrodollars to earn interest Oil States GS States GS: Borrow money to buy oil INTERDEPENDENCY Economic crisis in one country contagion Where Next it all began Great Depression 1929 - Mexico, 1982 Why couldn’t Mexico declare bankruptcy? Followed later by… Crisis Year Mexico “Tequila Crisis” 1994 “Asian Flu” Crisis 1997 Russian “Ruble Crisis” 1998 Argentina 2001, 2014 Global Recession (US, EU) 2008 Eurozone 2010 GN ADVANTAGES HISTORICAL ADVANTAGES Industrial Revolution Colonization & Imperialism Colonies = Resource suppliers GS become indebted Creation of Institutions (post WWII) ¤ CREATED INSTITUTIONS International Monetary Fund (IMF) Bretton Woods Agreement (1944) Purpose: Monetary stability Short-term crises GN dominance Choose Chief- Christine Lagarde Voting advantage Austerity plans ¤ Structural Adjustment Plans (SAPs) CREATED INSTITUTIONS International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) Also Bretton Woods (1944) Present-day World Bank Group (WB) Purpose: Rebuild Europe, promote growth GN policy dominance ¤ President- GN- Jim Yong Kim CREATED INSTITUTIONS European Coal & Steel Community (ECSC) Regional IGO (1951) of 6 states Purpose: Reduce tariffs Present-day EU- now 28 Western Europe dominance Significance to IMS Eurozone- 19 members Common currency ¤ http://www.economist.com/blogs/graphicdetail/2015/02/european-economy-guide CREATED INSTITUTIONS Group of Five (G-5) (1985) Purpose: Coordinate monetary policy US, UK, France, Germany, Japan Added Italy, Canada= G-7 Added Russia = G-8 Deleted Russia = G-7 (blame Putin) G-20 (1999) Sort of replaced G-8 (2009) Include EEs GDP (85%) Trade (80%) Population (66%) G-7 still active ¤ kkk IMS ISSUES: INFLATION Disparity between the value of a good/service and its cost Means less purchasing power Determined by consumer price index Looks at changes over time Need to find balance Raise interest rates to curb inflation Effect- help lower consumer prices More people save, fewer spend, prices drop Drop interest rates to encourage inflation Advantage= encourage spending to stimulate economy ¤ IMS ISSUES: EUROZONE CRISIS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What caused the Eurozone crisis? (video, news) What problems did the ECB encounter? What was Greece’s situation? How did the crisis in Greece cause a contagion? Why was Germany unscathed by the crisis? IMS ISSUES: EUROZONE CRISIS 1. What caused the Eurozone crisis? Long-term Short-term ¤ Structural problems Lack of competitiveness Bloated public sectors Lack of political and economic coordination Global recession EU banks took a hit, reduced lending Effect: reduced consumption, investment Sovereign debt crisis IMS ISSUES: EUROZONE CRISIS 2. What problems did the ECB encounter? Gov’ts had to borrow $ to bail out their banks, stimulate economies Too much government spending Higher unemployment Lower business profits Fewer tax revenues Set up permanent bailout fund (2011) European Stability Mechanism €500 B ¤ IMS ISSUES: EUROZONE CRISIS 3. What was Greece’s situation? High public debt Too much gov’t spending (high debt-to-GDP ratio) Couldn’t borrow $ Interest rates increased on borrowing Higher risk demands higher interest rates Subject to IMF, EU (ECB) austerity (SAP) policies Led to protests Gov’t fell ¤ IMS ISSUES: EUROZONE CRISIS 4. How did the crisis in Greece cause a contagion? Italy, Spain, Portugal, Ireland Loans at higher interest rates Forced to accept SAP terms for bailouts* Reduce budget deficits Public debt Private debt Lack of competitiveness Higher inflation rates Ignored Eurozone spending rules Deficits, debt level Led to ‘fiscal pact’ between most EU countries Rules agreed upon re: budget deficits ¤ *Situations/terms varied by country IMS ISSUES: EUROZONE CRISIS 5. Why was Germany unscathed by the crisis? Already reformed risky policies, improved competitiveness World’s second largest exporter by value and volume Within EU Outside EU ¤ Respectable products with same currency Borrowed money to buy goods Euro value decreased, made goods cheaper Drop in unemployment rates IMS ISSUES: EUROZONE EXPANSION 1. What issues did Latvians encounter when transitioning to the euro? Felt change was anti-nationalist Why would Latvia want to join the Eurozone, considering the crisis? 2. ¤ Easier to do business with other euro countries Avoid fees for exchanging lats into euros Want link to Western Europe (v. Russia) Small economy—likely to benefit from integration THE SPICE TRADE IMS ISSUES: PRICES & STABILITY 1. 2. 3. 4. How did the spice trade lead Europe into global monetary dominance? Why is reliance on cash crops so risky? What are the pros and cons of FTAs for farmers? Why did Vietnam enter pepper production? What global effect did this have? IMS ISSUES: PRICES & STABILITY 1. How did the spice trade lead Europe into global monetary dominance? Used to rely on commodities as ‘cash’ • Spices, metals, shells, etc. Colonization • Cash crops Trade Currency system ¤ Pieces of eight Gold Standard IMS ISSUES: PRICES & STABILITY 2. Why is reliance on cash crops so risky? Economies not diversified Large % dependent on cash crop income Currency speculation ¤ Affects purchasing power, prices of exports/imports Investment recovery not guaranteed Debt cycle IMS ISSUES: PRICES & STABILITY 2. Why is reliance on cash crops so risky? (cont.) Price volatility Vulnerable to weather, disasters Competition Lack insurance ¤ Effects of FTAs, new producers IMS ISSUES: PRICES & STABILITY 3. What are the pros and cons of FTAs for farmers? Competition • Domestic, foreign, new ¤ Cheaper, better quality goods Greater market access Limited options if can’t compete IMS ISSUES: PRICES & STABILITY 4. Why did Vietnam enter pepper production? Less pepper competition Better profits than current crops Less land, fewer inputs What global effect did this have? Greater supply = lower prices More competition for Indian farmers Earn less from lower world prices ¤ SPICE TRADE: RECAP Colonization; neocolonialism Established IMS Precursor for MNCs Prices and stability ¤ Primary v. manufactured goods Currency speculation Price volatility Lack of national unity THE INTERNATIONAL MONETARY SYSTEM 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. About the IMS Brief History High level of interdependence Advantages of GN Issues in the IMS