* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Title Slide
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
E-governance wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising management wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
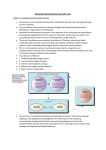
Chapter 16 Organizing for Integrated Marketing Communication Chapter Objectives • To understand how companies organize for advertising and other aspects of integrated marketing communications • To examine methods of selecting, compensating, and evaluating advertising agencies Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Chapter Objectives • To explain the role and functions of specialized marketing communications organizations • To examine various perspectives on the use of integrated services and responsibilities of advertising versus agencies Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Participants in the IMC Process • Figure 16-1 Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Participants in the IMC Process • Advertiser (Client) – Key participants in the process – Have the products, services, or causes to be marketed – Provide funds to pay for advertising/promotions • Advertising Agency – An outside firm that that specializes in the creation, production, and/or placement of the communications message Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Participants in the IMC Process • Media Organizations – Provide an environment for the firm’s marketing communications message • Specialized Marketing Communications Services – Include direct marketing agencies, sales promotion agencies, interactive agencies, and public relations firms – These organizations provides services in their areas of expertise Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC The Centralized System • Figure 16-2 Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC The Centralized System • Planning and budgeting • Administration and execution • Coordination with other departments • Coordination with outside agencies and services Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC The Decentralized System • Figure 16-3 Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC The Decentralized System • Generally occur in large corporations with multiple divisions and many different products • Separate manufacturing, research and development, sales, and marketing departments for various divisions, product lines or businesses Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC The Decentralized System • Responsibilities and functions associated with advertising and promotions are transferred to the brand manger, who works closely with the outside advertising agency and other marketing communications specialists as they develop the promotional program Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Management Issues of Advertising Agencies • Advertising Agency Decision – In-House Agency Option – Advertising Agency Option Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC In-House Agency Option • Reduces advertising and promotion costs • Can provide related work (such as sales presentations and public relations) at a lower cost than outside agencies • Increases time savings and eliminates potential problems with outside agencies Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC In-House Agency Option • Increases knowledge and understanding of the market that come from working on advertising and promotion • Companies have tighter control over the processes and can coordinate promotions with the firm’s overall marketing program Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Advertising Agency Option • Provide clients with service of highly skilled individuals who are specialists in their chosen fields • Provide objective viewpoint of the market and its business that is not subject to internal biases or limitations • Provide insight into the industry, and often the competition Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Canada’s Top 20 Marketing Communications Companies • Figure 16-5 Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Full Service Advertising Agencies • • • • • Account Services Marketing Services Creative Services Management and Finance Structure Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Full Service Agency • Figure 16-13 Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Account Services • Account services is the link between the ad agency and the client • The account executive is responsible for interpreting the advertiser’s needs to the agency Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Marketing Services • Research Department – Gather, analyze, and interpret information important in developing advertisements • Media Department – Analyzes, selects, and contracts for space or time in the media selected for the client Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Account Services • Coordinates agency efforts in planning, creating, and producing ads • Presents agency recommendations and obtains client approval Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Creative Services • Copywriters are responsible for the creation and execution of advertisements • May be involved in determining the basic appeal or theme of the campaign • The art department is responsible for how the ad looks Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Creative Services • Coordinating the creative and production processes can often be a major problem • A traffic department coordinates all phases of production to ensure all deadlines are met Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Management and Finance • Advertising agencies must be managed and perform operating functions such as accounting, human resources, etc. • Must generate new business • Bulk of an agency’s income goes to salary and benefits for employees Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Structure • Advertising agencies develop an organization structure to meet their clients needs • Most medium-size and large agencies are structured under either a departmental system or a group system Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Department System • Each agency function is set up as a separate department • Each department is called on as needed to perform its specialty • Some agencies prefer this system because it gives employees the opportunity to develop expertise in servicing a variety of accounts Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Group System • Individuals from each department work in groups to service particular accounts • Each group is headed by an account executive or supervisor • Many agencies prefer this system because employees become knowledgeable about the clients business • Provides continuity in servicing the account Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Other Types Of Agencies and Services • Creative Boutiques • Media Buying Services Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Creative Boutiques • Creative boutiques have developed in response to desires to utilize outside creative talent only • Clients may believe extra creative effort is required or its employees do not have sufficient skills • Boutiques usually perform creative functions on a fee basis Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Media Buying Services • Independent companies that specialize in the buying of media, particularly radio and television • Agencies and clients usually develop their own media strategies and hire a buying service to execute them • Media buying services have grown in recent years as clients seek alternatives to full-service agency relationships • Paid a fee or commission for their work Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Agency Compensation • Commissions from Media • Other Compensation Systems – – – – Fee Arrangement Cost-Plus Agreement Incentive-Based Compensation Percentage Charges Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Commissions from Media • Traditional method is a commission system, where the agency receives a specified commission from the media on any advertising time or space it purchases for its clients • Many advertisers have gone to a negotiated commission system: can be reduced percentage rates, variable commission rates, and commissions with minimum and maximum profit rates Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Example of Commission System Payment • Figure 16-14 Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Fee Arrangement • Fixed-Fee Method – Agency charges a monthly fee for services and credits to the client any media commissions earned • Fee-Commission Combination – Media commissions received by the agency are credited against the fee Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Cost-Plus Agreement • The client agrees to pay the agency a fee based on the costs of its work plus some agreed-on profit margin, often a percentage of total costs • Direct costs plus an allocation for overhead and a markup for profits determine the amount the agency bills the client Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Incentive-Based Compensation • The agency’s ultimate compensation level will depend on how well it meets predetermined performance goals • These goals often include objective measures such as sales, and market share • Compensation includes media commissions, fees, bonuses, or some combination Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Percentage Charges • Adding a mark up of percentage charges to various services the agency purchases from outside providers • These charges may include market research, artwork, printing, and other services • Markups range from 17.65 to 20 percent and are added to the clients overall bill Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Evaluation of Agencies • Financial Audit – Focuses on how the agency conducts its business – Designed to verify costs and expenses, personnel hours charged to an account, etc. • Qualitative Audit – Focuses on the agency’s efforts in planning, developing, and implementing the client’s advertising programs and considers the results achieved Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Gaining and Losing Clients • • • • • Poor performance or service Poor communication Unrealistic demands by the client Personality conflicts Personnel changes Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Gaining and Losing Clients • Changes in the size of the client or agency • Conflicts of interest • Changes in the client’s corporate and/or marketing strategy • Declining sales • Conflicting compensation philosophies • Changes in policies Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Sales Promotion Agencies • Independent companies that specialize in providing services needed to plan, develop, and execute a variety of sales promotion programs • Services provided by large sales promotion agencies include promotional planning, creative, research, tie-in coordination, etc. Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Public Relations Firms • Develop and implement programs to manage the organization’s publicity, image, and affairs with consumers and other relevant publics • Activities include planning the PR strategy and program, generating publicity, preparing news releases, managing crises, etc Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Direct-Response Agencies • Provide a variety of services – Database management – Direct Mail • Divided into three main departments – Account Management, Creative and Media • Direct-response agencies must solicit new business and be reviewed by existing clients Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Interactive Agencies • Specialize in the development and strategic use of various interactive marketing tools such as websites, banner ads, etc. • Range from smaller companies that specialize in website design to full-service interactive agencies that provide all necessary elements for a successful internet marketing program Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Pros of Integrated Service • Advocates of the “one-stop shop” contend that various individuals in the agencies and subsidiaries are learning to work together • More convenient for the client to coordinate all its marketing efforts through one agency • An agency with integrated marketing abilities can create a single image for the product or service and address everyone with one voice Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Cons of Integrated Service • Providers become involved in political wrangling over budgets and do not communicate with each other as they should • Agencies efforts to control all aspects of the promotional program are nothing more than an attempt to hold onto business • Synergy and economies of scale have been difficult to achieve Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Agency versus Client • Marketers and agency executives have different opinions regarding who should be in charge of the IMC process • Marketing executives say the biggest obstacle to implementing IMC is the lack of people with the perspective and skills to make it work Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC Agency versus Client • Many ad agencies are adding more resources to offer their clients a full line of services • As companies shift their promotional dollars away from media advertising to other IMC tools, agencies will explore ways to keep these monies under their roofs Chapter 16 : Organizing for IMC