* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5. Functional Groups
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
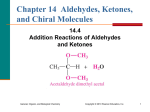
Chapter 11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Alkanes 11.5 Functional Groups General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Elements in Organic Compounds In organic molecules, C atoms form bonds mostly with H and other C atoms sometimes with atoms of O, S, N, P, and halogens F, Cl, and Br General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 2 Functional Groups Functional groups are a characteristic feature of organic molecules that behave in a predictable way are composed of an atom or group of atoms are groups that replace a H in the corresponding alkane provide a way to classify families of organic compounds General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 Some Functional Groups General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 4 Alkenes and Alkynes Alkenes contain a double bond between adjacent carbon atoms. Alkynes contain a triple bond. Aromatic compounds contain a benzene ring. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 5 Alcohols and Ethers An alcohol contains the hydroxyl (–OH) functional group. In an ether, an oxygen atom is bonded to two carbon atoms (–C–O–C–). General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 6 Thiols In a thiol, the functional group –SH is bonded to a carbon atom. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 7 Aldehydes and Ketones An aldehyde contains a carbonyl group (C=O), which is a carbon atom with a double bond to an oxygen atom, attached to at least one hydrogen. In a ketone, the carbon of the carbonyl group is attached to two other carbon atoms. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 8 Carboxylic Acids and Esters Carboxylic acids contain the carboxyl group, which is a carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group. An ester contains the carboxyl group between carbon atoms. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 9 Amines and Amides In an amine, the functional group is a nitrogen atom. In an amide, the hydroxyl group of a carboxylic acid is replaced by a nitrogen group. 10 General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Learning Check Classify each of the following as alcohol, ether, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, or amine. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 11 Solution Classify each of the following as alcohol, ether, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, or amine. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 12