* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Acids, Bases, & Salts
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
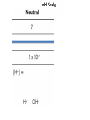
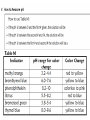
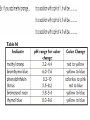
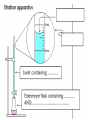
Acids, Bases, & Salts I.Acids, Bases & Salts • In water, acids produce H+ (hydrogen ions/proton) Hydrogen ions/protons can also be called hydronium ions (H3O+) How hydronium ions are formed:H+ + H2O → H3O+ Draw the electron dot structures: Common Acids: • • • • ethanoic acid (vinegar) citric acid in lemons sulfuric acid hydrochloric acid • In water, bases produce OH- (hydroxide ions) Ex: NaOH (s) → Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq) Common Bases • • • • soap sodium hydroxide ammonia aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) antacid in Maalox •A salt is an IONIC substance formed from a (+) metallic or polyatomic ion and a (-) ion (NOT hydroxide) •Ex: calcium carbonate_________ magnesium bromide_________ ammonium chloride__________ sodium chloride_____________ Draw electron dot: • Draw electron dot: • Magnesium bromide • Sodium Chloride II. Comparing/contrasting Acids and Bases Acids Bases Definitions *Arrhenius (most common) A substance that produces hydrogen (H+) or hydronium (H3O+) ions as the only positive ion in solution A substance that produces hydroxide (OH-) ions as the only negative ion in solution Alternative definition* A proton (+) DONOR A proton (+) ACCEPTOR General formula H-metal Metal-OH Properties -react with metals to produce H2 gas -react with bases to form salt and water -react with acids to form a salt and water Electrolytes!! Conduct electricity because they have moving ions Acid/base continued Acid Base Reactions acid+ metal →H2 (g) + salt Acid + base → water + salt Base + acid → water + salt pH Low (0 to 7) High (7-14) Ratio of H+ to OH- Lots of H+ or H3O+: little OH- Little H+ or H3O+ : Lots of OH- Strength Strong acid ↔ weak acid 0 to 6 Weak base ↔ strong base 8 to 14 Identifying acids, bases, salts based on the formula Acids Bases Salts Not Acids, bases, or salts These are ALCOHOLS CH3COOH – ethanoic acid HCl – hydrochloric acid H2SO4- sulfuric acid NH3- ammonia NaOH- sodium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 – calcium hydroxide NaF- sodium fluoride KCl – potassium chloride (NH4)2NO3ammonium nitrate CH3OH – methanol CH3CH2OH – ethanol CH3CH2CH2OH propanol -Have H at beginning or end of the formula -Other elements are Non metals *NH3 is an exception -Have OH at end of formula --other element metal -metal and non metal -NH4+ + nonmetal -OH end - C and H in the rest of the formula -Electrolyte -Electrolyte -Electrolyte -Do NOT conduct elec The exception to these rules: organic acids (organic means contains carbon) End In COOH Have a different set of naming rules that we will learn in Organic Chemistry Ex: CH3COOH ethanoic acid Doesn’t start with an H but it is still an acid • http://www.sasked.gov.sk.ca/branches/elearni ng/tsl/resources/subject_area/science/chem_ 30_resources/lesson_8/acids_and_bases.shtm l (acids donate H+, bases accept H+) • Strong vs. weak acid animation http://www.chembio.uoguelph.ca/educmat/c hm19104/chemtoons/chemtoons1.htm Phosphoric acid is added to soft drinks to give them a sharper flavor. It also slows the growth of molds and bacteria, which would otherwise multiply rapidly in the sugary solution. Original Tooth After 24 hours After 1 week After 1 month After 3 months Acid rain…a “bad acid” What causes it? burning fossil fuels Damages buildings plants aquatic animals Environmental Effects of Acid Rain on Lake and Stream Ecosystems ALL fish die (4.2) Healthy lake (6.5) Frog eggs, tadpoles, crayfish, and mayflies die (5.5) Rainbow trout begin to die (6.0) “Acid Buildup in Oceans Threatens Food Chain” What do a sprinter and yogurt have in common? Lactic Acid! Which of the following are bases? CH3COOH NH3 HCl HC2H3O2 Ca(OH)2 KCl NaF CH3CH2OH Do you want to see me break a penny with my bare hands? How did this happen? • Rub opposite edges of a penny made after 1984 with sandpaper to expose the zinc on the inside • Soak in hydrochloric acid • Rinse penny in sodium hydroxide solution • Rinse the penny in water • Place in ethanol (alcohol) • Let it dry and RIP! Using the equation on Reference Table T, you can solve for either the unknown molarity/ concentration (M) OR the volume (V) of base needed to neutralize an acid = molarity of H+ = volume of acid = molarity of OH– = volume of base Ex 1: A 25.0-milliliter sample of HNO3 (aq) is neutralized by 32.1 milliliters of 0.150 M KOH (aq). What is the concentration of the acid? Ex 2: How many milliliters of 0.200 M NaOH are needed to neutralize 100. mL of 0.100 M HCl?