* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Functional Groups Amines
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
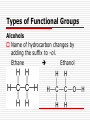
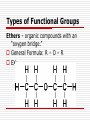
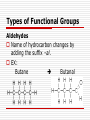
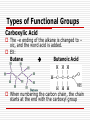
Advanced Chemistry Organic Chemistry: Functional Groups Derivatives of Hydrocarbons Halides Alcohols Ethers Aldehydes Ketones Esters Carboxylic Acids Amines Amides Functional Groups Functional Groups (FG) Atom or group of atoms that can be a substituent on a carbon chain These groups greatly modify the behavior of the hydrocarbon There are many kinds of FG – most contain different arrangements of oxygen and nitrogen Types of Functional Groups Halides – hydrocarbons plus a halogen EX: 1-chlorobutane C – C – C – C - Cl EX: 2,2-dibromopropane Br C–C–C Br Types of Functional Groups Halides Number chain so halide has lowest number If more than one halide use prefix di-, tri-, etc If more than one halide on same carbon write the # twice in the name 2,2-dibromopropane Types of Functional Groups Alcohols – hydrocarbons w/ an OH group Number so OH group gets lowest number possible General Formula: R – OH R represents the rest of the carbon chain Types of Functional Groups Alcohols Name of hydrocarbon changes by adding the suffix to –ol. Ethane Ethanol Types of Functional Groups Alcohol If more than one OH group, then use prefix indicating how many OH there are Also indicate the location of the OH groups using numbers EX: 1,1-propandiol C – C – C – OH OH Types of Functional Groups Ethers – organic compounds with an “oxygen bridge.” General Formula: R – O – R EX: Types of Functional Groups Ethers The name of the ether includes the names of the alkyl groups on each side of the oxygen and then the word ether on the end. Name alphabetically Symmetrical ethers get prefix EX: Methyl Propyl Ether C–O–C–C–C Types of Functional Groups Aldehydes – organic compounds that contain a double bonded oxygen at the terminal carbon General Formula: O R–C–H Types of Functional Groups Aldehydes Name of hydrocarbon changes by adding the suffix –al. EX: Butane Butanal Types of Functional Groups Ketone – a compound that has a double bonded oxygen attached to a carbon that is not at the end of the carbon chain. General Formula: O R1 – C – R2 Types of Functional Groups Ketones The name of the keytone is derived from the name of the alkane, the –e ending is switched to –one. For chains over four carbons, the location of the double bonded oxygen is denoted by a numerical prefix. EX: Pentane 3-Pentanone C C C Types of Functional Groups Carboxylic Acids – organic compounds that have a carboxyl group (COOH) at the end of the carbon chain. General Formula: O R–C–O–H Types of Functional Groups Carboxylic Acid The –e ending of the alkane is changed to – oic, and the word acid is added. EX: Butane Butanoic Acid When numbering the carbon chain, the chain starts at the end with the carboxyl group Types of Functional Groups Esters – organic compounds derived from carboxylic acids An ester is a carboxylic acid that replaces the –OH group with an –OR group General Formula: O R–C–O–R Types of Functional Groups Esters Name the R part of the –OR group first, followed by the name of the acid, with the –ic ending changed to ate. EX: ethanoic acid methyl ethanoate Types of Functional Groups Amines – organic compounds that have an amino group (NH2) attached somewhere on the carbon chain. General Formula (variations on NH3) R–N–H R–N–R R–N–R H Primary amine H Secondary amine H Tertiary amine Types of Functional Groups Amines The amine group is named as a substituent on the carbon chain If more than one amino group a prefix is used and a number denotes position EX: propanamine (aminopropane or propyl amine) Types of Functional Groups Amines Name primary amines as alkanamines (e.g. methanamine) There are several ways to name amines (seen below) Types of Functional Groups Amines Name secondary amines by using longest carbon chain for root name, the other chain becomes the substituent When the two alkyl groups are the same it can also be named as a dialkyl amine. EX: Diethyl amine Types of Functional Groups Amines Name tertiary amines similar to the secondary amines, the longest chain of carbons takes the root name and the other chains become a substituents located on the N When the three alkyl groups are the same it can be named as a trialkyl amine Ex: trimethyl amine Types of Functional Groups Amines In more complex molecules with multiple substituents, or ones containing higher priority functional groups, the amine is named as an amino- substituent. It is located by numbering the longest chain of carbons and locating the NH2 group by this numbering scheme EX: 3-amino-2,6-dimethyl-4-propyloctane Types of Functional Groups Amides - organic compounds derived from carboxylic acids An amide is a carboxylic acid that replaces the –OH group with an amino group General Formula: O R – C – O – NH2 Types of Functional Groups Amides When naming amides, replace the –ic with amide. EX: Ethanoic acid Ethanaminde Summary Definition of Functional Groups Types of Functional Groups