* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrition Lecture Three
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
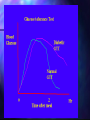
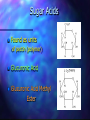
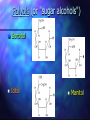
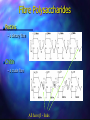
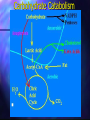
http://barry-b.tripod.com/nutl4.html Types of Carbohydrates Smallest sugar molecules Sugar alcohols Sugar acids Sugar amines Simple sugars Complex sugars polysaccharides – Polymers of simple sugars fibre Simple Sugars Monosaccharides Smallest sugars Can be absorbed without digestion Sweet tasting Can combine with others to make larger molecules: Disaccharides Polysaccharides Hexoses •Hexoses •C6H12O6 Glucose Galactose Galactose Fructose Monosaccharides •Pentoses C5H10O5 • Polymerise to form Pentosans DNA & RNA •Simple Sugars Disaccharides Maltose •Formed by joining two . monosaccharides: •Maltose •from two Glucose Lactose •Lactose •From glucose & galactose •Sucrose •From glucose & fructose Sucrose Use of Simple Sugars Sweeteners – good tasting Consistency – sauces, glazes, syrups Preservatives – Cordials, glazed fruit, dried fruit – jams, sweetened condensed milk Problems with Simple Sugars Absorbed too quickly form digestive tract. Causes the pancreas to produce excess insulin Tissues become insensitive to insulin > Type II diabetes More Problems with Simple Sugars Encourages tooth decay bacteria Empty kilojoules Not enough vitamins & minerals as needed for catabolism Takes Vitamins away from growth & repair Solutions to sugar problem Use artificial sweeteners Aspartame (nutrasweet), Saccharin, Sucralose • Some are banned in USA • Don’t have consistency Use Polyols • Not absorbed Eat more fibre • Slows rate of absorption Sweetness Of Sugars The relative sweetness power (RSP) for – five simple sugars in 5% solutions. Sugar RSP: Lactose Galactose Glucose 0.25 0.50 0.56 Sucrose 1.00 Fructose 1.30 Sugar Acids Found as units of pectin (polymer) Glucuronic Acid Glucuronic Acid Methyl Ester Sugar Amines Found as units of Polymers: chitin and in bacterial cell walls Glucosamine N-acyl glucosamine Polyols (or "sugar alcohols") Sorbitol Iditol Manitol Properties of Polyols Made from simple sugars – Functional properties – Vary in their sweetness and kilojoule density, but are non-calarigenic because they are not absorbed Polyol Sorbitol Isomalt Lactitol Mannitol % Sweetness 60% 55% 40% 65% kj/g 10.0 8.4 8.4 6.7 Complex Carbohydrates Digestible Complex CHO Indigestible Fibre a Links b Links Amylose --> straight chain Amylopectin --> Branched chain Digestible Complex Carbohydrates – All digested slower than simple sugars Starch - in plants – Amylose ( Straight chain) – Amylopectin ( Branched chain) Dextrin – Smaller fragments of starch Glycogen - in meats – branched chain Indigestible Polysaccharides (Fibre) Crude Fibre and Dietary Fibre: Insoluble and soluble fibre Crude fibre (Insoluble) – Non-starch polysaccharide (NSP): Lignin Cellulose Chitin Dietary Fibre Soluble Fibre : •Pectin •Undigested starch •Retrograded amylose b- Glucans •Inulin Inulin Polymer of Fructose found in: chicory, artichoke, dahlia , onion and garlic Fibre Polysaccharides Pectins – a dietary fibre Chitin – a crude fibre All have b - links Dietary Need For Fibre How much do we need? Digestible Carbohydrates No daily allowance has been recommended But we need a lot of it Fibre 20 to 30 gams per day Most Australians eat less than half this. Why do we need Digestible Carbohydrates? Energy – Brain, Red blood and Kidney Cells use only Glucose for energy Anaplerosis – Citric Acid Cycle intermediates are made only from sugar NADPH – Made via Direct Oxidative pathway from glucose is needed for synthesis Conversion to Pentoses – Needed for DNA and RNA Carbohydrate Catabolism