* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The peritoneum
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
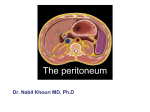
SAILENT FEATURES Peritoneum is a serous membrane that line the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and cover the organs within these cavities Parietal peritoneum -lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities Visceral peritoneum -covers the organs Peritoneal cavity -the potential space between the parietal and visceral layer of peritoneum. Function Of Peritoneum Secretes a serous fluid that continuously moistens the associated organs. Support viscera Interperitoneal viscera Relation of peritoneum in male pelvis. Omentum two-layered fold of peritoneum that extends from stomach and first part of Duodenum to adjacent organs Lessor omentum -two-layered fold of peritoneum which extends from porta hepatis (Liver) to lesser curvature of stomach and first part of duodenum Hepatogastric ligament -extends from porta hepatis to lesser curvature of stomach Hepatoduodenal ligament Extends from porta hepatis to first part of duodenum Omental foramen (Foramen of Winslow) Behind the right free margin of hepatoduodenal ligament Superiorly-caudate lobe of liver Inferiorly First part of duodenum Anterior-hepatodudenal ligament Posterior-peritoneum covering the inferior vena cava Greater omentum -four-layered fold. The anterior two layers descend from the greater curvature of stomach and First part of duodenum and hangs down like an apron turns upward and attaches to the transverse colon.. Position-situated beyond and behind the lesser omentum and stomach Mesentery-two-layered fold of peritoneum that attach part of the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall Mesentery -suspends the small intestine from the posterior abdominal wall Broad and a fan-shaped Consists of two peritoneal layers Intestinal border-folded, 6-7 m long Root of mesentery • 15 cm long • Directed obliquely from left side of L2 to in front of right sacroiliac joint Ligaments of Liver -two-layered folds of peritoneum that attached the lesser mobile solid visera to the abdominal wall Ligaments of liver Falciform ligament of liver • Consists of double peritoneal layer • Extends from anterior abdominal wall (umbilicus) to liver Coronary ligament -the area between upper and lower parts of the coronary ligament is the bare area of live, this area is devoid of peritoneum and lies in contract with the diaphragm Left and right triangular ligaments -formed by right extremity of coronary ligament and left leaf of falciform ligament, respectively Hepatogastric ligament Hepatoduodenal ligament Ligamentum teres hepatis Ligaments of stomach Hepatogastric ligament Gastrosplenic ligament Gastrophrenic ligament Gastrocolic ligament Gastropancrestic ligament Medial umbilical fold - contain the remnant of urachus (median umbilical ligaments) Medial umbilical fold - contains remnants of the umbilical arteries (medial umbilical ligaments) Lateral umbilical fold - contains the inferior epigastric vessels Pouches In male- rectovesical pouch In female • Rectouterine pouch -between rectum and uterus • Vesicouterine pouch -between bladder and uterus