* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NGEE ANN POLYTECHNIC MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
General Electric wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
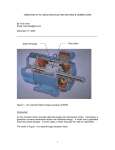
DC Machines and Drives . Books Principle Of Electrical Machines (V.K. Mehta, Rohit Mehta) Electric Machinery Fundamentals (CHAPMAN J STEPHEN) Electrical Technology Volume II (B.L.Theraja) Basic Concepts Lecture # 01 Basic Quantities and Definitions Energy? Types of Energy? Conversation of Energy What is electricity /electrical Energy? - flow of electric charge. Charge . (atom, Electrons Protons, Neutrons) 1- Current 2- Voltage 3-Resistance Electric Machines “Electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy is called motor ” while “A device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy is called generator” We need electric machines in almost every field of our life today. From transportation to construction. Cars, Clocks, Drills, Fans, Fridges, Vacuum Cleaners, Water pumps, Washing Machines, Computers, Lifts, lathes, robots etc. Machines are categorized or classified on the basis of input supply, construction and operation principles. Input supply ? In electrical system there are two kinds of supply systems means power source are provided. 1. AC system. 2. DC system. Alternating Current (AC). An electric current that reverses direction sinusoidally. Concept of phases and frequency. Direct Current (DC). Current flow is unidirectional and of constant magnitude . Negative and positive terminals (battery, cells) Type of Electric Machines Classification of Machines Electric machines Alternating Current (AC) Machines Synchronous Induction Single-Phase Three-Phase Direct Current (DC) Machines Separately Excited Series Self Excited Compound Shunt Construction and working of Electric machines An electric motor consists of many parts. Stator : The stationary part of an electric motor is called the stator. The stator will be provided with permanent magnets or windings. Rotor: The rotor is the part that actually converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The rotor is connected to the mechanical load through the shaft. These come in various designs. For Example if we are talking about Induction or asynchronous motor, (a) Squirrel cage rotor, (b) Slip ring rotor or wound rotor or phase wound rotor. Or if we are talking about synchronous motors (a) Salient pole (100 to 1500rpm.) (b) non salient pole(>1500rpm). Field windings: conductors used to produce electromagnetic field. Armature windings: conductors in which output voltage is produced (or input is provided) Electromagnetic Induction It is the fundamental operating principle of transformers, inductors, and many types of electrical motors, generators and solenoids. Faraday (1831): An emf is induced in a conductor if a magnetic field passes by a conductor Whenever in a conductor if change in current occurs it "induces”a voltage (electromotive force) in both the conductor itself (self-inductance) and in any nearby conductors (mutual inductance). Electromagnetic Induction • Magnitude of induced current can be increased by: – Increasing strength of magnetic field – Increasing speed of relative motion – Positioning of field & conductor to increase number of magnetic lines of flux cut • Magnetic field usually produced by electromagnet How motors work • Electricity supplied to stator • Magnetic field generated that moves around rotor • Current induced in rotor • Rotor produces second magnetic field that opposes stator magnetic field Electromagnetics • Rotor begins to rotate Rotor Stator Overview of Direct Current Machines Direct-current (DC) machines are divided into dc generators and dc motors. Most DC machines are similar to AC machines: i.e. they have AC voltages and current within them. DC machines have DC outputs just because they have a mechanism converting AC voltages to DC voltages at their terminals. This mechanism is called a commutator; therefore, DC machines are also called commutating machines. DC generators are not as common as they used to be, because direct current, when required, is mainly produced by electronic rectifiers. While dc motors are widely used, such automobile, aircraft, and portable electronics, in speed control applications…