* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Rotary encoder wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Dynamometer wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
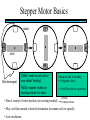
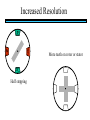
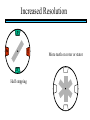
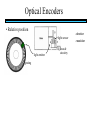
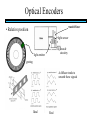
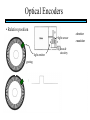
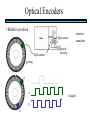
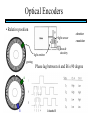
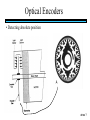
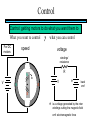
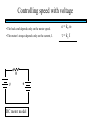
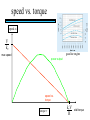
STEPPER MOTORS Name Designation Department Subject code : Mr.R.Anandaraj : Associate . Professor : Electrical and Electronics Engineering :EC 6252 Year Unit : II ECE A & B : IV Stepper Motor Basics stator N S N S S rotor N Stator: made out of coils of Electromagnet wire called “winding” Current switch in winding ==>Magnetic force Rotor: magnet rotates on ==>hold the rotor in a position bearings inside the stator • Direct control of rotor position (no sensing needed) printers computer drives • May oscillate around a desired orientation (resonance at low speeds) • Low resolution Increased Resolution S torque N S N Half stepping angle Increased Resolution S N S N Half stepping More teeth on rotor or stator Increased Resolution S N S N Half stepping More teeth on rotor or stator How to Control? 4 Lead Wire Configuration Step Table Step Red Blue Yellow White 0 + + 1 + + 2 + + 3 + + 4 + + - A+ Red 4 lead motor ABlue Yellow B+ White B- Clockwise Facing Mounting End Each step, like the second hand of a clock => tick, tick Increase the frequency of the steps => continuous motion Motoring along... • direct control of position • precise positioning (The amount of rotational movement per step depends on the construction of the motor) • Easy to Control • under-damping leads to oscillation at low speeds • torque is lower at high speeds than the primary alternative… DC motors -- exposed ! Position Sensors Optical Encoders Relative position Absolute position Other Sensors Resolver Potentiometer Optical Encoders • Relative position light sensor light emitter grating decode circuitry - direction - resolution Optical Encoders mask/diffuser • Relative position light sensor decode circuitry light emitter grating A diffuser tends to smooth these signals Ideal Real Optical Encoders • Relative position light sensor light emitter grating decode circuitry - direction - resolution Optical Encoders • Relative position light sensor light emitter - direction - resolution decode circuitry grating A A A lags B B B Optical Encoders • Relative position light sensor - direction - resolution decode circuitry light emitter grating Phase lag between A and B is 90 degree A B A leads B Optical Encoders • Detecting absolute position wires ? Other Sensors • Resolver = driving a stepper motor • Potentiometer = varying resistance Control Control: getting motors to do what you want them to What you want to control For DC motors: = what you can control speed voltage windings’ resistance N V N R w V S e back emf S e is a voltage generated by the rotor windings cutting the magnetic field emf: electromagnetic force Controlling speed with voltage • The back emf depends only on the motor speed. e = ke w • The motor’s torque depends only on the current, I. t = kt I R V e DC motor model Controlling speed with voltage • The back emf depends only on the motor speed. e = ke w • The motor’s torque depends only on the current, I. t = kt I Istall = V/R current when motor is stalled speed = 0 torque = max V = IR + e How is V related to w ? tR V= + ke w kt R V • Consider this circuit’s V: e - or - V w=- R t+ ke kt ke DC motor model Speed is proportional to voltage. speed vs. torque at a fixed voltage speed w V ke no torque at max speed max torque when stalled torque t ktV R speed vs. torque at a fixed voltage speed w V ke no torque at max speed Linear mechanical power Pm = F v Rotational version of Pm = t w torque t ktV R stall torque speed vs. torque at a fixed voltage speed w V ke Linear mechanical power Pm = F v Rotational version of Pm = t w max speed power output speed vs. torque torque t ktV R stall torque speed vs. torque speed w V ke gasoline engine max speed power output speed vs. torque torque t ktV R stall torque Back to control Basic input / output relationship: tR V= + ke w kt We can control the voltage applied V. We want a particular motor speed w . How to change the voltage? V is usually controlled via PWM -- “pulse width modulation” PWM PWM -- “pulse width modulation Duty cycle: The ratio of the “On time” and the “Off time” in one cycle Determines the fractional amount of full power delivered to the motor